Introductory Chemistry, 2nd Edition Nivaldo Tro
... site, certain bonds are weakened • This allows a particular chemical change to occur with greater ease and speed. 酶 ...
... site, certain bonds are weakened • This allows a particular chemical change to occur with greater ease and speed. 酶 ...
THERMOCHEMISTRY - University of the Witwatersrand
... If a reaction is carried out in a series of steps, H for the reaction will be equal to the sum of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps. A+BX+Y ...
... If a reaction is carried out in a series of steps, H for the reaction will be equal to the sum of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps. A+BX+Y ...
Final Study Guide (Semester 2) Answer Key
... ***The first thing you should do when solving this is look at the common ion chart and write down all the ions. It’s much easier than looking them up again for each question. a. Write the balanced molecular equation. Include phase symbols. Ba(NO3)2(aq) + K2SO4(aq) BaSO4(s) + 2KNO3 (aq) Switch the c ...
... ***The first thing you should do when solving this is look at the common ion chart and write down all the ions. It’s much easier than looking them up again for each question. a. Write the balanced molecular equation. Include phase symbols. Ba(NO3)2(aq) + K2SO4(aq) BaSO4(s) + 2KNO3 (aq) Switch the c ...
Tests for functional groups
... To 2 cm of aqueous sodium hydroxide add 1 cm of the ‘unknown’ followed by a few drops of iodine solution, stopper and shake well. The production of a pale yellow crystalline precipitate (of triiodomethane) confirms the presence of either the -CH(CH3)OH group (present in secondary methyl alcohols or ...
... To 2 cm of aqueous sodium hydroxide add 1 cm of the ‘unknown’ followed by a few drops of iodine solution, stopper and shake well. The production of a pale yellow crystalline precipitate (of triiodomethane) confirms the presence of either the -CH(CH3)OH group (present in secondary methyl alcohols or ...
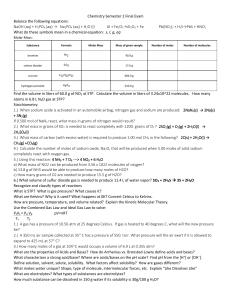
Chemistry Semester 2 Final Exam Chemistry Semester 2 Final Exam
... 1.) A gas has a pressure of 10.56 atm at 25 degrees Celcius. If gas is heated to 40 degrees C, what will the new pressure be? 10.0 atm 2.) A 350 mL air sample collected at 35 C has a pressure of 550. torr. What pressure will the air exert if it is allowed to expand to 425 mL at 57 C? 485 torr 3.) ...
... 1.) A gas has a pressure of 10.56 atm at 25 degrees Celcius. If gas is heated to 40 degrees C, what will the new pressure be? 10.0 atm 2.) A 350 mL air sample collected at 35 C has a pressure of 550. torr. What pressure will the air exert if it is allowed to expand to 425 mL at 57 C? 485 torr 3.) ...
Chapter 3 - Bruder Chemistry
... It is important to realize that the stoichiometric ratios are the ideal proportions in which reactants are needed to form products. The number of grams of reactant cannot be directly related to the number of grams of product. • To get grams of product from grams of reactant: • Convert grams of react ...
... It is important to realize that the stoichiometric ratios are the ideal proportions in which reactants are needed to form products. The number of grams of reactant cannot be directly related to the number of grams of product. • To get grams of product from grams of reactant: • Convert grams of react ...
Review of Moles and Stoichiometry
... 19.) How many milliliters of oxygen gas at STP are released from the decomposition of 3.2 grams of calcium chlorate as described by the equation: CaCl2 + 3O2 Ca(ClO3)2 ...
... 19.) How many milliliters of oxygen gas at STP are released from the decomposition of 3.2 grams of calcium chlorate as described by the equation: CaCl2 + 3O2 Ca(ClO3)2 ...
Final Review
... _______________ ionization energy and a ____________ electron affinity. a. large, large b. large, small c. small, small d. small, large e. None of the above. 41. The term which best describes the crystalline substance that results when a large number of metal atoms transfer electrons to a large numb ...
... _______________ ionization energy and a ____________ electron affinity. a. large, large b. large, small c. small, small d. small, large e. None of the above. 41. The term which best describes the crystalline substance that results when a large number of metal atoms transfer electrons to a large numb ...
Chemistry in Society - Cathkin High School
... Batch and Continuous Processes In a batch process the chemicals are loaded into the reaction vessel. The reaction is monitored and at the end of the reaction the product is separated and the reaction vessel cleaned out ready for the next batch. In a continuous process the reactants are continuously ...
... Batch and Continuous Processes In a batch process the chemicals are loaded into the reaction vessel. The reaction is monitored and at the end of the reaction the product is separated and the reaction vessel cleaned out ready for the next batch. In a continuous process the reactants are continuously ...
Many thermal and chemical reactions occur during the roasting
... Establishing the thermal environment protocol for the ideal roast is a balancing act. While it is desirable to maintain the BRR temperature and energy levels until the target reactions are achieved, the BRR temperature is well above the carmelization temperature of sucrose. Because many roasting sys ...
... Establishing the thermal environment protocol for the ideal roast is a balancing act. While it is desirable to maintain the BRR temperature and energy levels until the target reactions are achieved, the BRR temperature is well above the carmelization temperature of sucrose. Because many roasting sys ...
The s-Block Elements
... 2. For Group II sulphates, the cations are much smaller than the anions. The changing in size of cations does not cause a significant change in H lattice (proportional to 1/(r+ + r-). However, the changing in size of cations does cause H hydration (proportional to 1/r+ and 1/r-) to become less exo ...
... 2. For Group II sulphates, the cations are much smaller than the anions. The changing in size of cations does not cause a significant change in H lattice (proportional to 1/(r+ + r-). However, the changing in size of cations does cause H hydration (proportional to 1/r+ and 1/r-) to become less exo ...
9647 H2 Chemistry
... 10. bring together knowledge, principles and concepts from different areas of chemistry, and apply them in a particular context 11. use chemical skills in contexts which bring together different areas of the subject. These assessment objectives cannot be precisely specified in the Syllabus Content b ...
... 10. bring together knowledge, principles and concepts from different areas of chemistry, and apply them in a particular context 11. use chemical skills in contexts which bring together different areas of the subject. These assessment objectives cannot be precisely specified in the Syllabus Content b ...
Chemistry I Exam
... III. Electromagnetic waves do not require a medium through which to travel. IV. All electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light through a vacuum. A. I and IV only B. I, II, and IV only C. II, III, and IV only D. II and III only ...
... III. Electromagnetic waves do not require a medium through which to travel. IV. All electromagnetic waves travel at the speed of light through a vacuum. A. I and IV only B. I, II, and IV only C. II, III, and IV only D. II and III only ...
Unit 6 Moles and Stoichiometry Short Answer Review
... 5. A hydrated compound contains water molecules within its crystal structure. The percent composition by mass of water in the hydrated compound CaSO 4•2H 2O has an accepted value of 20.9%. A student did an experiment and determined that the percent composition by mass of water in CaSO 4•2H 2O was 21 ...
... 5. A hydrated compound contains water molecules within its crystal structure. The percent composition by mass of water in the hydrated compound CaSO 4•2H 2O has an accepted value of 20.9%. A student did an experiment and determined that the percent composition by mass of water in CaSO 4•2H 2O was 21 ...
Higher Chemistry summary 3a
... suitable for fast single step processes more easily automated using computer control smaller work force operates round the clock, 365 days per year tend to operate with relatively low volumes of reactants allowing easy removal of excess heat energy ...
... suitable for fast single step processes more easily automated using computer control smaller work force operates round the clock, 365 days per year tend to operate with relatively low volumes of reactants allowing easy removal of excess heat energy ...
AP Chemistry Standards and Benchmarks
... These descriptive facts, including chemistry involved in environmental and societal issues, should not be isolated form the principles being studied but should be taught throughout the course to illustrate and illuminate the principles. The following areas should be covered: • chemical reactivity an ...
... These descriptive facts, including chemistry involved in environmental and societal issues, should not be isolated form the principles being studied but should be taught throughout the course to illustrate and illuminate the principles. The following areas should be covered: • chemical reactivity an ...
2013-2014
... ΔH f [CO2(g)] = 395.0 kJ mol1 ΔH f [H2O(l)] = 286.0 kJ mol1 ΔH f [C2H5OH(l)] = 273.0 kJ mol1 Which of the following is the standard enthalpy change of combustion of ethanol,ΔH c [C2H5OH(l)]? A. ...
... ΔH f [CO2(g)] = 395.0 kJ mol1 ΔH f [H2O(l)] = 286.0 kJ mol1 ΔH f [C2H5OH(l)] = 273.0 kJ mol1 Which of the following is the standard enthalpy change of combustion of ethanol,ΔH c [C2H5OH(l)]? A. ...
UNIT 5 - H-W Science Website
... LAB: Bond Breaking and the Heat of Reaction All chemical reactions take place with either an absorption or release of energy. Generally this energy is in the form of heat, but in some processes it may take the form of mainly light, or a mixture of forms including some mechanical energy such as soun ...
... LAB: Bond Breaking and the Heat of Reaction All chemical reactions take place with either an absorption or release of energy. Generally this energy is in the form of heat, but in some processes it may take the form of mainly light, or a mixture of forms including some mechanical energy such as soun ...
Thermochemistry Exam Review Questions
... 3. The reaction: 2S(s) + 3O2 (g) ↔ 2SO3(g) + 800 kJ has reached the equilibrium in a closed container. Which change will shift the equilibrium to the right? A. adding a catalyst without changing the temperature or pressure B. increasing the pressure by reducing the volume C. increasing the temperatu ...
... 3. The reaction: 2S(s) + 3O2 (g) ↔ 2SO3(g) + 800 kJ has reached the equilibrium in a closed container. Which change will shift the equilibrium to the right? A. adding a catalyst without changing the temperature or pressure B. increasing the pressure by reducing the volume C. increasing the temperatu ...
Thermochem problems
... We can use tabulated ΔH values to calculate the enthalpy of reactions ΔH depends on amounts of reactants and products and their initial and final states ΔH is a state function, so does not depend upon how we get from reactants to products Example: N2(g) + 3H2(g) 2 NH3(g) Hrxn = ? N2(g) + 3H2(g) ...
... We can use tabulated ΔH values to calculate the enthalpy of reactions ΔH depends on amounts of reactants and products and their initial and final states ΔH is a state function, so does not depend upon how we get from reactants to products Example: N2(g) + 3H2(g) 2 NH3(g) Hrxn = ? N2(g) + 3H2(g) ...
H2 Chemistry Syllabus (9729)
... Chemistry is about the study of matter, its interactions and transformations. At a macroscopic level, we observe matter and its interactions everywhere in our daily life. The submicroscopic level looks at the structure of matter that gives rise to these interactions. At O Level, students have been i ...
... Chemistry is about the study of matter, its interactions and transformations. At a macroscopic level, we observe matter and its interactions everywhere in our daily life. The submicroscopic level looks at the structure of matter that gives rise to these interactions. At O Level, students have been i ...
Bioorthogonal chemistry
The term bioorthogonal chemistry refers to any chemical reaction that can occur inside of living systems without interfering with native biochemical processes. The term was coined by Carolyn R. Bertozzi in 2003. Since its introduction, the concept of the bioorthogonal reaction has enabled the study of biomolecules such as glycans, proteins, and lipids in real time in living systems without cellular toxicity. A number of chemical ligation strategies have been developed that fulfill the requirements of bioorthogonality, including the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between azides and cyclooctynes (also termed copper-free click chemistry), between nitrones and cyclooctynes, oxime/hydrazone formation from aldehydes and ketones, the tetrazine ligation, the isocyanide-based click reaction, and most recently, the quadricyclane ligation.The use of bioorthogonal chemistry typically proceeds in two steps. First, a cellular substrate is modified with a bioorthogonal functional group (chemical reporter) and introduced to the cell; substrates include metabolites, enzyme inhibitors, etc. The chemical reporter must not alter the structure of the substrate dramatically to avoid affecting its bioactivity. Secondly, a probe containing the complementary functional group is introduced to react and label the substrate.Although effective bioorthogonal reactions such as copper-free click chemistry have been developed, development of new reactions continues to generate orthogonal methods for labeling to allow multiple methods of labeling to be used in the same biosystems.