CHEM102 Chemistry II Spring 11-12 Mid
... 27) How many moles of solute are present in 5.00 L of 6.00 M HCl? 27) ______ A) 5.00 mol B) 6.00 mol C) 1.20 mol D) 0.833 mol E) 30.0 mol 28) Which of the following can serve as the solvent in a solution? 28) ______ A) a liquid B) a gas C) a solid D) a mixture of comingled liquids E) all of the abo ...
... 27) How many moles of solute are present in 5.00 L of 6.00 M HCl? 27) ______ A) 5.00 mol B) 6.00 mol C) 1.20 mol D) 0.833 mol E) 30.0 mol 28) Which of the following can serve as the solvent in a solution? 28) ______ A) a liquid B) a gas C) a solid D) a mixture of comingled liquids E) all of the abo ...
+ H 2 SO 4(aq) - Rothschild Science
... How did you do? MnO2- 86.94 g/mol, Manganese (IV) oxide H2SO4 98.09 g/mol, Sulfuric acid Be sure you go back and review the basics… ...
... How did you do? MnO2- 86.94 g/mol, Manganese (IV) oxide H2SO4 98.09 g/mol, Sulfuric acid Be sure you go back and review the basics… ...
Problems - Department of Chemistry HKU
... where p0 is the initial pressure and p is the final pressure of cyclopropane. What is the order and rate constant for the reaction under these conditions? 21.10 The addition of hydrogen halides to alkenes has played a fundamental role in the investigation of organic reaction mechanisms. In one study ...
... where p0 is the initial pressure and p is the final pressure of cyclopropane. What is the order and rate constant for the reaction under these conditions? 21.10 The addition of hydrogen halides to alkenes has played a fundamental role in the investigation of organic reaction mechanisms. In one study ...
Dr Davids Essential Chemistry Definitions Bk1
... Oxidation: In ionic reactions it is the removal of electrons from a substance. eg, the conversion of iron(II) to iron(III). More generally, it is a chemical change which makes the oxidation number of a reactant species (such as an element) more positive or less negative. Polymerisation: A reaction i ...
... Oxidation: In ionic reactions it is the removal of electrons from a substance. eg, the conversion of iron(II) to iron(III). More generally, it is a chemical change which makes the oxidation number of a reactant species (such as an element) more positive or less negative. Polymerisation: A reaction i ...
Chemistry Spring Final Review
... percent yield of this reaction? 3H2 + N2 2NH3 A. 57.7% C. 33.5% B. 1.73% D. 12.4% 50. Magnesium nitride is formed in the reaction of magnesium metal with nitrogen gas. The reaction of 112 g of nitrogen with 145 g of magnesium produces: 3Mg + N2 Mg3N2 A. 2.0 mol of Mg3N2 C. 4.0 mol Mg3N2 B. 6.0 m ...
... percent yield of this reaction? 3H2 + N2 2NH3 A. 57.7% C. 33.5% B. 1.73% D. 12.4% 50. Magnesium nitride is formed in the reaction of magnesium metal with nitrogen gas. The reaction of 112 g of nitrogen with 145 g of magnesium produces: 3Mg + N2 Mg3N2 A. 2.0 mol of Mg3N2 C. 4.0 mol Mg3N2 B. 6.0 m ...
Snc2d Chapter 5 Practice Test
... gained or lost. Include the symbol with net charge and the name of the ion formed. e) With regard to ion formation how are metals different from nonmetals? (Two differences) ...
... gained or lost. Include the symbol with net charge and the name of the ion formed. e) With regard to ion formation how are metals different from nonmetals? (Two differences) ...
Final Review: L17-25
... Boyle’s Law states that the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to the pressure at constant temperature. ...
... Boyle’s Law states that the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to the pressure at constant temperature. ...
S3 Chemistry - eduBuzz.org
... Identify whether a species has an equal or unequal number of protons and electrons and use this to state whether it is an atom or ion. State the charge of an ion. Calculate the charge on a ion using nuclide notation Use the periodic table to identify whether an element is a metal or non-meta ...
... Identify whether a species has an equal or unequal number of protons and electrons and use this to state whether it is an atom or ion. State the charge of an ion. Calculate the charge on a ion using nuclide notation Use the periodic table to identify whether an element is a metal or non-meta ...
Learning Outcomes for Chemical Reactions and
... • Identify whether a species has an equal or unequal number of protons and electrons and use this to state whether it is an atom or ion. • State the charge of an ion. • Calculate the charge on a ion using nuclide notation • Use the periodic table to identify whether an element is a metal or non-meta ...
... • Identify whether a species has an equal or unequal number of protons and electrons and use this to state whether it is an atom or ion. • State the charge of an ion. • Calculate the charge on a ion using nuclide notation • Use the periodic table to identify whether an element is a metal or non-meta ...
California Chemistry Standards Test
... Which has a sour taste a. base b. metal c. acid d. salt Which of the following elements would combine w/ chlorine to form an ionic bond a. Ar b. S c. Si d. Mg The formula for the hydronium ion is a. H+ b. H3O+ c. OH- d. HCa5(PO4)3 is held together by a. freely moving electrons b. hydrogen bonds bet ...
... Which has a sour taste a. base b. metal c. acid d. salt Which of the following elements would combine w/ chlorine to form an ionic bond a. Ar b. S c. Si d. Mg The formula for the hydronium ion is a. H+ b. H3O+ c. OH- d. HCa5(PO4)3 is held together by a. freely moving electrons b. hydrogen bonds bet ...
FINAL EXAM Spring 2012
... 1) The reaction has the rate law, Rate = k[A][B]2. Which will cause the rate to increase the most? A) doubling [A] B) doubling [B] C) tripling [B] D) quadrupling [A] E) doubling both [A] and [B] 2) At a given temperature, a first-order reaction has a rate constant of 2.5 x 10-3 s-1. The time require ...
... 1) The reaction has the rate law, Rate = k[A][B]2. Which will cause the rate to increase the most? A) doubling [A] B) doubling [B] C) tripling [B] D) quadrupling [A] E) doubling both [A] and [B] 2) At a given temperature, a first-order reaction has a rate constant of 2.5 x 10-3 s-1. The time require ...
SAMPLE EXAM #2
... 15. According to the kinetic molecular theory for gases, particles of a gas a. are very large particles. b. are very far apart. c. lose their valence electrons. d. move slowly. e. decrease kinetic energy as temperature increases. 16. Which relationship is INCORRECT? a. as the temperature of a gas in ...
... 15. According to the kinetic molecular theory for gases, particles of a gas a. are very large particles. b. are very far apart. c. lose their valence electrons. d. move slowly. e. decrease kinetic energy as temperature increases. 16. Which relationship is INCORRECT? a. as the temperature of a gas in ...
Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
... solution is formed. The substance that is dissolved is the solute and the liquid in which the dissolution occurred is the solvent. Concentration: The measure of dissolution of a particular solute in a given volume of solvent. it is measured in molarity. Molarity: The number of solute molecule per un ...
... solution is formed. The substance that is dissolved is the solute and the liquid in which the dissolution occurred is the solvent. Concentration: The measure of dissolution of a particular solute in a given volume of solvent. it is measured in molarity. Molarity: The number of solute molecule per un ...
Dr. Baxley`s Thermodynamics Worksheet
... b) Calculate ∆G° for the combustion of one mole of acetylene by two different methods. ...
... b) Calculate ∆G° for the combustion of one mole of acetylene by two different methods. ...
2014 Academic Challenge Sectional Chemistry Exam Solution Set 1
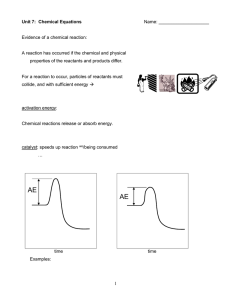
... the forward reaction is the vertical distance from the reactants to the top of the hill. The activation energy of the reverse reaction is the distance from the products to the top of the hill. The exothermic nature of the reaction requires EAfwd to be less than EArev. It is not required that this ob ...
... the forward reaction is the vertical distance from the reactants to the top of the hill. The activation energy of the reverse reaction is the distance from the products to the top of the hill. The exothermic nature of the reaction requires EAfwd to be less than EArev. It is not required that this ob ...
Reactions (The Basics)
... Four abbreviations are used to indicate physical states of chemicals: shown as subscripts in the chemical equation ...
... Four abbreviations are used to indicate physical states of chemicals: shown as subscripts in the chemical equation ...
Bioorthogonal chemistry
The term bioorthogonal chemistry refers to any chemical reaction that can occur inside of living systems without interfering with native biochemical processes. The term was coined by Carolyn R. Bertozzi in 2003. Since its introduction, the concept of the bioorthogonal reaction has enabled the study of biomolecules such as glycans, proteins, and lipids in real time in living systems without cellular toxicity. A number of chemical ligation strategies have been developed that fulfill the requirements of bioorthogonality, including the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between azides and cyclooctynes (also termed copper-free click chemistry), between nitrones and cyclooctynes, oxime/hydrazone formation from aldehydes and ketones, the tetrazine ligation, the isocyanide-based click reaction, and most recently, the quadricyclane ligation.The use of bioorthogonal chemistry typically proceeds in two steps. First, a cellular substrate is modified with a bioorthogonal functional group (chemical reporter) and introduced to the cell; substrates include metabolites, enzyme inhibitors, etc. The chemical reporter must not alter the structure of the substrate dramatically to avoid affecting its bioactivity. Secondly, a probe containing the complementary functional group is introduced to react and label the substrate.Although effective bioorthogonal reactions such as copper-free click chemistry have been developed, development of new reactions continues to generate orthogonal methods for labeling to allow multiple methods of labeling to be used in the same biosystems.