Binomial Trees
... If you can replicate, you can hedge: Long the option contract, short the replicating portfolio. The replication portfolio is composed of stock and bond. Since bond only generates parallel shifts in payoff and does not play any role in offsetting/hedging risks, it is the stock that really plays the h ...
... If you can replicate, you can hedge: Long the option contract, short the replicating portfolio. The replication portfolio is composed of stock and bond. Since bond only generates parallel shifts in payoff and does not play any role in offsetting/hedging risks, it is the stock that really plays the h ...
Options on Futures Contracts - Feuz Cattle and Beef Market Analysis
... meet margin calls if the underlying futures contract price moves below the option strike price. Receives the option premium after the option expires. ...
... meet margin calls if the underlying futures contract price moves below the option strike price. Receives the option premium after the option expires. ...
RMTF - The Greeks - Society of Actuaries
... market prices when using a lognormal pricing model which assumes constant volatility (BlackScholes, e.g.), The reasons for this are that the market does reflect, to some extent, the nonnormal distribution of returns, and the expectation for future volatility that is different from historical volatil ...
... market prices when using a lognormal pricing model which assumes constant volatility (BlackScholes, e.g.), The reasons for this are that the market does reflect, to some extent, the nonnormal distribution of returns, and the expectation for future volatility that is different from historical volatil ...
an investor`s guide to index futures
... In recent years, derivatives have become increasingly important in the field of finance. Futures and options, the most popular derivatives are now actively traded on many exchanges. Forward contracts, swaps, and many other derivative instruments are regularly traded both in the exchanges and in the ...
... In recent years, derivatives have become increasingly important in the field of finance. Futures and options, the most popular derivatives are now actively traded on many exchanges. Forward contracts, swaps, and many other derivative instruments are regularly traded both in the exchanges and in the ...
The Black-Scholes-Merton Approach to Pricing Options
... Thus, if we invest w1 = Delta units in the stock and w2 = W − Delta ∗ s in the bond, so the total value of the portfolio will change very little for small changes in the stock price. We remark that such a portfolio and hedge is useful for example when a bank sells a call option. The proceeds from se ...
... Thus, if we invest w1 = Delta units in the stock and w2 = W − Delta ∗ s in the bond, so the total value of the portfolio will change very little for small changes in the stock price. We remark that such a portfolio and hedge is useful for example when a bank sells a call option. The proceeds from se ...
Binomial lattice model for stock prices
... Now consider a European call option for one share of the stock, with strike price K, and expiration date t = 1. The payoff to the holder of this option at time t = 1 is a random variable given by C1 = (S1 − K)+ ; the buyer of such an option is thus betting that the stock price will be above K at the ...
... Now consider a European call option for one share of the stock, with strike price K, and expiration date t = 1. The payoff to the holder of this option at time t = 1 is a random variable given by C1 = (S1 − K)+ ; the buyer of such an option is thus betting that the stock price will be above K at the ...
OPTIONS, GREEKS, AND RISK MANAGEMENT Jelena Paunović *
... Options are financial derivatives representing a contract which gives the right to the holder, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a pre-defined strike price during a certain period of time. These derivative contracts can derive their value from almost any underlying asset ...
... Options are financial derivatives representing a contract which gives the right to the holder, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset at a pre-defined strike price during a certain period of time. These derivative contracts can derive their value from almost any underlying asset ...
colour ppt
... While there are similarities between exchange-traded options and futures contract, there are also some important differences. • An option owner-an investor with a long position- can simply allow the option to die, unexercised. The same opportunity is not available to an investor with a long position ...
... While there are similarities between exchange-traded options and futures contract, there are also some important differences. • An option owner-an investor with a long position- can simply allow the option to die, unexercised. The same opportunity is not available to an investor with a long position ...
Lachov G
... The Bulgarian land market has been under development for the past 15 years. Many of the actual owners have got back their land but the problems with land market, land pricing and opportunity to invest in agricultural land still exist. At the moment, sale transactions in Bulgarian land exist only bet ...
... The Bulgarian land market has been under development for the past 15 years. Many of the actual owners have got back their land but the problems with land market, land pricing and opportunity to invest in agricultural land still exist. At the moment, sale transactions in Bulgarian land exist only bet ...
Chapter Five
... but the stock price has remained the same. Explain three factors that could cause the option premium to change while the stock price remains unchanged. ANSWER: Interest rates could have changed, time passed, and anticipated future volatility might have changed. It is also possible that dividend expe ...
... but the stock price has remained the same. Explain three factors that could cause the option premium to change while the stock price remains unchanged. ANSWER: Interest rates could have changed, time passed, and anticipated future volatility might have changed. It is also possible that dividend expe ...
im09
... charge a premium to provide this insurance. Financial institutions can use options to hedge balance sheet risk, much as described above for futures contracts. Option prices rise when the price of the underlying security is more volatile or when the expiration date is further in the future, because t ...
... charge a premium to provide this insurance. Financial institutions can use options to hedge balance sheet risk, much as described above for futures contracts. Option prices rise when the price of the underlying security is more volatile or when the expiration date is further in the future, because t ...
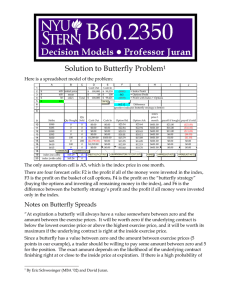
Installment options and static hedging
... continuation boundary. Figure 4 shows the distribution of P&L under the riskneutral measure; this turns out to be close to the uniform distribution. Of course this distribution would be different under different price modelling assumptions, but the main point is that under any reasonable model the e ...
... continuation boundary. Figure 4 shows the distribution of P&L under the riskneutral measure; this turns out to be close to the uniform distribution. Of course this distribution would be different under different price modelling assumptions, but the main point is that under any reasonable model the e ...
Risk-neutral modelling with exponential Levy processes - Math-UMN
... Here are a few cross sections of σ imp (T, K) vs. K/S (moneyness) for a given T for a few different commodity futures markets. ...
... Here are a few cross sections of σ imp (T, K) vs. K/S (moneyness) for a given T for a few different commodity futures markets. ...
chapter 2: the structure of options markets
... Exercise limits are restrictions on the number of options that can be exercised by an investor in a given day or series of days. ...
... Exercise limits are restrictions on the number of options that can be exercised by an investor in a given day or series of days. ...
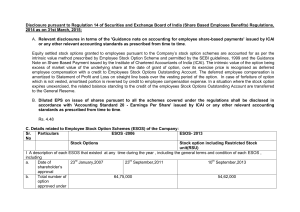
Share Based Employee Benefits
... Number of options granted during the year Number of options forfeited / lapsed during the year Number of options vested during the year Number of options exercised during the year Number of shares arising as a result of exercise of options Money realised by exercise of options (INR), if Scheme is im ...
... Number of options granted during the year Number of options forfeited / lapsed during the year Number of options vested during the year Number of options exercised during the year Number of shares arising as a result of exercise of options Money realised by exercise of options (INR), if Scheme is im ...
option to purchase right of pre-emption (first refusal)
... offer open for a period of time. It is possible that a purchaser could give a seller an option to purchase a property for a specified time but this is not the norm. ...
... offer open for a period of time. It is possible that a purchaser could give a seller an option to purchase a property for a specified time but this is not the norm. ...
The Greek Letters
... Each of the Greek letters measures a different dimension to the risk in an option position. The aim of a trader is to manage the Greeks so that all risks are acceptable. A bank has sold for $300,000 a European call option on 100,000 shares of a non-dividend paying stock. The points that will be made ...
... Each of the Greek letters measures a different dimension to the risk in an option position. The aim of a trader is to manage the Greeks so that all risks are acceptable. A bank has sold for $300,000 a European call option on 100,000 shares of a non-dividend paying stock. The points that will be made ...