Energetics
... is independent of the route by which the chemical reaction takes place and depends only on the difference between the total enthalpy of the reactants and that of the products. ...
... is independent of the route by which the chemical reaction takes place and depends only on the difference between the total enthalpy of the reactants and that of the products. ...
Adsorption and desorption
... If the transition state requires a complicated or “demanding” configuration which has a low probability of realization q# and νdes may get much smaller. The agreement between measured and calculated values of νdes is poor. Nevertheless, transition state theory gives an idea why νdes values vary so s ...
... If the transition state requires a complicated or “demanding” configuration which has a low probability of realization q# and νdes may get much smaller. The agreement between measured and calculated values of νdes is poor. Nevertheless, transition state theory gives an idea why νdes values vary so s ...
LaBrake, Fundamentals Diagnostic Questions
... d) A compound is a specific combination of atoms of more than one element. e) In a chemical reaction, atoms are neither created nor destroyed; they exchange partners to produce new substances. 19. All of the following statements are true regarding the nuclear model of the atom, except: a) The positi ...
... d) A compound is a specific combination of atoms of more than one element. e) In a chemical reaction, atoms are neither created nor destroyed; they exchange partners to produce new substances. 19. All of the following statements are true regarding the nuclear model of the atom, except: a) The positi ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... • Compounds containing C, H and O are routinely analyzed through combustion in a chamber like this – C is determined from the mass of CO2 produced – H is determined from the mass of H2O produced – O is determined by difference after the C and H have been ...
... • Compounds containing C, H and O are routinely analyzed through combustion in a chamber like this – C is determined from the mass of CO2 produced – H is determined from the mass of H2O produced – O is determined by difference after the C and H have been ...
Heterogeneous Electron-Transfer Kinetics for
... at a surprisingly small value of this preexponential factor (much lower than would be expected on the basis of aqueous solvent dynamics). This limit is independent of both the identity of the redox couple and the nature of the linkage of the couple to the bridge, and it is definitely different (smal ...
... at a surprisingly small value of this preexponential factor (much lower than would be expected on the basis of aqueous solvent dynamics). This limit is independent of both the identity of the redox couple and the nature of the linkage of the couple to the bridge, and it is definitely different (smal ...
When wood, paper, and wax are burned, they ap
... expressed in terms of its percent composition, which is the percent by mass of each element the compound contains. A knowledge of its chemical formula allows us to calculate the percent composition. Experimental determination of percent composition and the molar mass of a compound enables us to dete ...
... expressed in terms of its percent composition, which is the percent by mass of each element the compound contains. A knowledge of its chemical formula allows us to calculate the percent composition. Experimental determination of percent composition and the molar mass of a compound enables us to dete ...
CHAPTER 6 THERMOCHEMISTRY
... miles traveled, fuel consumption of the airplane, time traveling, airplane snacks eaten, etc. State functions are path-independent; they only depend on the initial and final states. Some state functions for an airplane trip from Chicago to Denver would be longitude change, latitude change, elevation ...
... miles traveled, fuel consumption of the airplane, time traveling, airplane snacks eaten, etc. State functions are path-independent; they only depend on the initial and final states. Some state functions for an airplane trip from Chicago to Denver would be longitude change, latitude change, elevation ...
No Slide Title
... Calculate standard enthalpy changes using bond enthalpy values Calculate standard enthalpy changes using enthalpies of formation and combustion Know simple calorimetry methods for measuring enthalpy changes Calculate enthalpy changes from calorimetry measurements ...
... Calculate standard enthalpy changes using bond enthalpy values Calculate standard enthalpy changes using enthalpies of formation and combustion Know simple calorimetry methods for measuring enthalpy changes Calculate enthalpy changes from calorimetry measurements ...
Isopropanol oxidation by pure metal oxide
... Metal oxides of the IB group (CuO, Ag2 O, Au2 O3 ) exhibited high activity. An XPS analysis was carried out to determine surface impurities. The XPS analysis of CuO revealed the surface to be primarily CuO with traces of C and N. The surface of Ag2 O was mostly Ag2 O with traces of C and Na. XPS ana ...
... Metal oxides of the IB group (CuO, Ag2 O, Au2 O3 ) exhibited high activity. An XPS analysis was carried out to determine surface impurities. The XPS analysis of CuO revealed the surface to be primarily CuO with traces of C and N. The surface of Ag2 O was mostly Ag2 O with traces of C and Na. XPS ana ...
Stoichiometry
... reach from the Sun to Pluto and back 7.5 million times. It would take light 9500 years to travel from the bottom to the top of a stack of 1 mole of $1 bills. ...
... reach from the Sun to Pluto and back 7.5 million times. It would take light 9500 years to travel from the bottom to the top of a stack of 1 mole of $1 bills. ...
enthalpy changes
... Calculate standard enthalpy changes using bond enthalpy values Calculate standard enthalpy changes using enthalpies of formation and combustion Know simple calorimetry methods for measuring enthalpy changes Calculate enthalpy changes from calorimetry measurements ...
... Calculate standard enthalpy changes using bond enthalpy values Calculate standard enthalpy changes using enthalpies of formation and combustion Know simple calorimetry methods for measuring enthalpy changes Calculate enthalpy changes from calorimetry measurements ...
DELTAHPP
... Calculate standard enthalpy changes using bond enthalpy values Calculate standard enthalpy changes using enthalpies of formation and combustion Know simple calorimetry methods for measuring enthalpy changes Calculate enthalpy changes from calorimetry measurements ...
... Calculate standard enthalpy changes using bond enthalpy values Calculate standard enthalpy changes using enthalpies of formation and combustion Know simple calorimetry methods for measuring enthalpy changes Calculate enthalpy changes from calorimetry measurements ...
Chapter 15: Chemical Equilibrium
... Biology: The oxygenation of heme is crucial to life, but so is the absorption and release of other gases, such as carbon dioxide, from body fluids. Other equilibrium processes that occur in the body include the reversible binding of metal ions by proteins and the acid-base balance of biochemical sys ...
... Biology: The oxygenation of heme is crucial to life, but so is the absorption and release of other gases, such as carbon dioxide, from body fluids. Other equilibrium processes that occur in the body include the reversible binding of metal ions by proteins and the acid-base balance of biochemical sys ...
Supplemental Problems
... mine the ages of objects that were once living, such as wood, bones, and fossils. While alive, living things take in all the isotopes of carbon, including carbon-14. Carbon-14 undergoes radioactive decay continuously. After an organism dies, the carbon-14 in its body continues to decay. However, its ...
... mine the ages of objects that were once living, such as wood, bones, and fossils. While alive, living things take in all the isotopes of carbon, including carbon-14. Carbon-14 undergoes radioactive decay continuously. After an organism dies, the carbon-14 in its body continues to decay. However, its ...
chapter 5 gases
... electrons. A reducing agent is a substance that can donate electrons to another substance, thereby reducing this other substance. An oxidizing agent is a substance that can accept electrons from another substance, thereby oxidizing this other substance. Redox reactions are electron-transfer reaction ...
... electrons. A reducing agent is a substance that can donate electrons to another substance, thereby reducing this other substance. An oxidizing agent is a substance that can accept electrons from another substance, thereby oxidizing this other substance. Redox reactions are electron-transfer reaction ...
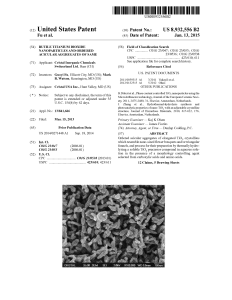
Rutile titanium dioxide nanoparticles and ordered acicular
... tallites are rod-like, e.g., slender and/ or needle-like, having a thickness of from 3 nm to 5 nm and a length which can vary ...
... tallites are rod-like, e.g., slender and/ or needle-like, having a thickness of from 3 nm to 5 nm and a length which can vary ...
Visible Light Photoredox Catalysis with Transition
... Much of the promise of visible light photoredox catalysis hinges on its ability to achieve unique, if not exotic bond constructions that are not possible using established protocols. For instance, photoredox catalysis may be employed to perform overall redox neutral reactions. As both oxidants and r ...
... Much of the promise of visible light photoredox catalysis hinges on its ability to achieve unique, if not exotic bond constructions that are not possible using established protocols. For instance, photoredox catalysis may be employed to perform overall redox neutral reactions. As both oxidants and r ...
IIT-JEE (Advanced) - Brilliant Public School Sitamarhi
... Silver salt method : (for organic acids) Basicity of an acid : No. of replacable H+ atoms in an acid (H contained to more electronegative atom is acidic) Procedure : Some known amount of silver salt (w1 gm) is heated to obtain w2 gm of while shining residue of silver. Then if the basicity of acid is ...
... Silver salt method : (for organic acids) Basicity of an acid : No. of replacable H+ atoms in an acid (H contained to more electronegative atom is acidic) Procedure : Some known amount of silver salt (w1 gm) is heated to obtain w2 gm of while shining residue of silver. Then if the basicity of acid is ...
9/10/10 1 Chemistry 121: Atomic and Molecular Chemistry
... The Mole and Molar Mass: Chemists measure atoms and molecules in moles. • In the SI system the mole (mol) is the amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities (atoms, molecules, or other particles) as there are atoms in exactly 12 g (or 0.012 kg) of the carbon-12 isotope. The actu ...
... The Mole and Molar Mass: Chemists measure atoms and molecules in moles. • In the SI system the mole (mol) is the amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities (atoms, molecules, or other particles) as there are atoms in exactly 12 g (or 0.012 kg) of the carbon-12 isotope. The actu ...
Chapter 4
... Table 4.1 lists examples of strong electrolytes, weak electrolytes, and nonelectrolytes. Ionic compounds, such as sodium chloride, potassium iodide (KI), and calcium nitrate [Ca(NO3)2], are strong electrolytes. It is interesting to note that human body fluids contain many strong and weak electrolyte ...
... Table 4.1 lists examples of strong electrolytes, weak electrolytes, and nonelectrolytes. Ionic compounds, such as sodium chloride, potassium iodide (KI), and calcium nitrate [Ca(NO3)2], are strong electrolytes. It is interesting to note that human body fluids contain many strong and weak electrolyte ...
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
... • CVD is a chemical process used to produce high-purity, high-performance solid materials. • This technique is suitable for the manufacture of coatings, powders, fibers and monolithic components. • This technique is often used in many thin film applications. • By varying the experimental conditions— ...
... • CVD is a chemical process used to produce high-purity, high-performance solid materials. • This technique is suitable for the manufacture of coatings, powders, fibers and monolithic components. • This technique is often used in many thin film applications. • By varying the experimental conditions— ...
Bioorthogonal chemistry
The term bioorthogonal chemistry refers to any chemical reaction that can occur inside of living systems without interfering with native biochemical processes. The term was coined by Carolyn R. Bertozzi in 2003. Since its introduction, the concept of the bioorthogonal reaction has enabled the study of biomolecules such as glycans, proteins, and lipids in real time in living systems without cellular toxicity. A number of chemical ligation strategies have been developed that fulfill the requirements of bioorthogonality, including the 1,3-dipolar cycloaddition between azides and cyclooctynes (also termed copper-free click chemistry), between nitrones and cyclooctynes, oxime/hydrazone formation from aldehydes and ketones, the tetrazine ligation, the isocyanide-based click reaction, and most recently, the quadricyclane ligation.The use of bioorthogonal chemistry typically proceeds in two steps. First, a cellular substrate is modified with a bioorthogonal functional group (chemical reporter) and introduced to the cell; substrates include metabolites, enzyme inhibitors, etc. The chemical reporter must not alter the structure of the substrate dramatically to avoid affecting its bioactivity. Secondly, a probe containing the complementary functional group is introduced to react and label the substrate.Although effective bioorthogonal reactions such as copper-free click chemistry have been developed, development of new reactions continues to generate orthogonal methods for labeling to allow multiple methods of labeling to be used in the same biosystems.