Chapter 3
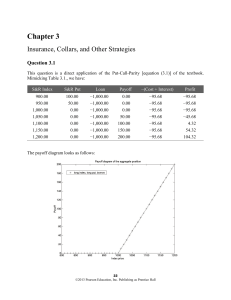
... cost of entering in the bull spread positions. We have: Cost of call bull spread: ($120.405 − $93.809) × 1.02 = $27.13 Cost of put bull spread: ($51.777 − $74.201) × 1.02 = −$22.87 The payoff diagram shows that the payoffs to the put bull spread are uniformly less than the payoffs to the call bull s ...
... cost of entering in the bull spread positions. We have: Cost of call bull spread: ($120.405 − $93.809) × 1.02 = $27.13 Cost of put bull spread: ($51.777 − $74.201) × 1.02 = −$22.87 The payoff diagram shows that the payoffs to the put bull spread are uniformly less than the payoffs to the call bull s ...
Incomplete-Market Prices for Real Estate
... the option payoff. To our knowledge, the good-deal bounds have never been suggested as an application for real estate, but they have been successfully used to price other types of options, like index options or options on non-traded events (see Cochrane and Saa-Requejo, ...
... the option payoff. To our knowledge, the good-deal bounds have never been suggested as an application for real estate, but they have been successfully used to price other types of options, like index options or options on non-traded events (see Cochrane and Saa-Requejo, ...
Derivatives - Karvy Fortune
... We first look at how trading futures differs from trading the underlying spot. Buying security involves putting up all the money upfront. With the purchase of shares of a company, the holder becomes a part owner of the company. The shareholder typically receives the rights and privileges associate ...
... We first look at how trading futures differs from trading the underlying spot. Buying security involves putting up all the money upfront. With the purchase of shares of a company, the holder becomes a part owner of the company. The shareholder typically receives the rights and privileges associate ...
Online Appendix: Payoff Diagrams for Futures and Options
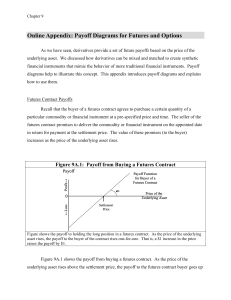
... Writing a put is the reverse of buying one. Again, the writer loses when the holder gains, so the maximum payoff is the premium. The best outcome for an option writer is to have the option expire worthless, so that it is never exercised. Looking at Figure 9A.6, we can see that the put writer’s losse ...
... Writing a put is the reverse of buying one. Again, the writer loses when the holder gains, so the maximum payoff is the premium. The best outcome for an option writer is to have the option expire worthless, so that it is never exercised. Looking at Figure 9A.6, we can see that the put writer’s losse ...
Contract Specifications for Option Contract on EURUSD
... Deep-out-of-the-money short options may show zero or minimal Scan Risk given the price and volatility moves in the 16 market scenarios, yet still present risk in the event that these options move closer-to-the-money or in-the-money, thereby generating potentially large losses. Hence a Short Option M ...
... Deep-out-of-the-money short options may show zero or minimal Scan Risk given the price and volatility moves in the 16 market scenarios, yet still present risk in the event that these options move closer-to-the-money or in-the-money, thereby generating potentially large losses. Hence a Short Option M ...
OPTIONS HEDGING AS A MEAN OF PRICE RISK ELIMINATION
... to sell when the market improves and in doing so they are relieving industry of the need to finance merchandise it does not need. Futures trading or stock exchange trading has already been used for more than a century, but trading in advanced instruments of futures markets still represents one of th ...
... to sell when the market improves and in doing so they are relieving industry of the need to finance merchandise it does not need. Futures trading or stock exchange trading has already been used for more than a century, but trading in advanced instruments of futures markets still represents one of th ...
JSE Equity Options Brochure
... predetermined strike price. If it is based on a FTSE/JSE TOP40 stock, it will settle on the average of the last traded price per minute taken over 100 minutes between 12:01 and 13:40 in the underlying equities market on closeout day by the JSE. What this means is that the price will be an average of ...
... predetermined strike price. If it is based on a FTSE/JSE TOP40 stock, it will settle on the average of the last traded price per minute taken over 100 minutes between 12:01 and 13:40 in the underlying equities market on closeout day by the JSE. What this means is that the price will be an average of ...
Module 8 Strategies for a flat market – Australian Securities
... at expiry, you cannot know for certain whether or not your option will be exercised. For this reason, if on the day of expiry the stock is trading at or very close to the strike, you may consider buying back both legs of a written straddle. Although this involves a small premium expense, and transac ...
... at expiry, you cannot know for certain whether or not your option will be exercised. For this reason, if on the day of expiry the stock is trading at or very close to the strike, you may consider buying back both legs of a written straddle. Although this involves a small premium expense, and transac ...
FINANCIAL MARKETS AND INSTITIUTIONS: A Modern Perspective
... • A long position is the purchase of a futures contract • A short position is the sale of a futures contract • A clearinghouse is the unit that oversees trading on the exchange and guarantees all trades made by the exchange • Open interest is the total number of the futures, put options, or call opt ...
... • A long position is the purchase of a futures contract • A short position is the sale of a futures contract • A clearinghouse is the unit that oversees trading on the exchange and guarantees all trades made by the exchange • Open interest is the total number of the futures, put options, or call opt ...
Sample questions
... non-interest bearing liabilities are greater than non-interest bearing assets more assets than liabilities will be repriced in the near term more assets than liabilities have variable rates or short residual maturities ...
... non-interest bearing liabilities are greater than non-interest bearing assets more assets than liabilities will be repriced in the near term more assets than liabilities have variable rates or short residual maturities ...
Black-Scholes and the Volatility Surface
... 2. At any given maturity, T , the skew cannot be too steep. Otherwise butterfly arbitrages will exist. 3. Likewise the term structure of implied volatility cannot be too inverted. Otherwise calendar spread arbitrages will exist. In practice the implied volatility surface will not violate any of thes ...
... 2. At any given maturity, T , the skew cannot be too steep. Otherwise butterfly arbitrages will exist. 3. Likewise the term structure of implied volatility cannot be too inverted. Otherwise calendar spread arbitrages will exist. In practice the implied volatility surface will not violate any of thes ...
С П Е Ц И Ф И К А Ц И Я
... The Option shall be American. The Option right may be requested on any trading day on the Exchange during the validity period of the Option according to the procedure established herein and by the Trading Rules and Clearing ...
... The Option shall be American. The Option right may be requested on any trading day on the Exchange during the validity period of the Option according to the procedure established herein and by the Trading Rules and Clearing ...
Valuing and Hedging American Put Options Using
... and Scholes, 1973). This solution cannot, however, price options such as the American put option, because with the American put option exercise prior to the date of maturity may be optimal. As a result, the present discounted value of the option must be calculated at each point in time until maturit ...
... and Scholes, 1973). This solution cannot, however, price options such as the American put option, because with the American put option exercise prior to the date of maturity may be optimal. As a result, the present discounted value of the option must be calculated at each point in time until maturit ...
The Black-Scholes
... stock should never be exercised early An American call on a dividend-paying stock should only ever be exercised immediately prior to an ex-dividend date Suppose dividend dates are at times t1, t2, …tn. Early exercise is sometimes optimal at time ti if the dividend at that time is greater than ...
... stock should never be exercised early An American call on a dividend-paying stock should only ever be exercised immediately prior to an ex-dividend date Suppose dividend dates are at times t1, t2, …tn. Early exercise is sometimes optimal at time ti if the dividend at that time is greater than ...
The Black-Scholes
... After the options have been issued it is not necessary to take account of dilution when they are valued Before they are issued we can calculate the cost of each option as N/(N+M) times the price of a regular option with the same terms where N is the number of existing shares and M is the number of n ...
... After the options have been issued it is not necessary to take account of dilution when they are valued Before they are issued we can calculate the cost of each option as N/(N+M) times the price of a regular option with the same terms where N is the number of existing shares and M is the number of n ...
The Greek Letters
... Stop-Loss Strategy This involves: • Buying 100,000 shares as soon as price reaches $50 • Selling 100,000 shares as soon as price falls below $50 This deceptively simple hedging strategy does not work well Options, Futures, and Other Derivatives, 5th edition © 2002 by John C. Hull ...
... Stop-Loss Strategy This involves: • Buying 100,000 shares as soon as price reaches $50 • Selling 100,000 shares as soon as price falls below $50 This deceptively simple hedging strategy does not work well Options, Futures, and Other Derivatives, 5th edition © 2002 by John C. Hull ...