Unit 2 Biochemistry Chp 4 Organic Chemistry Notes
... These chemical groups may be involved in chemical reactions or may contribute to the shape and function of the organic molecule in a characteristic way, giving it unique properties. o ...
... These chemical groups may be involved in chemical reactions or may contribute to the shape and function of the organic molecule in a characteristic way, giving it unique properties. o ...
Group 2 - UC Davis Canvas
... 11. The bond energy of the noble gas fluorine is too small to offset the energy required to break the F—F bond. 13. Iodide ion is slowly oxidized to iodine, which is yellow-brown in aqueous solution, by oxygen in the air: 4 I − ( aq ) + O 2 ( g ) + 4 H + ( aq ) → 2 I 2 ( aq ) + 2 H 2 O(l) . 15. D ...
... 11. The bond energy of the noble gas fluorine is too small to offset the energy required to break the F—F bond. 13. Iodide ion is slowly oxidized to iodine, which is yellow-brown in aqueous solution, by oxygen in the air: 4 I − ( aq ) + O 2 ( g ) + 4 H + ( aq ) → 2 I 2 ( aq ) + 2 H 2 O(l) . 15. D ...
Document
... In this chapter, you learned how to recognize, name, and predict the physical properties of organic compounds that belong to the alcohol, ether, amine, aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, ester, and amide families. You discovered many important uses for organic compounds. You know that 2-propanol (is ...
... In this chapter, you learned how to recognize, name, and predict the physical properties of organic compounds that belong to the alcohol, ether, amine, aldehyde, ketone, carboxylic acid, ester, and amide families. You discovered many important uses for organic compounds. You know that 2-propanol (is ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 5. Give the IUPAC names and the structures of the products formed by the reaction of 1-pentyne with one mole of HBr and a peroxide. 6. What is Markownikoff rule? Explain with an example. 7. Why is acetylene acidic? 8. What is Diels-Alder addition reaction? 9. Differentiate between enantiomers and di ...
... 5. Give the IUPAC names and the structures of the products formed by the reaction of 1-pentyne with one mole of HBr and a peroxide. 6. What is Markownikoff rule? Explain with an example. 7. Why is acetylene acidic? 8. What is Diels-Alder addition reaction? 9. Differentiate between enantiomers and di ...
ap biology study guide
... Proteins, DNA, carbohydrates, and other molecules that distinguish living matter from inorganic material are all composed of carbon atoms bonded to each other and to atoms of other elements. o ...
... Proteins, DNA, carbohydrates, and other molecules that distinguish living matter from inorganic material are all composed of carbon atoms bonded to each other and to atoms of other elements. o ...
Document
... 2. Add prefixes to indicate # of atoms. Omit mono- prefix on the FIRST element. Mono- is OPTIONAL on the ...
... 2. Add prefixes to indicate # of atoms. Omit mono- prefix on the FIRST element. Mono- is OPTIONAL on the ...
CCCH110D Inorganic vs Organic NOTES
... of alkanes from the gas oil (C12 and higher) fraction are heated at very high temperatures ( approx 500 degrees Celsius) in the presence of a variety of catalysts, the molecules break apart and rearrange to smaller, more highly branched alkanes containing 5 to 10 carbons. This process is called cata ...
... of alkanes from the gas oil (C12 and higher) fraction are heated at very high temperatures ( approx 500 degrees Celsius) in the presence of a variety of catalysts, the molecules break apart and rearrange to smaller, more highly branched alkanes containing 5 to 10 carbons. This process is called cata ...
Document
... hardest to break, whereas the C-I bond is relatively weaker (228 kJmol-1) and therefore easier to break. C-Hal bonds get weaker, and so more reactive, down group 7. Chloro compounds are fairly unreactive and remain in the troposphere long enough to reach the stratosphere, where they react with and ...
... hardest to break, whereas the C-I bond is relatively weaker (228 kJmol-1) and therefore easier to break. C-Hal bonds get weaker, and so more reactive, down group 7. Chloro compounds are fairly unreactive and remain in the troposphere long enough to reach the stratosphere, where they react with and ...
CHAPTER 4 CARBON AND THE MOLECULAR DIVERSITY OF LIFE
... These chemical groups may be involved in chemical reactions or may contribute to the shape and function of the organic molecule in a characteristic way, giving it unique properties. o ...
... These chemical groups may be involved in chemical reactions or may contribute to the shape and function of the organic molecule in a characteristic way, giving it unique properties. o ...
Notes - Ch 2
... determined to contain 10.320 g carbon and 0.742 g hydrogen. What is its simplest formula? ...
... determined to contain 10.320 g carbon and 0.742 g hydrogen. What is its simplest formula? ...
OrganicChemistry
... = two carbon chains are joined together by an oxygen atom bonded between two carbon atoms - named by first naming the two methyl groups, followed by the word ether (when both R groups are the same, use prefix di-) ...
... = two carbon chains are joined together by an oxygen atom bonded between two carbon atoms - named by first naming the two methyl groups, followed by the word ether (when both R groups are the same, use prefix di-) ...
AP Chemistry
... Made by cracking an alkane (heating long-chain alkane in presence of catalyst). This causes (among other things) a double bond to form, and the elimination of two H's. General rule: 2n, creates at least one pi bond. Has sp2 hybridization on the double bond. ...
... Made by cracking an alkane (heating long-chain alkane in presence of catalyst). This causes (among other things) a double bond to form, and the elimination of two H's. General rule: 2n, creates at least one pi bond. Has sp2 hybridization on the double bond. ...
Name__________________________________________ Answers to Sample Exam Questions #1 Chemistry 112
... 4. Which of the following elements would you expect to behave most like magnesium? a) sodium b) calcium c) aluminum d) scandium 5. Which of the following has the longest wavelength? a) X rays b) microwaves c) green light ...
... 4. Which of the following elements would you expect to behave most like magnesium? a) sodium b) calcium c) aluminum d) scandium 5. Which of the following has the longest wavelength? a) X rays b) microwaves c) green light ...
Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules Reading: Wade
... Hydrogen Bonds are particularly strong dipole-dipole attractions due to a highly polarized O–H or N–H bond (only when H is bonded to an electronegative element). The partial positive charge on H in each of these bonds gives this atom a high affinity for nonbonded electrons (lone pairs). The strength ...
... Hydrogen Bonds are particularly strong dipole-dipole attractions due to a highly polarized O–H or N–H bond (only when H is bonded to an electronegative element). The partial positive charge on H in each of these bonds gives this atom a high affinity for nonbonded electrons (lone pairs). The strength ...
Organic Chemistry (HL) Revision Questions
... The product C5H11OH formed from the reaction with 1-bromopentane is warmed with ethanoic acid in the presence of a few drops of concentrated sulfuric acid. State the name of the type of reaction taking place and the structural formula of the ...
... The product C5H11OH formed from the reaction with 1-bromopentane is warmed with ethanoic acid in the presence of a few drops of concentrated sulfuric acid. State the name of the type of reaction taking place and the structural formula of the ...
Organic Chemistry
... = involves the joining of monomers of unsaturated compounds (b) Condensation polymerization = involves the joining of monomers by removing water from hydroxyl groups and joining the monomers by an ether or ester ...
... = involves the joining of monomers of unsaturated compounds (b) Condensation polymerization = involves the joining of monomers by removing water from hydroxyl groups and joining the monomers by an ether or ester ...
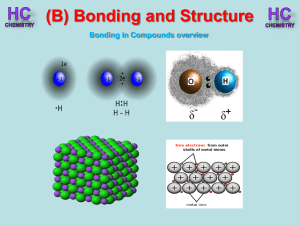
Lesson 1 - Bonding in compounds overview
... Silicon and oxygen make up nearly 75% of the Earth’s crust. They are therefore the most common elements in the Earth’s crust. They combine together to make a covalent network compound called silicon dioxide. This is usually found in the form of sand or quartz. Each Si atom is bonded to 4 O atoms, an ...
... Silicon and oxygen make up nearly 75% of the Earth’s crust. They are therefore the most common elements in the Earth’s crust. They combine together to make a covalent network compound called silicon dioxide. This is usually found in the form of sand or quartz. Each Si atom is bonded to 4 O atoms, an ...
TT T p
... which one kind of atom or group of atomsis replaced by anotherkind of atom or group of atoms are called substitutionreactions.Except for combustion and thermal decomposition,reactionsof saturated hydrocarbonsare usually substitution reactions in which one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced. When a ...
... which one kind of atom or group of atomsis replaced by anotherkind of atom or group of atoms are called substitutionreactions.Except for combustion and thermal decomposition,reactionsof saturated hydrocarbonsare usually substitution reactions in which one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced. When a ...
Chapter 1-Continue
... Draw Lewis structure and condensed structural formulas for the four alcohol with molecular formula C4H10O. Classify each alcohol as primary, secondary or tertiary. ◦ Hints: Consider the connectivity of the four carbon atoms; they can be bonded either four in a chain or three in a chain with the four ...
... Draw Lewis structure and condensed structural formulas for the four alcohol with molecular formula C4H10O. Classify each alcohol as primary, secondary or tertiary. ◦ Hints: Consider the connectivity of the four carbon atoms; they can be bonded either four in a chain or three in a chain with the four ...
Organic chemistry
... If more then one sidechain comes off the main chain, label each one, and write which carbon it branched from. ...
... If more then one sidechain comes off the main chain, label each one, and write which carbon it branched from. ...
Chemical Nomenclature (ionic compounds)
... Scientists have agreed on a set of rules that govern the naming and formulation of compounds. It is universal! The following pages are a programmed approach to the problem of obtaining either the formula or name of a chemical compound. a) The compound will be formed by combining a metal and a non-me ...
... Scientists have agreed on a set of rules that govern the naming and formulation of compounds. It is universal! The following pages are a programmed approach to the problem of obtaining either the formula or name of a chemical compound. a) The compound will be formed by combining a metal and a non-me ...
Calcium
... the weather. Also, there is a modern trend now is to use hydrogen gas as an alternative fuel for petroleum products. ...
... the weather. Also, there is a modern trend now is to use hydrogen gas as an alternative fuel for petroleum products. ...
Introduction to Biodiesel Chemistry
... Organic chemistry is the branch of chemistry that deals with organic compounds. Organic compounds are compounds that (with a few exceptions such as carbon dioxide gas) contain the element carbon. The properties of organic compounds are dependent primarily on the physical structure of the molecules a ...
... Organic chemistry is the branch of chemistry that deals with organic compounds. Organic compounds are compounds that (with a few exceptions such as carbon dioxide gas) contain the element carbon. The properties of organic compounds are dependent primarily on the physical structure of the molecules a ...
Lecture outline handouts
... Proteins, DNA, carbohydrates, and other molecules that distinguish living matter from inorganic material are all composed of carbon atoms bonded to each other and to atoms of other elements. o ...
... Proteins, DNA, carbohydrates, and other molecules that distinguish living matter from inorganic material are all composed of carbon atoms bonded to each other and to atoms of other elements. o ...
Ch. 4
... Proteins, DNA, carbohydrates, and other molecules that distinguish living matter from inorganic material are all composed of carbon atoms bonded to each other and to atoms of other elements. o ...
... Proteins, DNA, carbohydrates, and other molecules that distinguish living matter from inorganic material are all composed of carbon atoms bonded to each other and to atoms of other elements. o ...
Organosulfur compounds

Organosulfur compounds are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature abounds with organosulfur compounds—sulfur is essential for life. Of the 20 common amino acids, two (cysteine and methionine) are organosulfur compounds, and the antibiotics penicillin (pictured below) and sulfa drugs both contain sulfur. While sulfur-containing antibiotics save many lives, sulfur mustard is a deadly chemical warfare agent. Fossil fuels, coal, petroleum, and natural gas, which are derived from ancient organisms, necessarily contain organosulfur compounds, the removal of which is a major focus of oil refineries.Sulfur shares the chalcogen group with oxygen, selenium and tellurium, and it is expected that organosulfur compounds have similarities with carbon–oxygen, carbon–selenium and carbon–tellurium compounds, which is true to some extent.A classical chemical test for the detection of sulfur compounds is the Carius halogen method.