Lecture 4 From Binomial Trees to the Black
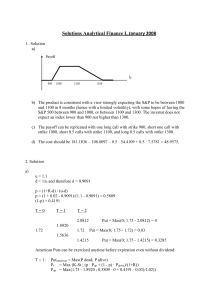
... from an initial (positive) price S(0), assume in each time period the stock price either goes up by a factor u > 1 with probability p, or goes down by a factor 0 < d < 1 with probability 1 − p. The moves over time are iid Bernoulli random variables. For each t, S(t) = S(0)unt dt−nt , where nt repres ...
... from an initial (positive) price S(0), assume in each time period the stock price either goes up by a factor u > 1 with probability p, or goes down by a factor 0 < d < 1 with probability 1 − p. The moves over time are iid Bernoulli random variables. For each t, S(t) = S(0)unt dt−nt , where nt repres ...
Options
... • Investor now owns the right to sell a specified amount of an underlying security at a specified price within a time frame (maturity) • Put options are great for hedging when purchasing a security • Selling a put option is bullish ...
... • Investor now owns the right to sell a specified amount of an underlying security at a specified price within a time frame (maturity) • Put options are great for hedging when purchasing a security • Selling a put option is bullish ...
A Real Options Theory
... The problem: - The possibility that a tenant will renew his lease contract is currently based upon intuitive aspects and is not quantified in a scientific and objective manner - In which way is it possible to quantify the possibility of a ...
... The problem: - The possibility that a tenant will renew his lease contract is currently based upon intuitive aspects and is not quantified in a scientific and objective manner - In which way is it possible to quantify the possibility of a ...
DEXIA « Impact Seminar
... Need to model the stock price evolution Binomial model: – discrete time, discrete variable – volatility captured by u and d Markov process • Future movements in stock price depend only on where we are, not the history of how we got where we are • Consistent with weak-form market efficiency Risk neut ...
... Need to model the stock price evolution Binomial model: – discrete time, discrete variable – volatility captured by u and d Markov process • Future movements in stock price depend only on where we are, not the history of how we got where we are • Consistent with weak-form market efficiency Risk neut ...
Valuing Stock Options: The Black
... The Concepts Underlying BlackScholes • The option price and the stock price depend on the same underlying source of uncertainty • We can form a portfolio consisting of the stock and the option which eliminates this source of uncertainty • The portfolio is instantaneously riskless and must instantan ...
... The Concepts Underlying BlackScholes • The option price and the stock price depend on the same underlying source of uncertainty • We can form a portfolio consisting of the stock and the option which eliminates this source of uncertainty • The portfolio is instantaneously riskless and must instantan ...
Exam March 13, 2015
... -i- (0.7 pt.) The fair price of the option. -ii- (0.7 pt.) The hedging strategy for the seller. -iii- (0.7 pt.) The optimal exercise times for the buyer. (d) (0.5 pt.) One of the criteria to decide which option is more convenient is to compare the expected net market payoff for each option. That is, ...
... -i- (0.7 pt.) The fair price of the option. -ii- (0.7 pt.) The hedging strategy for the seller. -iii- (0.7 pt.) The optimal exercise times for the buyer. (d) (0.5 pt.) One of the criteria to decide which option is more convenient is to compare the expected net market payoff for each option. That is, ...
Risk-neutral modelling with exponential Levy processes - Math-UMN
... opposed sticky strike (generally stochastic volatility models. cf Chap 15) which have a correlation between St and σ imp (T − t, K) • Short term skew is well represented by the jumps of levy processes • Flattening of the skew with option √ maturity. This occurs in accord with the central limit theor ...
... opposed sticky strike (generally stochastic volatility models. cf Chap 15) which have a correlation between St and σ imp (T − t, K) • Short term skew is well represented by the jumps of levy processes • Flattening of the skew with option √ maturity. This occurs in accord with the central limit theor ...
the black–scholes type financial models and the arbitrage
... where V is the value of the call option (theoretical call premium), S the current stock price at the moment of time t, r is the risk-free interest rate, and σ is the volatility (the last two parameters being supposed constant). The condition at the boundaries is: V = max(S − K; 0). The constants K a ...
... where V is the value of the call option (theoretical call premium), S the current stock price at the moment of time t, r is the risk-free interest rate, and σ is the volatility (the last two parameters being supposed constant). The condition at the boundaries is: V = max(S − K; 0). The constants K a ...
THE CONTRIUBTION OF BLACK, MERTON AND SCHOLES TO FINANCIAL ECONOMICS I G
... sell a designated security at or within a certain period of time at a particular price’ (Elton et al 2007: 576). Two of the most common and simple options are ‘calls’ and ‘puts’. A call gives the holder the right to purchase a security at a predetermined price, while a put gives the holder the right ...
... sell a designated security at or within a certain period of time at a particular price’ (Elton et al 2007: 576). Two of the most common and simple options are ‘calls’ and ‘puts’. A call gives the holder the right to purchase a security at a predetermined price, while a put gives the holder the right ...
Option Pricing by Simulation
... zero and variance one. If St follows a lognormal distribution, the one-period-later price St+1 is simulated as ...
... zero and variance one. If St follows a lognormal distribution, the one-period-later price St+1 is simulated as ...
bsopm
... r = The "risk free rate". As with many derivative models, the current LIBOR (for a time period equivalent to the remaining life of the option) is used as the risk free rate. However, note that there is always some academic debate as to what quoted rate should be used as the “risk free rate”. T = The ...
... r = The "risk free rate". As with many derivative models, the current LIBOR (for a time period equivalent to the remaining life of the option) is used as the risk free rate. However, note that there is always some academic debate as to what quoted rate should be used as the “risk free rate”. T = The ...