AP Chemistry Unit 5
... o + H (water gains energy to change from solid to liquid) 1 g of butane (C4H10) undergoes complete combustion o H (heat is released) What if the system is contained so no heat can be released? Will a piston rise or fall? o 2 C4H10 + 13 O2 8 CO2 + 10 H2O volume of products > volume of reactants o ...
... o + H (water gains energy to change from solid to liquid) 1 g of butane (C4H10) undergoes complete combustion o H (heat is released) What if the system is contained so no heat can be released? Will a piston rise or fall? o 2 C4H10 + 13 O2 8 CO2 + 10 H2O volume of products > volume of reactants o ...
CHEMISTRY 102 Spring 2012 Hour Exam III Page 20 1. For the
... In each experiment, different amounts of gases were mixed together initially and were then allowed to react to reach equilibrium. The table below summarizes the initial concentrations of the gases for each experiment before any reaction took place. Experiment Initial Concentrations ...
... In each experiment, different amounts of gases were mixed together initially and were then allowed to react to reach equilibrium. The table below summarizes the initial concentrations of the gases for each experiment before any reaction took place. Experiment Initial Concentrations ...
Exam 3 - Canvas by Instructure
... MoS2 → MoO4-1 + SO42A. 24 H+ B. 16 H+ C. 8 H+ D. 4 H+ E. None—when properly balanced, this half reaction does NOT include hydrogen. 16. Consider the balanced redox reaction below: 2 MnO4- + 6 H+ + 5 H2O2 → 2 Mn2+ + 8 H2O + 5 O2 If this reaction was properly balanced under BASIC conditions (with the ...
... MoS2 → MoO4-1 + SO42A. 24 H+ B. 16 H+ C. 8 H+ D. 4 H+ E. None—when properly balanced, this half reaction does NOT include hydrogen. 16. Consider the balanced redox reaction below: 2 MnO4- + 6 H+ + 5 H2O2 → 2 Mn2+ + 8 H2O + 5 O2 If this reaction was properly balanced under BASIC conditions (with the ...
apchem - practice midterm_shs
... they are uncertain. In this section of the examination, as a correction for haphazard guessing, one-fourth of the number of questions you answer incorrectly will be subtracted from the number of questions you answer correctly. It is improbable, therefore, that mere guessing will improve your score s ...
... they are uncertain. In this section of the examination, as a correction for haphazard guessing, one-fourth of the number of questions you answer incorrectly will be subtracted from the number of questions you answer correctly. It is improbable, therefore, that mere guessing will improve your score s ...
Final Exam Review- no solutions
... 24. The complete combustion of propane can be represented by the following equation: CH3CH2CH3(g) + 5 O2(g) 3 CO2(g) + 4 H2O(l) Find the ΔH for the reactions given the following bond enthalpies. C-H C-C O=O C=O H-O ...
... 24. The complete combustion of propane can be represented by the following equation: CH3CH2CH3(g) + 5 O2(g) 3 CO2(g) + 4 H2O(l) Find the ΔH for the reactions given the following bond enthalpies. C-H C-C O=O C=O H-O ...
1. What is the best definition of rate of reaction? A. The time it takes
... Construct the enthalpy level diagram and label the activation energy, Ea, the enthalpy change, ∆H, and the position of the transition state. ...
... Construct the enthalpy level diagram and label the activation energy, Ea, the enthalpy change, ∆H, and the position of the transition state. ...
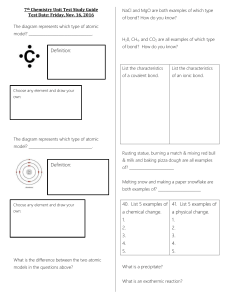
7th Chemistry Unit Test Study Guide Test Date: Friday, Nov. 16
... If Fe2O3 is the product, which of the following chemical equations shows the reaction? ...
... If Fe2O3 is the product, which of the following chemical equations shows the reaction? ...
Chapter 6 Chemical Reactions and Change
... charged in the process; the loss of electrons is called oxidation. The oxygen gained electrons and this is called reduction. All elements in their elemental state are neutral and are assigned an oxidation state of zero. Similarly, when Na and K reacted with H2O they became positively charged. In thi ...
... charged in the process; the loss of electrons is called oxidation. The oxygen gained electrons and this is called reduction. All elements in their elemental state are neutral and are assigned an oxidation state of zero. Similarly, when Na and K reacted with H2O they became positively charged. In thi ...
Lecture 6
... charged in the process; the loss of electrons is called oxidation. The oxygen gained electrons and this is called reduction. All elements in their elemental state are neutral and are assigned an oxidation state of zero. Similarly, when Na and K reacted with H2O they became positively charged. In thi ...
... charged in the process; the loss of electrons is called oxidation. The oxygen gained electrons and this is called reduction. All elements in their elemental state are neutral and are assigned an oxidation state of zero. Similarly, when Na and K reacted with H2O they became positively charged. In thi ...
Hydrogen, Alkalis, and Alkaline Earths
... placement on the Periodic Table is questionable: is it an alkali metal, is it a halogen, or should it be placed above carbon (half-filled valence shell)? ...
... placement on the Periodic Table is questionable: is it an alkali metal, is it a halogen, or should it be placed above carbon (half-filled valence shell)? ...
EOC Review - Dorman Freshman Campus
... the pollution and other gases emitted from the environment which is surrounded by dust and dirt in clouds….the dust and dirt fall as rain bringing with it the pollution which is ...
... the pollution and other gases emitted from the environment which is surrounded by dust and dirt in clouds….the dust and dirt fall as rain bringing with it the pollution which is ...
Chemistry - El Camino College
... a. ___________ formulas in which each pair of shared electrons is represented by a line (e.g.: O=C=O). b. __________ formulas that show only the number of each type of atom in the molecule (e.g.: CO2) c. Atoms such as __ and __ can form single, double, and even triple covalent bonds with other atoms ...
... a. ___________ formulas in which each pair of shared electrons is represented by a line (e.g.: O=C=O). b. __________ formulas that show only the number of each type of atom in the molecule (e.g.: CO2) c. Atoms such as __ and __ can form single, double, and even triple covalent bonds with other atoms ...
Chemistry Name: LeChâtlier`s Principle Date: Chemical Equilibrium
... LeChâtlier’s Principle: When a stress is applied to a system in equilibrium, the reaction will shift to relieve the stress. What is meant by stress? For example: The concentration of a gas is increased, shift away The concentration of a gas is decreased, shift toward Total pressure is increased (or ...
... LeChâtlier’s Principle: When a stress is applied to a system in equilibrium, the reaction will shift to relieve the stress. What is meant by stress? For example: The concentration of a gas is increased, shift away The concentration of a gas is decreased, shift toward Total pressure is increased (or ...
Question 1. Phosgene was used during the World War - IQ
... the forward reaction presents activation energy of E a = 2 kJ mol-1 and rate constant of ka = 0.01 s-1. The backward reaction presents activation energy of E b = 4 kJ mol-1 and rate constant of kb = 0.01 L mol-1s-1. (a) What should be the direction of spontaneous reaction? (b) What should be the rat ...
... the forward reaction presents activation energy of E a = 2 kJ mol-1 and rate constant of ka = 0.01 s-1. The backward reaction presents activation energy of E b = 4 kJ mol-1 and rate constant of kb = 0.01 L mol-1s-1. (a) What should be the direction of spontaneous reaction? (b) What should be the rat ...
Chemical Reactions & Balancing Equations
... • Shows all the reactants and products • Does not show balanced quantities ...
... • Shows all the reactants and products • Does not show balanced quantities ...
Review 3
... what happens when a seed crystal is added. 2. What do colligative properties depend on? 3. What type of substances are less soluble in hot water than in cold water? From Chapter 16: 1. At equilibrium, what is the rate of production of reactants compared with the rate of production of products? 2. Ca ...
... what happens when a seed crystal is added. 2. What do colligative properties depend on? 3. What type of substances are less soluble in hot water than in cold water? From Chapter 16: 1. At equilibrium, what is the rate of production of reactants compared with the rate of production of products? 2. Ca ...
IB:Enthalpy Review Questions
... b) Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic? c) Explain what this implies in terms of the chemical potential energy contained in the reactants and products. d) Draw an energy level diagram for this reaction. Clearly label the reactant side, product side, the enthalpy of reaction, and the activation ...
... b) Is the reaction endothermic or exothermic? c) Explain what this implies in terms of the chemical potential energy contained in the reactants and products. d) Draw an energy level diagram for this reaction. Clearly label the reactant side, product side, the enthalpy of reaction, and the activation ...
Discussion 8
... Next to that scale, we use horizontal lines and arrows to show either a particular value of energy, or a change in energy. The size of the horizontal lines do not matter, only their vertal location along the scale. The size of the vertial arrows, however, show a specific range on the energy scale an ...
... Next to that scale, we use horizontal lines and arrows to show either a particular value of energy, or a change in energy. The size of the horizontal lines do not matter, only their vertal location along the scale. The size of the vertial arrows, however, show a specific range on the energy scale an ...
Chemical Equations and Reaction Types Lab
... molecular equations and as ionic equations. We shall only consider molecular equations in this exercise. ...
... molecular equations and as ionic equations. We shall only consider molecular equations in this exercise. ...
Bioorthogonal chemistry
The term bioorthogonal chemistry refers to any chemical reaction that can occur inside of living systems without interfering with native biochemical processes. The term was coined by Carolyn R. Bertozzi in 2003. Since its introduction, the concept of the bioorthogonal reaction has enabled the study of biomolecules such as glycans, proteins, and lipids in real time in living systems without cellular toxicity. A number of chemical ligation strategies have been developed that fulfill the requirements of bioorthogonality, including the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between azides and cyclooctynes (also termed copper-free click chemistry), between nitrones and cyclooctynes, oxime/hydrazone formation from aldehydes and ketones, the tetrazine ligation, the isocyanide-based click reaction, and most recently, the quadricyclane ligation.The use of bioorthogonal chemistry typically proceeds in two steps. First, a cellular substrate is modified with a bioorthogonal functional group (chemical reporter) and introduced to the cell; substrates include metabolites, enzyme inhibitors, etc. The chemical reporter must not alter the structure of the substrate dramatically to avoid affecting its bioactivity. Secondly, a probe containing the complementary functional group is introduced to react and label the substrate.Although effective bioorthogonal reactions such as copper-free click chemistry have been developed, development of new reactions continues to generate orthogonal methods for labeling to allow multiple methods of labeling to be used in the same biosystems.