chapter 9: aqueous solutions
... 1. write the separate aqueous ions (including their correct charges) on the right side 2. write the formula of the compound followed by an arrow 3. balance using coefficients 4. add state symbols (state of pure substance on the left, ((s) usually), (aq) for ions on the right) Example 1: Solid Sodium ...
... 1. write the separate aqueous ions (including their correct charges) on the right side 2. write the formula of the compound followed by an arrow 3. balance using coefficients 4. add state symbols (state of pure substance on the left, ((s) usually), (aq) for ions on the right) Example 1: Solid Sodium ...
2011-2012 ACAD REVIEW SHEET Chapter 16
... following reaction: 2 CO(g) + O2(g) 2 CO2(g)? (ANS: It will shift to PRODUCTS.) 19. How does the reaction shift to reestablish equilibrium if you take away CO to the system in the following reaction: 2 CO(g) + O2(g) 2 CO2(g)? (ANS: It will shift to REACTANTS.) 20. How does the reaction shift to ...
... following reaction: 2 CO(g) + O2(g) 2 CO2(g)? (ANS: It will shift to PRODUCTS.) 19. How does the reaction shift to reestablish equilibrium if you take away CO to the system in the following reaction: 2 CO(g) + O2(g) 2 CO2(g)? (ANS: It will shift to REACTANTS.) 20. How does the reaction shift to ...
CHE 1401 - Fall 2016 - Chapter 5 Homework 5 (Chapter 5
... B) The system loses heat and does work on the surroundings. C) The system gains heat and has work done on it by the surroundings. D) The system loses heat and has work done on it by the surroundings. E) None of the above is correct. ...
... B) The system loses heat and does work on the surroundings. C) The system gains heat and has work done on it by the surroundings. D) The system loses heat and has work done on it by the surroundings. E) None of the above is correct. ...
CHE 1401 - Spring 2016 - Chapter 5 Homework 5 (Chapter 5
... B) The ΔH for a process in the forward direction is equal in magnitude and opposite in sign to the ΔH for the process in the reverse direction. C) If a reaction is carried out in a series of steps, the ΔH for the reaction will equal the product of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps. D) If ...
... B) The ΔH for a process in the forward direction is equal in magnitude and opposite in sign to the ΔH for the process in the reverse direction. C) If a reaction is carried out in a series of steps, the ΔH for the reaction will equal the product of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps. D) If ...
CHE 1401 - Spring 2015 - Chapter 5 Homework 5 (Chapter 5
... B) The system gains heat and has work done on it by the surroundings. C) The system loses heat and does work on the surroundings. D) The system loses heat and has work done on it by the surroundings. E) None of the above is correct. ...
... B) The system gains heat and has work done on it by the surroundings. C) The system loses heat and does work on the surroundings. D) The system loses heat and has work done on it by the surroundings. E) None of the above is correct. ...
CHE 1401 - Fall 2015 - Chapter 5 Homework 5 (Chapter 5
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The British thermal unit (Btu) is commonly used in engineering applications. A Btu is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 lb of water by 1°F. There are _________ ...
... MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The British thermal unit (Btu) is commonly used in engineering applications. A Btu is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 lb of water by 1°F. There are _________ ...
2.4 Chemical equilibria
... What are the products of the forward reaction? What are the reactants of the reverse reaction? What are the products of the reverse reaction? ...
... What are the products of the forward reaction? What are the reactants of the reverse reaction? What are the products of the reverse reaction? ...
Practice Test Stoichiometry
... 17.) A hydrocarbon (a compound consisting solely of carbon and hydrogen) is found to be 85.6% carbon by mass. What is the empirical formula for this compound? A) CH B) CH2 C) C2H D) C3H E) CH4 18.) The empirical formula of a group of compounds is CHCl. Lindane, a powerful insecticide, is a member o ...
... 17.) A hydrocarbon (a compound consisting solely of carbon and hydrogen) is found to be 85.6% carbon by mass. What is the empirical formula for this compound? A) CH B) CH2 C) C2H D) C3H E) CH4 18.) The empirical formula of a group of compounds is CHCl. Lindane, a powerful insecticide, is a member o ...
1 2016-17 Honors Chemistry Review for the Final Exam Each unit
... b) This is a product made from a metal and a nonmetal. However, the bonds have a more covalent character to them than ionic. Name this product using both the ionic and covalent nomenclature systems. c) ...
... b) This is a product made from a metal and a nonmetal. However, the bonds have a more covalent character to them than ionic. Name this product using both the ionic and covalent nomenclature systems. c) ...
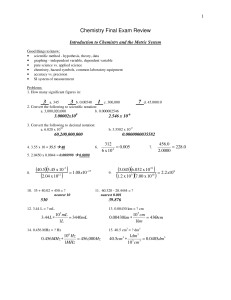
Chemistry Final Exam Review
... • 5 types of reactions: synthesis, decomposition, single replacement, double replacement, combustion • monatomic and diatomic elements • reactant, product, precipitate, know your solubility rules • net ionic equation, spectator ion ...
... • 5 types of reactions: synthesis, decomposition, single replacement, double replacement, combustion • monatomic and diatomic elements • reactant, product, precipitate, know your solubility rules • net ionic equation, spectator ion ...
Chemistry Midterm Review 2006
... 3. Draw in the activation energy for each line. Label the pathways as “with catalyst” & “without the catalyst”. Which line represents the faster reaction. 4. On the pathway to the left, label the activated complex, activation energy, reactants, products, and enthalpy released or absorbed by the reac ...
... 3. Draw in the activation energy for each line. Label the pathways as “with catalyst” & “without the catalyst”. Which line represents the faster reaction. 4. On the pathway to the left, label the activated complex, activation energy, reactants, products, and enthalpy released or absorbed by the reac ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
... of the equation has the same number of atoms of each element as the right side of the equation. 4. Check your answer to see if: – The numbers of atoms of each element, on both each side of the equation should be the same. – The coefficients are in the lowest possible whole number ...
... of the equation has the same number of atoms of each element as the right side of the equation. 4. Check your answer to see if: – The numbers of atoms of each element, on both each side of the equation should be the same. – The coefficients are in the lowest possible whole number ...
Reactions in Aqueous Solution
... What volume of a 1.420 M NaOH solution is required to titrate 25.00 mL of a 4.50 M H2SO4 solution? ...
... What volume of a 1.420 M NaOH solution is required to titrate 25.00 mL of a 4.50 M H2SO4 solution? ...
Study Guide
... 48. Which of the following has the greatest electronegativity? A) Si B) P C) Cl D) Ar E) Br 49. In the compound CH3Cl the bond between carbon and chlorine is A) intermolecular B) ionic C) nonpolar covalent D) polar covalent 50. Which one of the following is NOT true about elements that form cations ...
... 48. Which of the following has the greatest electronegativity? A) Si B) P C) Cl D) Ar E) Br 49. In the compound CH3Cl the bond between carbon and chlorine is A) intermolecular B) ionic C) nonpolar covalent D) polar covalent 50. Which one of the following is NOT true about elements that form cations ...
Final Exam Review
... _______________ ionization energy and a ____________ electron affinity. a. large, large b. large, small c. small, small d. small, large e. None of the above. 41. The term which best describes the crystalline substance that results when a large number of metal atoms transfer electrons to a large numb ...
... _______________ ionization energy and a ____________ electron affinity. a. large, large b. large, small c. small, small d. small, large e. None of the above. 41. The term which best describes the crystalline substance that results when a large number of metal atoms transfer electrons to a large numb ...
Paper 3 - TheAllPapers
... possible. Every reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included, the publisher will be pleased to make amends at the earliest possible opportunity. University of Cambridge International Examinati ...
... possible. Every reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included, the publisher will be pleased to make amends at the earliest possible opportunity. University of Cambridge International Examinati ...
Thermochemistry
... Determine the overall change in enthalpy for the reaction C(graphite)(s) --> C(diamond)(s) given the following reactions and enthalpy changes: ...
... Determine the overall change in enthalpy for the reaction C(graphite)(s) --> C(diamond)(s) given the following reactions and enthalpy changes: ...
THERMOCHEMISTRY
... If a reaction is carried out in a series of steps, H for the reaction will be equal to the sum of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps. A+BX+Y ...
... If a reaction is carried out in a series of steps, H for the reaction will be equal to the sum of the enthalpy changes for the individual steps. A+BX+Y ...
Enzyme Activity
... molecule produced by living organisms that can speed up a specific chemical reaction without itself being destroyed or changed in any way. • K m: (Michaelis constant) The substrate concentration at which an enzyme catalysed reaction proceeds at half the maximum ...
... molecule produced by living organisms that can speed up a specific chemical reaction without itself being destroyed or changed in any way. • K m: (Michaelis constant) The substrate concentration at which an enzyme catalysed reaction proceeds at half the maximum ...
Unit3_Notes - Lesmahagow High School
... Batch and Continuous Processes In a batch process the chemicals are loaded into the reaction vessel. The reaction is monitored and at the end of the reaction the product is separated and the reaction vessel cleaned out ready for the next batch. In a continuous process the reactants are continuously ...
... Batch and Continuous Processes In a batch process the chemicals are loaded into the reaction vessel. The reaction is monitored and at the end of the reaction the product is separated and the reaction vessel cleaned out ready for the next batch. In a continuous process the reactants are continuously ...
Bioorthogonal chemistry
The term bioorthogonal chemistry refers to any chemical reaction that can occur inside of living systems without interfering with native biochemical processes. The term was coined by Carolyn R. Bertozzi in 2003. Since its introduction, the concept of the bioorthogonal reaction has enabled the study of biomolecules such as glycans, proteins, and lipids in real time in living systems without cellular toxicity. A number of chemical ligation strategies have been developed that fulfill the requirements of bioorthogonality, including the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between azides and cyclooctynes (also termed copper-free click chemistry), between nitrones and cyclooctynes, oxime/hydrazone formation from aldehydes and ketones, the tetrazine ligation, the isocyanide-based click reaction, and most recently, the quadricyclane ligation.The use of bioorthogonal chemistry typically proceeds in two steps. First, a cellular substrate is modified with a bioorthogonal functional group (chemical reporter) and introduced to the cell; substrates include metabolites, enzyme inhibitors, etc. The chemical reporter must not alter the structure of the substrate dramatically to avoid affecting its bioactivity. Secondly, a probe containing the complementary functional group is introduced to react and label the substrate.Although effective bioorthogonal reactions such as copper-free click chemistry have been developed, development of new reactions continues to generate orthogonal methods for labeling to allow multiple methods of labeling to be used in the same biosystems.