Chapter 8powerp point for chemical reactions
... The equation must represent known facts The equation must contain the correct formulas for the reactants & products The law of conservation of mass must be satisfied- which means the same # and type of atoms are present on both sides of the equation. ...
... The equation must represent known facts The equation must contain the correct formulas for the reactants & products The law of conservation of mass must be satisfied- which means the same # and type of atoms are present on both sides of the equation. ...
2 unit Chemistry-2
... b. Describe the difference between ions and atoms and the importance of ions in biological processes c. Compare the types of bonding between atoms to form molecules d. Show how chemical reactions (e.g., photosynthesis, fermentation, cellular respiration) can be represented by chemical formulas e. Ex ...
... b. Describe the difference between ions and atoms and the importance of ions in biological processes c. Compare the types of bonding between atoms to form molecules d. Show how chemical reactions (e.g., photosynthesis, fermentation, cellular respiration) can be represented by chemical formulas e. Ex ...
Topic 2: Molecular Biology
... Essential Idea: Living Organisms control their composition by complex web of chemical reactions. U1 Molecular biology explains living processes in terms of the chemical substances involved U2 Carbon atoms can form four covalent bonds allowing a diversity of stable compounds to exist U3 Life is based ...
... Essential Idea: Living Organisms control their composition by complex web of chemical reactions. U1 Molecular biology explains living processes in terms of the chemical substances involved U2 Carbon atoms can form four covalent bonds allowing a diversity of stable compounds to exist U3 Life is based ...
one
... • Step 2 – change one or more coefficients until the equation is balanced. – Start by balancing an element that appears in only one reactant and product. – Once one element is balanced, proceed to balance another, and another, until all elements are balanced. – Balance chemical formulas by placing c ...
... • Step 2 – change one or more coefficients until the equation is balanced. – Start by balancing an element that appears in only one reactant and product. – Once one element is balanced, proceed to balance another, and another, until all elements are balanced. – Balance chemical formulas by placing c ...
Chemical digestion
... Isotopes have a different # of neutrons. Isotopes have the same number of electrons and behave the same way chemically. ...
... Isotopes have a different # of neutrons. Isotopes have the same number of electrons and behave the same way chemically. ...
HONORS: UNIT 2B: Antacids Below are the class objectives
... Define components of a chemical reaction/criteria to determine is a chemical reaction has occurred Practice converting from word equations to formula equations Define and predict products for synthesis (standard: binary ionic compound model) &decomposition reactions (binary ionic and metal carbonate ...
... Define components of a chemical reaction/criteria to determine is a chemical reaction has occurred Practice converting from word equations to formula equations Define and predict products for synthesis (standard: binary ionic compound model) &decomposition reactions (binary ionic and metal carbonate ...
The Structure of the Atom 1 Philosophers And Early Scientists
... failed, Thomson worked to compare the ratio of the cathode ray charge to its mass Determined that the mass of the charged particle was less than a hydrogen atom (the lightest atom ...
... failed, Thomson worked to compare the ratio of the cathode ray charge to its mass Determined that the mass of the charged particle was less than a hydrogen atom (the lightest atom ...
Chemistry Midterm Review Study Guide 2012
... b. The electrons available to be gained, lost, or shared in the formation of chemical compounds are called Valence electrons. c. The measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons is called electronegativity d. The energy required to remove an electron from an atom is ...
... b. The electrons available to be gained, lost, or shared in the formation of chemical compounds are called Valence electrons. c. The measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons is called electronegativity d. The energy required to remove an electron from an atom is ...
Quantum Well Electron Gain Structures and Infrared Detector Arrays
... • This diversity is why “organic” (meaning, “carbon”!) chemistry is SO complex !! ...
... • This diversity is why “organic” (meaning, “carbon”!) chemistry is SO complex !! ...
the atom
... matter, uniform in its chemical composition and properties. Examples: Oxygen gas, copper, sugar, water, etc… Mixture: A blend of two or more pure substances in any ratio, each retaining its identity; physical and chemical properties vary as the relative amounts of different parts change. Dissolving ...
... matter, uniform in its chemical composition and properties. Examples: Oxygen gas, copper, sugar, water, etc… Mixture: A blend of two or more pure substances in any ratio, each retaining its identity; physical and chemical properties vary as the relative amounts of different parts change. Dissolving ...
Lecture Suggestions and Guidelines
... Answer: The structure of carbon dioxide molecules is such that, when carried inside red blood cells, it allows for binding at different sites than oxygen on the hemoglobin molecule. Thus, oxygen and carbon dioxide do not compete for the same binding site. Carbon monoxide, however, competes with oxyg ...
... Answer: The structure of carbon dioxide molecules is such that, when carried inside red blood cells, it allows for binding at different sites than oxygen on the hemoglobin molecule. Thus, oxygen and carbon dioxide do not compete for the same binding site. Carbon monoxide, however, competes with oxyg ...
Essential Question: What is biochemistry
... C, H, N, O, P, and S are the most important elements for organisms. Na, K, and Fe are also important. Atoms of elements are almost never found alone, thus they combine to form larger substances called molecules Exs. O2 , F2 or to form compounds Exs. H2O, C6H12O6 . The attraction that hold to atoms t ...
... C, H, N, O, P, and S are the most important elements for organisms. Na, K, and Fe are also important. Atoms of elements are almost never found alone, thus they combine to form larger substances called molecules Exs. O2 , F2 or to form compounds Exs. H2O, C6H12O6 . The attraction that hold to atoms t ...
Chapter 5 Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... Nitrogen's atomic number is 7, has an average mass of 14.007 amu and nitrogen's most common isotope has a mass of 14 amu. Therefore the most common type of nitrogen atom has 7 protons, 7 neutrons and 7 electrons. Sodium's atomic number is 11, has an average mass of 22.990 amu and nitrogen's most com ...
... Nitrogen's atomic number is 7, has an average mass of 14.007 amu and nitrogen's most common isotope has a mass of 14 amu. Therefore the most common type of nitrogen atom has 7 protons, 7 neutrons and 7 electrons. Sodium's atomic number is 11, has an average mass of 22.990 amu and nitrogen's most com ...
Year 11 Chemistry Balancing Equations
... How do the number of protons, number of neutrons, and the mass number relate to each other? ...
... How do the number of protons, number of neutrons, and the mass number relate to each other? ...
Atom - U of L Class Index
... identical in mass and in all other properties. 3. Different elements have different kinds of atoms; these atoms differ in mass from element to element. 4. Atoms are indestructible & retain their identity in all chemical reactions. 5. The formation of a compound from its elements occurs through the c ...
... identical in mass and in all other properties. 3. Different elements have different kinds of atoms; these atoms differ in mass from element to element. 4. Atoms are indestructible & retain their identity in all chemical reactions. 5. The formation of a compound from its elements occurs through the c ...
Solid state NMR of isotope labelled murine fur: A powerful tool to
... two or more frequency dimensions. Apart from the obvious increase in spectral resolution, these methods also provide structure sensitive atomic bonding and/or distance information ...
... two or more frequency dimensions. Apart from the obvious increase in spectral resolution, these methods also provide structure sensitive atomic bonding and/or distance information ...
Review topics-blog
... Stoichiometry is another key topic chapter 3, which is the bookkeeping system for reactions. So say if 3.0 grams of methane reacts with excess oxygen, stoichiometry will help us figure out how much CO2 and H2O would form. The mole is a common unit we will use. A mole of an object refers to 6.0221 ...
... Stoichiometry is another key topic chapter 3, which is the bookkeeping system for reactions. So say if 3.0 grams of methane reacts with excess oxygen, stoichiometry will help us figure out how much CO2 and H2O would form. The mole is a common unit we will use. A mole of an object refers to 6.0221 ...
Chemistry Fall-2016 Final
... J. the difference between the number of protons and the number of electrons in an atom or ion; if there are more protons than electrons, the net charge is positive; if there are more ...
... J. the difference between the number of protons and the number of electrons in an atom or ion; if there are more protons than electrons, the net charge is positive; if there are more ...
Chapter 3 Biochemistry Section 1 – Carbon Compounds Section 2
... Enzymes can be denatured-which causes them to change shape and they will no longer function ...
... Enzymes can be denatured-which causes them to change shape and they will no longer function ...
Introductory Chemistry Test Review
... 25. In the laboratory, potassium chlorate will decompose when heated to form potassium chloride and oxygen gas according to the following equation. Calculate how much oxygen in grams is produced when 35.0 grams of potassium chlorate decomposes. 2 KClO3(s) ...
... 25. In the laboratory, potassium chlorate will decompose when heated to form potassium chloride and oxygen gas according to the following equation. Calculate how much oxygen in grams is produced when 35.0 grams of potassium chlorate decomposes. 2 KClO3(s) ...
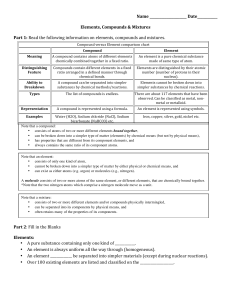
Compound vs Element chart
... • consists of only one kind of atom, • cannot be broken down into a simpler type of matter by either physical or chemical means, and • can exist as either atoms (e.g. argon) or molecules (e.g., nitrogen). A molecule consists of two or more atoms of the same element, or different elements, that are c ...
... • consists of only one kind of atom, • cannot be broken down into a simpler type of matter by either physical or chemical means, and • can exist as either atoms (e.g. argon) or molecules (e.g., nitrogen). A molecule consists of two or more atoms of the same element, or different elements, that are c ...
Capillary electrophoresis tandem mass spectrometry of bromine
... migration times of labeled and unlabeled peptides would help in determining the position of labeling; hence it can be a useful support in elucidating their MS/MS spectra. The MS/MS (Fig. 7) spectrum recorded by following the method described above shows different fragmentation pattern. In this spect ...
... migration times of labeled and unlabeled peptides would help in determining the position of labeling; hence it can be a useful support in elucidating their MS/MS spectra. The MS/MS (Fig. 7) spectrum recorded by following the method described above shows different fragmentation pattern. In this spect ...
Balancing Chemical Equations
... • Describe a chemical reaction by using a word equation and a formula equation. • Relate the conservation of mass to the rearrangement of atoms in a chemical reaction • Write and interpret a balanced chemical equation for a reaction, and relate conservation of mass to the balanced equation ...
... • Describe a chemical reaction by using a word equation and a formula equation. • Relate the conservation of mass to the rearrangement of atoms in a chemical reaction • Write and interpret a balanced chemical equation for a reaction, and relate conservation of mass to the balanced equation ...
Macromolecule Notes
... 1. Has 4 Valence electrons 2. Forms 4 covalent bonds (single, double, or triple) with oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorous, and sulfur 3. Can form chains - straight, branching or rings - varies in length, number and location of double bonds and presence of other elements 4. Forms ISOMERS (same chemical for ...
... 1. Has 4 Valence electrons 2. Forms 4 covalent bonds (single, double, or triple) with oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorous, and sulfur 3. Can form chains - straight, branching or rings - varies in length, number and location of double bonds and presence of other elements 4. Forms ISOMERS (same chemical for ...
Isotopic labeling

Isotopic labeling (or isotopic labelling) is a technique used to track the passage of an isotope, or an atom with a variation, through a reaction, metabolic pathway, or cell. The reactant is 'labeled' by replacing specific atoms by their isotope. The reactant is then allowed to undergo the reaction. The position of the isotopes in the products is measured to determine the sequence the isotopic atom followed in the reaction or the cell's metabolic pathway. The nuclides used in isotopic labeling may be stable nuclides or radionuclides. In the latter case, the labeling is called radiolabeling.In isotopic labeling, there are multiple ways to detect the presence of labeling isotopes; through their mass, vibrational mode, or radioactive decay. Mass spectrometry detects the difference in an isotope's mass, while infrared spectroscopy detects the difference in the isotope's vibrational modes. Nuclear magnetic resonance detects atoms with different gyromagnetic ratios. The radioactive decay can be detected through an ionization chamber or autoradiographs of gels.An example of the use of isotopic labeling is the study of phenol (C6H5OH) in water by replacing common hydrogen (protium) with deuterium (deuterium labeling). Upon adding phenol to deuterated water (water containing D2O in addition to the usual H2O), the substitution of deuterium for the hydrogen is observed in phenol's hydroxyl group (resulting in C6H5OD), indicating that phenol readily undergoes hydrogen-exchange reactions with water. Only the hydroxyl group was affected, indicating that the other 5 hydrogen atoms did not participate in these exchange reactions.