Chp. 1.1 Simple Interest
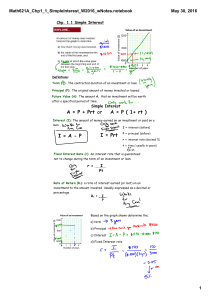
... Term (T): The contracted duration of an investment or loan. Principal (P): The original amount of money invested or loaned Future Value (A): The amount A, that an investment will be worth after a specified period of time. ...
... Term (T): The contracted duration of an investment or loan. Principal (P): The original amount of money invested or loaned Future Value (A): The amount A, that an investment will be worth after a specified period of time. ...
solve(A*m^NR*(m^N-1)/(m
... period of the loan. We are going to assume (as is usually the case in the U. S.) that payments are made monthly, even though the interest rate is given as an annual rate. Let's define peryear=1/12; percent=1/100; ...
... period of the loan. We are going to assume (as is usually the case in the U. S.) that payments are made monthly, even though the interest rate is given as an annual rate. Let's define peryear=1/12; percent=1/100; ...
We need to solve the mortgage problem before interest rates rise
... would push them over the standard affordability threshold, leaving them ‘highly geared’. This is worrying, but doesn’t mean that one-in-four mortgagors won’t be able to cope. Many will have the resources to ride out the rise in repayments and many will be able to find new mortgage deals, typically r ...
... would push them over the standard affordability threshold, leaving them ‘highly geared’. This is worrying, but doesn’t mean that one-in-four mortgagors won’t be able to cope. Many will have the resources to ride out the rise in repayments and many will be able to find new mortgage deals, typically r ...
Lecture / Chapter 3
... May be able to obtain a lower interest rate than a FRM mortgage because a lender is not locked-down in a high-rate market Borrower accepts risk of floating interest rates Buyer somewhat protected by interest rate caps Interest rates marked by indices such as LIBOR, U.S. Treasury Securities, etc. Off ...
... May be able to obtain a lower interest rate than a FRM mortgage because a lender is not locked-down in a high-rate market Borrower accepts risk of floating interest rates Buyer somewhat protected by interest rate caps Interest rates marked by indices such as LIBOR, U.S. Treasury Securities, etc. Off ...
Continuous compound interest
... A Pr t P = principal amount (initial investment) r = annual interest rate (as a decimal) t = number of years A = amount after time t e.g:-An amount of $2,340.00 is deposited in a bank paying an annual interest rate of 3.1%, compounded continuously. Find the balance after 3 years. Solution:-Use the ...
... A Pr t P = principal amount (initial investment) r = annual interest rate (as a decimal) t = number of years A = amount after time t e.g:-An amount of $2,340.00 is deposited in a bank paying an annual interest rate of 3.1%, compounded continuously. Find the balance after 3 years. Solution:-Use the ...
Consumer Loan Scavenger Hunt
... Interest and principal is paid at maturity in a lump sum. An example where a single payment loan would be useful is the construction of a home; the money is used to build the home then the sale of the home is used to pay off the loan. ...
... Interest and principal is paid at maturity in a lump sum. An example where a single payment loan would be useful is the construction of a home; the money is used to build the home then the sale of the home is used to pay off the loan. ...
If you have Mortgage Interest “rate envy”, does it make sense to
... greater of either a) three months’ interest, or b) the interest-rate differential. The interest rate differential can be high in some cases; your mortgage lender will expect you to pay them the equivalent of what they will lose by releasing you from your mortgage and lending the money at current rat ...
... greater of either a) three months’ interest, or b) the interest-rate differential. The interest rate differential can be high in some cases; your mortgage lender will expect you to pay them the equivalent of what they will lose by releasing you from your mortgage and lending the money at current rat ...
More... - Kevin Kavakeb
... Typically, the standard for fixed-rate loans is the 20 to 25 year fixed rate loan. You can also find fixed-rate loans with shorter pay-off periods. When loan periods are shorter, you will have higher monthly payments, but slightly lower interest. When are Fixed Rate Loans better? The advantage of th ...
... Typically, the standard for fixed-rate loans is the 20 to 25 year fixed rate loan. You can also find fixed-rate loans with shorter pay-off periods. When loan periods are shorter, you will have higher monthly payments, but slightly lower interest. When are Fixed Rate Loans better? The advantage of th ...
Adjustable Rate Mortgage
... Adjustable Rate Mortgages Advantages For Borrower Usually __________________ interest rate than fixed rate With lower rate borrower can qualify for __________________ loan BUT when interest rates rise, payment rises For Lender Allows lenders to better match long term loan interest rates to short ter ...
... Adjustable Rate Mortgages Advantages For Borrower Usually __________________ interest rate than fixed rate With lower rate borrower can qualify for __________________ loan BUT when interest rates rise, payment rises For Lender Allows lenders to better match long term loan interest rates to short ter ...
REAL ESTATE ECONOMICS - Chapter Quizzes
... 1. A demand deposit that must be paid by the depositor’s bank to the payee upon presentation is known as: a. cash. b. check. c. money order. d. all of the above. 2. California is in which district of the Federal Reserve System? a. 16th b. 13th c. 12th d. 11th 3. The rate of interest at which member ...
... 1. A demand deposit that must be paid by the depositor’s bank to the payee upon presentation is known as: a. cash. b. check. c. money order. d. all of the above. 2. California is in which district of the Federal Reserve System? a. 16th b. 13th c. 12th d. 11th 3. The rate of interest at which member ...
New Economic Bubbles
... • Consumers were required to put a 20% down payment • For a $500,000 home: – $100,000 down payment & borrow $400,000 (mortgage) – loan is paid back over 30-years at a Fixed interest rate ...
... • Consumers were required to put a 20% down payment • For a $500,000 home: – $100,000 down payment & borrow $400,000 (mortgage) – loan is paid back over 30-years at a Fixed interest rate ...
ARM 7-6 Term Sheet
... This term sheet is only for the purpose of setting forth a basis upon which the parties may be agreeable to proceed toward the contemplated transaction, and is not intended to be a legally binding contract or to impose any liabilities or obligations on any party. The terms reflected in this term she ...
... This term sheet is only for the purpose of setting forth a basis upon which the parties may be agreeable to proceed toward the contemplated transaction, and is not intended to be a legally binding contract or to impose any liabilities or obligations on any party. The terms reflected in this term she ...