Lecture 5 (2.1-2.3)
... 2.3 Dalton’s Atomic Theory • Postulates of Dalton’s atomic theory (1808) 1. Matter consist of small, indivisible and indestructible atoms. 2. All atoms of an element are identical in mass and different from the atoms of other elements. 3. Compounds result from chemical combinations of different ele ...
... 2.3 Dalton’s Atomic Theory • Postulates of Dalton’s atomic theory (1808) 1. Matter consist of small, indivisible and indestructible atoms. 2. All atoms of an element are identical in mass and different from the atoms of other elements. 3. Compounds result from chemical combinations of different ele ...
CHM 222 Organic Chemistry II
... After completing CHM 222, Organic Chemistry II, the student will be able to: A. Demonstrate an understanding of the structure, nomenclature, reactions, mechanisms and synthesis of the different classes of carbon compounds. B. Describe the characteristics of the different classes of organic compounds ...
... After completing CHM 222, Organic Chemistry II, the student will be able to: A. Demonstrate an understanding of the structure, nomenclature, reactions, mechanisms and synthesis of the different classes of carbon compounds. B. Describe the characteristics of the different classes of organic compounds ...
Preparation of alkyl halides There are lots of ways to make alkyl
... You use some kind of base in each of these cases (either triethylamine or pyridine) so that you can neutralize the acid that is formed during the reaction. The key feature of these reactions is that you are converting OH into a much better leaving group as well. 2. Preparation o ...
... You use some kind of base in each of these cases (either triethylamine or pyridine) so that you can neutralize the acid that is formed during the reaction. The key feature of these reactions is that you are converting OH into a much better leaving group as well. 2. Preparation o ...
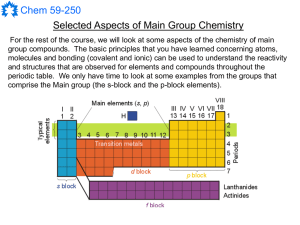
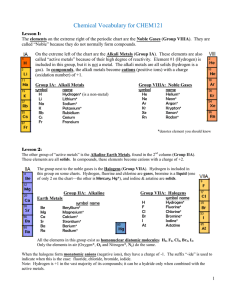
Main Group Notes 1
... Group 1: M(s) + HOR M+ + (OR)- + ½ H2(g) Group 2: M(s) + 2 HOR M+2 + 2 (OR)- + H2(g) These reactions make metal alkoxides that are very useful for the synthesis of other products using metathesis reactions. Metathesis indicates that the reagents exchange ligands with one another. Such reactions ...
... Group 1: M(s) + HOR M+ + (OR)- + ½ H2(g) Group 2: M(s) + 2 HOR M+2 + 2 (OR)- + H2(g) These reactions make metal alkoxides that are very useful for the synthesis of other products using metathesis reactions. Metathesis indicates that the reagents exchange ligands with one another. Such reactions ...
Ch. 4: Carbon
... form large, complex, diverse organic molecules Describe how carbon skeletons may vary and explain how this variation contributes to the diversity and complexity of organic molecules Distinguish among the three types of isomers: ...
... form large, complex, diverse organic molecules Describe how carbon skeletons may vary and explain how this variation contributes to the diversity and complexity of organic molecules Distinguish among the three types of isomers: ...
Chapter 2: Structure and Properties of Organic Molecules
... A) Hydrocarbons (contains only C, H) B) Compounds containing “O” C) Compounds containing “N” ...
... A) Hydrocarbons (contains only C, H) B) Compounds containing “O” C) Compounds containing “N” ...
Chemistry activity 10 organic structures
... Students studying A2 Chemistry who are interested in organic chemistry, chemical structures, synthesis. Key Concepts Organic chemistry, functional groups, chemical structures. The Activity How organic molecules react depends on the functional groups they contain. Very often during a reaction the car ...
... Students studying A2 Chemistry who are interested in organic chemistry, chemical structures, synthesis. Key Concepts Organic chemistry, functional groups, chemical structures. The Activity How organic molecules react depends on the functional groups they contain. Very often during a reaction the car ...
Lecture 39 - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... Progressively Oxidizing (adding Oxygen) the alcohol allows us to go from an alcohol to a carboxylic acid ...
... Progressively Oxidizing (adding Oxygen) the alcohol allows us to go from an alcohol to a carboxylic acid ...
File - Mr Francis` Weebly
... • Within organic chemistry carbon forms 4 bonds, this gives it a tetrahedral shape. • Whenever you are counting the bonds a carbon atom makes-look for 4! • It has 6 electrons in its outer shell arranged ...
... • Within organic chemistry carbon forms 4 bonds, this gives it a tetrahedral shape. • Whenever you are counting the bonds a carbon atom makes-look for 4! • It has 6 electrons in its outer shell arranged ...
11.1 Organic Chemistry
... without the elimination of atoms. Molecules with double bonds open one of the bonds which allows them to link together in a long chain. The monomer ethene opens one of its double bonds to form a long polymer, polyethylene. ...
... without the elimination of atoms. Molecules with double bonds open one of the bonds which allows them to link together in a long chain. The monomer ethene opens one of its double bonds to form a long polymer, polyethylene. ...
elements of chemistry unit
... 3. The arrangement of atoms in molecules and polyatomic ions is depicted by: (A) abbreviated configurations (B) configurations (C) condensed structural diagrams (D) orbital diagrams (E) structural diagrams 4. Two atoms share four electrons. What type of bond exists between the two atoms? (A) single ...
... 3. The arrangement of atoms in molecules and polyatomic ions is depicted by: (A) abbreviated configurations (B) configurations (C) condensed structural diagrams (D) orbital diagrams (E) structural diagrams 4. Two atoms share four electrons. What type of bond exists between the two atoms? (A) single ...
1 - vnhsteachers
... 3. The arrangement of atoms in molecules and polyatomic ions is depicted by: (A) abbreviated configurations (B) configurations (C) condensed structural diagrams (D) orbital diagrams (E) structural diagrams 4. Two atoms share four electrons. What type of bond exists between the two atoms? (A) single ...
... 3. The arrangement of atoms in molecules and polyatomic ions is depicted by: (A) abbreviated configurations (B) configurations (C) condensed structural diagrams (D) orbital diagrams (E) structural diagrams 4. Two atoms share four electrons. What type of bond exists between the two atoms? (A) single ...
Name: Chem 22 Final exam Spring `00 What product is formed when
... a) Thiols have a pka values of about 16, and they are stronger acids than alcohols. b) Thiols have a pka values of about 16, and they are weaker acids than alcohols c) Thiols have a pka values of about 10, and they are stronger acids than alcohols d) Thiols do not have a pka values. e) Thiols have a ...
... a) Thiols have a pka values of about 16, and they are stronger acids than alcohols. b) Thiols have a pka values of about 16, and they are weaker acids than alcohols c) Thiols have a pka values of about 10, and they are stronger acids than alcohols d) Thiols do not have a pka values. e) Thiols have a ...
Review Chapters 8-18 - Bakersfield College
... 14. Which of these compounds show cis-trans isomerism? For each that does, draw structural formulas for both isomers. Which one has a higher boiling point (cis or trans)? a) 2-methyl-2-butene ...
... 14. Which of these compounds show cis-trans isomerism? For each that does, draw structural formulas for both isomers. Which one has a higher boiling point (cis or trans)? a) 2-methyl-2-butene ...
Organic Chemistry Unit Test! /50
... 3. Look around you. There are plastics everywhere! How have organic chemists been able to do so much with such a basic starting material (ethene derivatives)? Explain why such variety in plastic properties is possible, and give an example of a plastic to illustrate one of your points (4 ...
... 3. Look around you. There are plastics everywhere! How have organic chemists been able to do so much with such a basic starting material (ethene derivatives)? Explain why such variety in plastic properties is possible, and give an example of a plastic to illustrate one of your points (4 ...
Scientific Method - Virtual Medical Academy
... Polyatomic Ions:-Ammonium>NH4+ Perchlorate>ClO4Cyanide>CNhydroxid OHNitrate>NO3Nitrite>NO2Nitride>N3- ...
... Polyatomic Ions:-Ammonium>NH4+ Perchlorate>ClO4Cyanide>CNhydroxid OHNitrate>NO3Nitrite>NO2Nitride>N3- ...
Chapter 23
... Primary Amides: • contains –CONH2 group (e.g. peptides) can form strong hydrogen bonds to each other; therefore amides have high melting and boiling points • naming: 1. Can be named as derivatives of carboxylic acids -- Or, by replacing the –e ending with –amide ...
... Primary Amides: • contains –CONH2 group (e.g. peptides) can form strong hydrogen bonds to each other; therefore amides have high melting and boiling points • naming: 1. Can be named as derivatives of carboxylic acids -- Or, by replacing the –e ending with –amide ...
Scientific Method - Virtual Medical Academy
... Polyatomic Ions:-Ammonium>NH4+ Perchlorate>ClO4Cyanide>CNhydroxid OHNitrate>NO3Nitrite>NO2Nitride>N3- ...
... Polyatomic Ions:-Ammonium>NH4+ Perchlorate>ClO4Cyanide>CNhydroxid OHNitrate>NO3Nitrite>NO2Nitride>N3- ...
Hydro carbons
... hydrogen. They are the organic compounds of simplest composition and may be considered theoretically as the parent substances from which all other organic compounds are derived. The hydrocarbons are conveniently classified into two major groups, openchain and cyclic. In open-chain compounds containi ...
... hydrogen. They are the organic compounds of simplest composition and may be considered theoretically as the parent substances from which all other organic compounds are derived. The hydrocarbons are conveniently classified into two major groups, openchain and cyclic. In open-chain compounds containi ...
Organic Chemistry 5 Problems (2014)
... An organic compound A is 54.5% carbon by mass, 9.1% hydrogen by mass and the remainder is oxygen. a) ...
... An organic compound A is 54.5% carbon by mass, 9.1% hydrogen by mass and the remainder is oxygen. a) ...
CHEMISTRY 3.5 Paper 1 Describe the structure and reactions of
... acidic conditions, the amino acid forms an ion that will move towards one electrode. In basic conditions, it forms another ion that will move towards the other electrode. Explain how the conditions described above give rise to two ions that will move towards the two different electrodes and state wh ...
... acidic conditions, the amino acid forms an ion that will move towards one electrode. In basic conditions, it forms another ion that will move towards the other electrode. Explain how the conditions described above give rise to two ions that will move towards the two different electrodes and state wh ...
Slide 1
... Photosynthesis is the only process that produces the elemental oxygen that is essential for animals on Earth. ...
... Photosynthesis is the only process that produces the elemental oxygen that is essential for animals on Earth. ...
Organosulfur compounds

Organosulfur compounds are organic compounds that contain sulfur. They are often associated with foul odors, but many of the sweetest compounds known are organosulfur derivatives, e.g., saccharin. Nature abounds with organosulfur compounds—sulfur is essential for life. Of the 20 common amino acids, two (cysteine and methionine) are organosulfur compounds, and the antibiotics penicillin (pictured below) and sulfa drugs both contain sulfur. While sulfur-containing antibiotics save many lives, sulfur mustard is a deadly chemical warfare agent. Fossil fuels, coal, petroleum, and natural gas, which are derived from ancient organisms, necessarily contain organosulfur compounds, the removal of which is a major focus of oil refineries.Sulfur shares the chalcogen group with oxygen, selenium and tellurium, and it is expected that organosulfur compounds have similarities with carbon–oxygen, carbon–selenium and carbon–tellurium compounds, which is true to some extent.A classical chemical test for the detection of sulfur compounds is the Carius halogen method.