* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Options
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
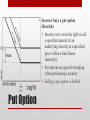
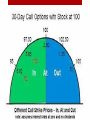
Financial Derivatives Greater Gains Greater Risk • • • • Forward Futures Options Swaps • These are the most common Financial Derivatives • Recall • Owning a stock is owning growth • Owning a bond is owning debt • Options • Call Option the right to buy at a specified price • Put Option the right to sell at a specified price • A stock option is a privilege to buy or sell a stock at an agreed-upon price within a period of time Stock Options • Investor buys a call option (Bullish trade) • Now owns the right to buy the ‘underlying asset’ at a specified price within a given time frame (maturity) • Investor sells a call option • ‘Bearish’ trade • Assumes the obligation to supply the underlying asset Call Option • Investor buys a put option (Bearish) • Investor now owns the right to sell a specified amount of an underlying security at a specified price within a time frame (maturity) • Put options are great for hedging when purchasing a security • Selling a put option is bullish Put Option • Option contracts all have expiration dates • Just as most derivatives • Options have value until expiration • After that, they are worthless • Options with longer time until maturity will be more expensive Price Factors: Time • Strike Price affects the premium (Intrinsic + Extrinsic [time value] because the strike price is the location of the value • Whether it contains intrinsic value, extrinsic value or both Price Factors: Strike Price ITM, OTM and ATM • A strike price that is below the current market price for a security is to be considered in the money • In the money trades mostly like a stock position • Relative to the difference between the strike price and underlying • ITM options require a smaller price move in the underlying in order to be profitable • The downside is that the percentage gain will not be as large • ITM options have the most intrinsic value In the ‘Money’ • The strike price of the option is equal to the underlying price • ATM option has the greatest uncertainty • Uncertainty is the risk associated • ATM can be the worst position if everything moves against you • Can also result in massive gains • ATM can hurt you the most if the underlying moves in the direction opposite of what you hoped At The ‘Money’ • OTM options require a large move in order to be profitable • A move large enough in the direction you want it too, the OTM option can deliver large gains • But if the move is against you, the loss will be less than ATM and ITM • OTM near expiration dates tends to fare well Out of the ‘Money’ • The actual value of a company or an asset based on an underlying perception of its’ true value including all aspects of business Intrinsic Value • The difference between an option’s market price (current price) and its’ intrinsic value • It is also the portion of an item’s worth that is determined by external factors • Extrinsic Value is typically time value of an option • For example: • An option premium price of $10 with an intrinsic value of $9, the extrinsic value is $1 Extrinsic Value • Buy (Long) call • bullish • Sell (Short) Call • bearish • Buy Put • bearish • Short Put • bullish • If your option doesn’t obligate you to something, the risk is less • Shorting an option is riskier, but can pay out big Option Strategies •Pattern • a combination of qualities, acts, tendencies, etc., forming a consistent or characteristic arrangement