PowerPoint
... Problem: A titration is performed between sodium hydroxide and potassium hydrogenphthalate (KHP) to standardize the base solution, by placing 50.00 mg of solid potassium hydrogenphthalate in a flask with a few drops of an indicator. A buret is filled with the base, and the initial buret reading is 0 ...
... Problem: A titration is performed between sodium hydroxide and potassium hydrogenphthalate (KHP) to standardize the base solution, by placing 50.00 mg of solid potassium hydrogenphthalate in a flask with a few drops of an indicator. A buret is filled with the base, and the initial buret reading is 0 ...
Practice Test: Equilibrium
... Use this reaction to answer the next two questions: C2H6(g) + Cl2(g) ↔ C2H5Cl(s) + HCl(g) What happens to the amount of C2H6 when HCl gas is added? _____________________ What happens to the amount of C2H6 when C2H5Cl is added? _____________________ ...
... Use this reaction to answer the next two questions: C2H6(g) + Cl2(g) ↔ C2H5Cl(s) + HCl(g) What happens to the amount of C2H6 when HCl gas is added? _____________________ What happens to the amount of C2H6 when C2H5Cl is added? _____________________ ...
Derivatization reagents
... ● Reacts to replace labile hydrogens on a wide range of polar compounds with a Si(CH3)3 group ● Used to prepare volatile and thermally stable derivatives for GC and MS ● Volatile byproduct, N-methyltrifluoroacetamide, has an even lower retention time than MSTFA ● Often TMS derivatives of small molec ...
... ● Reacts to replace labile hydrogens on a wide range of polar compounds with a Si(CH3)3 group ● Used to prepare volatile and thermally stable derivatives for GC and MS ● Volatile byproduct, N-methyltrifluoroacetamide, has an even lower retention time than MSTFA ● Often TMS derivatives of small molec ...
Acids-bases and Organic Review
... When a person perspires (sweats), the body loses many sodium ions and potassium ions. The evaporation of sweat cools the skin. After a strenuous workout, people often quench their thirst with sports drinks that contain NaCl and KCl. A single 250.-gram serving of one sports drink contains 0.055 gram ...
... When a person perspires (sweats), the body loses many sodium ions and potassium ions. The evaporation of sweat cools the skin. After a strenuous workout, people often quench their thirst with sports drinks that contain NaCl and KCl. A single 250.-gram serving of one sports drink contains 0.055 gram ...
Practice problems
... Now we can use the summary in Figure 20.6 to help us describe the voltaic cell. The first half-reaction is the reduction process (electrons shown on the reactant side of the equation), and by definition, this process occurs at the cathode. The second half-reaction is the oxidation (electrons shown o ...
... Now we can use the summary in Figure 20.6 to help us describe the voltaic cell. The first half-reaction is the reduction process (electrons shown on the reactant side of the equation), and by definition, this process occurs at the cathode. The second half-reaction is the oxidation (electrons shown o ...
Aqueous chemistry is a very important component to laboratory
... (conductors of electricity) are placed in a solution and connected to a battery, the cations will migrate through the solution to the negatively charged electrode and the anions will migrate towards the positively charged electrode. If a light bulb is inserted into the circuit, the bulb will light u ...
... (conductors of electricity) are placed in a solution and connected to a battery, the cations will migrate through the solution to the negatively charged electrode and the anions will migrate towards the positively charged electrode. If a light bulb is inserted into the circuit, the bulb will light u ...
electrical energy and capacitance
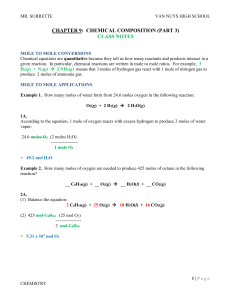
... CHAPTER 9: CHEMICAL COMPOSITION (PART 3) CLASS NOTES MOLE TO MOLE CONVERSIONS Chemical equations are quantitative because they tell us how many reactants and products interact in a given reaction. In particular, chemical reactions are written in mole to mole ratios. For example, 3 H2(g) + N2(g) 2 ...
... CHAPTER 9: CHEMICAL COMPOSITION (PART 3) CLASS NOTES MOLE TO MOLE CONVERSIONS Chemical equations are quantitative because they tell us how many reactants and products interact in a given reaction. In particular, chemical reactions are written in mole to mole ratios. For example, 3 H2(g) + N2(g) 2 ...
Massachusetts Tests for Educator Licensure (MTEL ) www.mtel
... The practice test is designed to provide an additional resource to help you effectively prepare for the MTEL Chemistry (12) test. The primary purpose of the practice test is to help you become familiar with the structure and content of the test. It is also intended to help you identify areas in whic ...
... The practice test is designed to provide an additional resource to help you effectively prepare for the MTEL Chemistry (12) test. The primary purpose of the practice test is to help you become familiar with the structure and content of the test. It is also intended to help you identify areas in whic ...
AP Chemistry: Total Notes Review
... 3: Fill the octets 4: use double and triple bonds as necessary o Formal charges: subtract the amount of electrons on the periodic table (for that element) from the electrons you drew in ~ 0 means right on ~ the negative charge should be on the most electronegative atom o Resonance: when one Lewis st ...
... 3: Fill the octets 4: use double and triple bonds as necessary o Formal charges: subtract the amount of electrons on the periodic table (for that element) from the electrons you drew in ~ 0 means right on ~ the negative charge should be on the most electronegative atom o Resonance: when one Lewis st ...
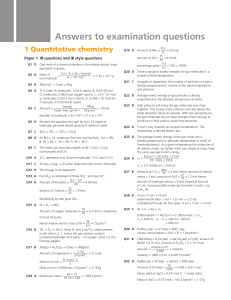
Answers to examination questions
... However, lone pairs cause more repulsion than bonding pairs. The oxygen in water is surrounded by two lone pairs (maximum repulsion), the nitrogen atom in ammonia contains one lone pair, but the carbon in methane has no lone pairs (least repulsion). Q3 B H2S has a higher molecular mass than H2O ...
... However, lone pairs cause more repulsion than bonding pairs. The oxygen in water is surrounded by two lone pairs (maximum repulsion), the nitrogen atom in ammonia contains one lone pair, but the carbon in methane has no lone pairs (least repulsion). Q3 B H2S has a higher molecular mass than H2O ...
Computers in Chemistry - University of St Andrews
... We want to construct a theoretical model that will predict solubility for druglike molecules … We expect our model to use real physics and chemistry and to give some insight … We don’t expect it to be fast by informatics standards, but it should be reasonably accurate … ...
... We want to construct a theoretical model that will predict solubility for druglike molecules … We expect our model to use real physics and chemistry and to give some insight … We don’t expect it to be fast by informatics standards, but it should be reasonably accurate … ...
Unit 6: Reactions and Stoichiometry
... Chemical formulas are ratios of atoms or moles of atoms. To solve a chemical analysis problem you must convert mass percent of each element to a molar ratio of each element. Step 1 Assume your unknown sample has a mass of 100 grams. ...
... Chemical formulas are ratios of atoms or moles of atoms. To solve a chemical analysis problem you must convert mass percent of each element to a molar ratio of each element. Step 1 Assume your unknown sample has a mass of 100 grams. ...
Oxidation-Reduction and Electrochemistry
... our present expression, enters: it is the negative extremity of the decomposing body; is where oxygen, chlorine, acids, etc., are evolved; and is against or opposite the positive electrode. The cathode is that surface at which the current leaves the decomposing body, and is its positive extremit ...
... our present expression, enters: it is the negative extremity of the decomposing body; is where oxygen, chlorine, acids, etc., are evolved; and is against or opposite the positive electrode. The cathode is that surface at which the current leaves the decomposing body, and is its positive extremit ...
mass mass calc
... C(s) + O2(g) CO2(g) In a particular lab set up, 50.0 g of oxygen gas are available for the combustion of 25.0 g of carbon.. a) Calculate the number of moles of oxygen gas and carbon solid that are each available to react. b) Calculate the number of moles of oxygen gas that will actually be needed ...
... C(s) + O2(g) CO2(g) In a particular lab set up, 50.0 g of oxygen gas are available for the combustion of 25.0 g of carbon.. a) Calculate the number of moles of oxygen gas and carbon solid that are each available to react. b) Calculate the number of moles of oxygen gas that will actually be needed ...
OXIDATION NUMBERS
... as the uncombined element or when combined in a compound; it consists of a + or – sign followed by a number, or it is zero. Atoms of elements have no overall charge and are therefore given an oxidation number of zero. When two elements combine, the atoms or ions of the more electropositive element h ...
... as the uncombined element or when combined in a compound; it consists of a + or – sign followed by a number, or it is zero. Atoms of elements have no overall charge and are therefore given an oxidation number of zero. When two elements combine, the atoms or ions of the more electropositive element h ...
Thermochemistry 122
... reactions to start (break old bonds). Chemical reactions need energy to take place, bond breakage is endothermic (energy required to break atoms apart) and bond formation is exothermic (atoms become more stable as new bonds form). During chemical reactions chemical bonds change. A substance has pote ...
... reactions to start (break old bonds). Chemical reactions need energy to take place, bond breakage is endothermic (energy required to break atoms apart) and bond formation is exothermic (atoms become more stable as new bonds form). During chemical reactions chemical bonds change. A substance has pote ...
File
... reactions to start (break old bonds). Chemical reactions need energy to take place, bond breakage is endothermic (energy required to break atoms apart) and bond formation is exothermic (atoms become more stable as new bonds form). During chemical reactions chemical bonds change. A substance has pote ...
... reactions to start (break old bonds). Chemical reactions need energy to take place, bond breakage is endothermic (energy required to break atoms apart) and bond formation is exothermic (atoms become more stable as new bonds form). During chemical reactions chemical bonds change. A substance has pote ...
Chemistry Revision Checklist F4 2017 (inc F3)
... Describe the properties of alkanes (exemplified by methane) as being generally unreactive, except in terms of burning Describe substitution reactions of alkanes with chlorine Describe the bonding in alkanes Describe the properties of alkenes in terms of addition reactions with bromine, hydrogen and ...
... Describe the properties of alkanes (exemplified by methane) as being generally unreactive, except in terms of burning Describe substitution reactions of alkanes with chlorine Describe the bonding in alkanes Describe the properties of alkenes in terms of addition reactions with bromine, hydrogen and ...
Kinetics Presentation - Chemistrybyscott.org
... 2. CO2 (aq) + H2O(liq) e H2CO3(aq) 3. H2CO3(aq) e H+(aq) + HCO3–(aq) • Adding trace of NaOH uses up H+. Equilibrium shifts to produce more H2CO3. • Enzyme in blood (above) speeds up reactions 1 and 2 ...
... 2. CO2 (aq) + H2O(liq) e H2CO3(aq) 3. H2CO3(aq) e H+(aq) + HCO3–(aq) • Adding trace of NaOH uses up H+. Equilibrium shifts to produce more H2CO3. • Enzyme in blood (above) speeds up reactions 1 and 2 ...
Towards a Theory of Organizations
... or departments of a company. These exact statements shall be applied to five examples of systems, stemming from the field of artificial chemistry (AC). Artificial chemistries are able to generate organizations with different characteristics. The concept of an artificial chemistry is an elegant means ...
... or departments of a company. These exact statements shall be applied to five examples of systems, stemming from the field of artificial chemistry (AC). Artificial chemistries are able to generate organizations with different characteristics. The concept of an artificial chemistry is an elegant means ...
File - Fidaa`s Level 2 Portfolio
... An ester was produced in each reaction because after all of the carboxylic acids were added to the alcohols; some bonds are broken and create two new bonds. One bond of water and one bond of a new chemical including an ester. The evidence we have is that an ester is a double bond oxygen that is bond ...
... An ester was produced in each reaction because after all of the carboxylic acids were added to the alcohols; some bonds are broken and create two new bonds. One bond of water and one bond of a new chemical including an ester. The evidence we have is that an ester is a double bond oxygen that is bond ...
Bioorthogonal chemistry
The term bioorthogonal chemistry refers to any chemical reaction that can occur inside of living systems without interfering with native biochemical processes. The term was coined by Carolyn R. Bertozzi in 2003. Since its introduction, the concept of the bioorthogonal reaction has enabled the study of biomolecules such as glycans, proteins, and lipids in real time in living systems without cellular toxicity. A number of chemical ligation strategies have been developed that fulfill the requirements of bioorthogonality, including the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between azides and cyclooctynes (also termed copper-free click chemistry), between nitrones and cyclooctynes, oxime/hydrazone formation from aldehydes and ketones, the tetrazine ligation, the isocyanide-based click reaction, and most recently, the quadricyclane ligation.The use of bioorthogonal chemistry typically proceeds in two steps. First, a cellular substrate is modified with a bioorthogonal functional group (chemical reporter) and introduced to the cell; substrates include metabolites, enzyme inhibitors, etc. The chemical reporter must not alter the structure of the substrate dramatically to avoid affecting its bioactivity. Secondly, a probe containing the complementary functional group is introduced to react and label the substrate.Although effective bioorthogonal reactions such as copper-free click chemistry have been developed, development of new reactions continues to generate orthogonal methods for labeling to allow multiple methods of labeling to be used in the same biosystems.