Proceedings of 7th Annual American Business Research Conference
... contract by varying a certain amount of money put aside: the Credit Valuation Adjustment. The CVA can be seen as unilateral or bilateral. From either end of the contract, the counterparty risk is not the same. In the case of a swap, both parties can possibly default, so the CVA calculated by first p ...
... contract by varying a certain amount of money put aside: the Credit Valuation Adjustment. The CVA can be seen as unilateral or bilateral. From either end of the contract, the counterparty risk is not the same. In the case of a swap, both parties can possibly default, so the CVA calculated by first p ...
Financial Markets in Electricity: Introduction to Derivative Instruments
... Physical delivery: The traditional method of settling a derivative contract by delivering the actual commodity or asset specified in the contract from the seller to the buyer. Position: A description of the amount of price risk a trader is taking. For example, a trader who has bought 1000 platinum f ...
... Physical delivery: The traditional method of settling a derivative contract by delivering the actual commodity or asset specified in the contract from the seller to the buyer. Position: A description of the amount of price risk a trader is taking. For example, a trader who has bought 1000 platinum f ...
Another counter-example to antithetic sampling
... This supplement gives a more convincing counter-example based on a popular option trading strategy, the butter°y spread (see, e.g., [1, chapter 8]). The butter°y spread is a trading strategy involving options on the same underlying asset, with the same maturity, but with di®erent strike prices. The ...
... This supplement gives a more convincing counter-example based on a popular option trading strategy, the butter°y spread (see, e.g., [1, chapter 8]). The butter°y spread is a trading strategy involving options on the same underlying asset, with the same maturity, but with di®erent strike prices. The ...
Barcelona
... Motivations • Find a numerical method consistent with: – Smile model: (Dupire 93 Derman Kani 94) – Discrete non proportional dividend ...
... Motivations • Find a numerical method consistent with: – Smile model: (Dupire 93 Derman Kani 94) – Discrete non proportional dividend ...
2.2 The Formal Set-Up
... Example 2.12 presents a situation of this kind. Example 2.12. Consider a single-period market model specified by the following data: the sample space contains only two elementary events, ⌦ = {!1 , !2 }, the interest rate is r = 1, the stock price at time 0 is S0 = 10 and takes the following values a ...
... Example 2.12 presents a situation of this kind. Example 2.12. Consider a single-period market model specified by the following data: the sample space contains only two elementary events, ⌦ = {!1 , !2 }, the interest rate is r = 1, the stock price at time 0 is S0 = 10 and takes the following values a ...
2. Basics of Options
... The seller of a call option is said to write a call, and he receives the options price called a premium. He has an obligation to deliver the underlying asset on the expiration date (European), for the exercise price which may be lower than the market value of the asset. The payoff of a short call po ...
... The seller of a call option is said to write a call, and he receives the options price called a premium. He has an obligation to deliver the underlying asset on the expiration date (European), for the exercise price which may be lower than the market value of the asset. The payoff of a short call po ...
Chapter 5
... b. Buying futures to hedge payables. Example: Firm A have c$500,000.00 payables due on 6/1. So it can purchase a future contract delivered on 6/1 to lock in the price to pay for Canadian dollars on 6/1. c. Selling Futures to Hedge Receivables Example: Firm A have c$500,000.00 receivable due on 6/1. ...
... b. Buying futures to hedge payables. Example: Firm A have c$500,000.00 payables due on 6/1. So it can purchase a future contract delivered on 6/1 to lock in the price to pay for Canadian dollars on 6/1. c. Selling Futures to Hedge Receivables Example: Firm A have c$500,000.00 receivable due on 6/1. ...
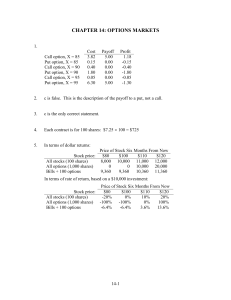
C14_Reilly1ce
... options because it allows security price changes to occur in distinct upward or downward movements • Prices can change continuously throughout time • Advantage of Black-Scholes approach is relatively simple, closed-form equation capable of valuing options accurately under a wide array of circumstanc ...
... options because it allows security price changes to occur in distinct upward or downward movements • Prices can change continuously throughout time • Advantage of Black-Scholes approach is relatively simple, closed-form equation capable of valuing options accurately under a wide array of circumstanc ...
Document
... Over the last years a number of new techniques have been developed that allow for the extraction of considerably more information from option prices than just the expected value or the expected standard deviation (i.e. implied volatility). By using these techniques it is possible to construct implie ...
... Over the last years a number of new techniques have been developed that allow for the extraction of considerably more information from option prices than just the expected value or the expected standard deviation (i.e. implied volatility). By using these techniques it is possible to construct implie ...
Institute of Actuaries of India November 2011 Examinations
... inthe underlying stocks in the relevant markets. In the case of a short term switch there would be of the order of four contract notes to be processed for each stock in one of the markets (assuming say 25 stocks are held in each market this would run to 100 contract notes to be processed); using ind ...
... inthe underlying stocks in the relevant markets. In the case of a short term switch there would be of the order of four contract notes to be processed for each stock in one of the markets (assuming say 25 stocks are held in each market this would run to 100 contract notes to be processed); using ind ...
solutions
... stock. The cost to establish the portfolio is (X – S 0). The payoff at time T (with zero interest earnings on the loan) is (X – S T). In contrast, a put option has a payoff at time T of (X – S T) if that value is positive, and zero otherwise. The put’s payoff is at least as large as the portfolio’s, ...
... stock. The cost to establish the portfolio is (X – S 0). The payoff at time T (with zero interest earnings on the loan) is (X – S T). In contrast, a put option has a payoff at time T of (X – S T) if that value is positive, and zero otherwise. The put’s payoff is at least as large as the portfolio’s, ...
Lecture 3
... disclose investment policies, makes shares redeemable at any time, limit use of leverage take no short positions. ...
... disclose investment policies, makes shares redeemable at any time, limit use of leverage take no short positions. ...
Risk Management and Financial Institutions
... option with a portfolio of vanilla options Underlying principle: if we match the value of an exotic option on some boundary, we have matched it at all interior points of the boundary Static options replication can be contrasted with dynamic options replication where we have to trade continuously to ...
... option with a portfolio of vanilla options Underlying principle: if we match the value of an exotic option on some boundary, we have matched it at all interior points of the boundary Static options replication can be contrasted with dynamic options replication where we have to trade continuously to ...
Amendments to the Operational Clearing Procedures for
... 9.2.1 Mark-to-Market Margin Each day, after the close of trading, SEOCH marks the marginable positions to market with the fixing price of each option series determined by SEOCH. The resulting amount is called the Mark-to-Market margin. Unless otherwise determined by SEOCH under special circumstances ...
... 9.2.1 Mark-to-Market Margin Each day, after the close of trading, SEOCH marks the marginable positions to market with the fixing price of each option series determined by SEOCH. The resulting amount is called the Mark-to-Market margin. Unless otherwise determined by SEOCH under special circumstances ...
Stock price
... i. In response to the increase in Ytel’s common equity price, the straight bond value should stay the same and the option value should increase. The increase in equity price does not affect the straight bond value component of the Ytel convertible. The increase in equity price increases the option v ...
... i. In response to the increase in Ytel’s common equity price, the straight bond value should stay the same and the option value should increase. The increase in equity price does not affect the straight bond value component of the Ytel convertible. The increase in equity price increases the option v ...