physical setting chemistry
... This is a test of your knowledge of chemistry. Use that knowledge to answer all questions in this examination. Some questions may require the use of the 2011 Edition Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry. You are to answer all questions in all parts of this examination according to the dir ...
... This is a test of your knowledge of chemistry. Use that knowledge to answer all questions in this examination. Some questions may require the use of the 2011 Edition Reference Tables for Physical Setting/Chemistry. You are to answer all questions in all parts of this examination according to the dir ...
2 The Nature of Matter
... elements of matter: earth, air, fire, and water. These elements were not equivalent to matter in modern chemistry. For the alchemists, earth, air, fire, and water represented four fundamental properties of matter. Alchemists believed that these properties existed independent of matter and could be a ...
... elements of matter: earth, air, fire, and water. These elements were not equivalent to matter in modern chemistry. For the alchemists, earth, air, fire, and water represented four fundamental properties of matter. Alchemists believed that these properties existed independent of matter and could be a ...
Unit 8: Reactions - Mark Rosengarten
... Driving Force: The “motivation” of a reaction to occur: In nature, changes that require the least amount of energy will be the ones that happen. After all, when you let go of a bowling ball, it falls down. The motivation is gravity. It would take more energy to make the ball go up than down, so the ...
... Driving Force: The “motivation” of a reaction to occur: In nature, changes that require the least amount of energy will be the ones that happen. After all, when you let go of a bowling ball, it falls down. The motivation is gravity. It would take more energy to make the ball go up than down, so the ...
Chapter 12 Packet
... 20) In dilute nitric acid, HNO3, copper metal dissolves according to the following equation: 3Cu(s) + 8HNO3(aq) 3Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2NO(g) + 4H2O(aq) How many grams of HNO3 are needed to dissolve 11.45g of Cu? 21) The reaction of powdered aluminum and iron(II)oxide, 2Al(s) + Fe2O3(s) Al2O3(s) + 2Fe ...
... 20) In dilute nitric acid, HNO3, copper metal dissolves according to the following equation: 3Cu(s) + 8HNO3(aq) 3Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2NO(g) + 4H2O(aq) How many grams of HNO3 are needed to dissolve 11.45g of Cu? 21) The reaction of powdered aluminum and iron(II)oxide, 2Al(s) + Fe2O3(s) Al2O3(s) + 2Fe ...
An Experiment on Equipotential Curves
... An AC (50 Hz) power supply, which has number of fixed voltage output terminals (in a step of 1.5 V) from 0.0 V to 12.0 V, is provided. A 230 V AC voltage stabilizer is used to maintain a constant input voltage to the AC power supply. The power supply is used to establish the necessary potential diff ...
... An AC (50 Hz) power supply, which has number of fixed voltage output terminals (in a step of 1.5 V) from 0.0 V to 12.0 V, is provided. A 230 V AC voltage stabilizer is used to maintain a constant input voltage to the AC power supply. The power supply is used to establish the necessary potential diff ...
Chemistry
... as 440 BC, the Greek Leucippus and his pupil Democritus coined the term atomos to describe the smallest particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth century, chemist, John Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made up of unique ...
... as 440 BC, the Greek Leucippus and his pupil Democritus coined the term atomos to describe the smallest particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth century, chemist, John Dalton, revived the term when he suggested that each element was made up of unique ...
Principles of Chemistry 1 and 2 Notes
... a. Look at the tables 10.1 and 10.2 (pages 369 and 375, respectively) in the textbook and figure out the electron bonding pair geometry and the molecular geometry of the whole molecule. a. Note that in cases where there are no lone pairs (nonbonding pairs), the electron pairs geometry will equal the ...
... a. Look at the tables 10.1 and 10.2 (pages 369 and 375, respectively) in the textbook and figure out the electron bonding pair geometry and the molecular geometry of the whole molecule. a. Note that in cases where there are no lone pairs (nonbonding pairs), the electron pairs geometry will equal the ...
chem equation Pkt Student2
... 1) Which side of the yields arrow do you find reactants? ______________________________ 2) Which side of the yields arrow do you find products? _______________________________ 3) In a chemical equation, what do the coefficients represent? ______________________________ 4) In a chemical equation, wha ...
... 1) Which side of the yields arrow do you find reactants? ______________________________ 2) Which side of the yields arrow do you find products? _______________________________ 3) In a chemical equation, what do the coefficients represent? ______________________________ 4) In a chemical equation, wha ...
2/22 Lecture Slides
... processes that are exothermic (Δ H < 0) and increase disorder (Δ S > 0) are favored at all T processes that have Δ H > 0 and Δ S > 0 are favored at high T ...
... processes that are exothermic (Δ H < 0) and increase disorder (Δ S > 0) are favored at all T processes that have Δ H > 0 and Δ S > 0 are favored at high T ...
UNIVERSITY OF TARTU THE GIFTED AND
... Every amino acid contains a carboxyl group and an amine group; the difference lies in the side group R of the 2nd carbon. a) Draw the following peptide: glycine-alanine-serine-glutamic acid. It is possible to decarboxylate amino acids – in the process the –COOH group is replaced with hydrogen and CO ...
... Every amino acid contains a carboxyl group and an amine group; the difference lies in the side group R of the 2nd carbon. a) Draw the following peptide: glycine-alanine-serine-glutamic acid. It is possible to decarboxylate amino acids – in the process the –COOH group is replaced with hydrogen and CO ...
AVOGADRO EXAMS 1991 - 2002 PRACTICE BOOKLET
... 14. ”A valence electron in a pure metal is not held by any specific atom, but all valence electrons are used to hold together the atoms of the metal.” This statement is best classified as (a) a specific experimental fact (b) an opinion not based upon evidence (c) a correct definition of a chemical t ...
... 14. ”A valence electron in a pure metal is not held by any specific atom, but all valence electrons are used to hold together the atoms of the metal.” This statement is best classified as (a) a specific experimental fact (b) an opinion not based upon evidence (c) a correct definition of a chemical t ...
Chemical Equations
... In the method of half-reactions, you first break down the reaction into the unbalanced oxidation and reduction half-reactions. Then you balance each half-reaction separately by the following procedure: First do steps 1-4 to each half-reaction: 1. Balance the elements other than O and H. 2. Balance t ...
... In the method of half-reactions, you first break down the reaction into the unbalanced oxidation and reduction half-reactions. Then you balance each half-reaction separately by the following procedure: First do steps 1-4 to each half-reaction: 1. Balance the elements other than O and H. 2. Balance t ...
Mechanistic Studies of the Reactions of Silicon
... Two sets of experiments were carried out at a constant [MeOH]/[t-BuOH] ratio (0.42 or 0.31) but with the total alcohol concentration varying between 0.006 M and 0.093 M. The concentration of 8 was also adjusted so that it was roughly 10% of the methanol concentration, and photolyses were carried out ...
... Two sets of experiments were carried out at a constant [MeOH]/[t-BuOH] ratio (0.42 or 0.31) but with the total alcohol concentration varying between 0.006 M and 0.093 M. The concentration of 8 was also adjusted so that it was roughly 10% of the methanol concentration, and photolyses were carried out ...
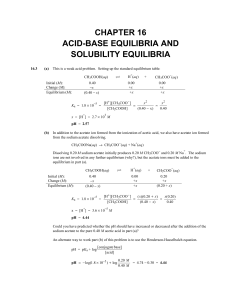
CHAPTER 16 ACID-BASE EQUILIBRIA AND SOLUBILITY
... The charges of the M and X ions are +3 and −2, respectively (are other values possible?). We first calculate the number of moles of M2X3 that dissolve in 1.0 L of water 1 mol ...
... The charges of the M and X ions are +3 and −2, respectively (are other values possible?). We first calculate the number of moles of M2X3 that dissolve in 1.0 L of water 1 mol ...
Additional Review
... o pH is an indication of the ________________________________________ in a solution o the higher the concentration of H+ ions the stronger the acid, the higher the pH acids: _________________ neutral _________________ bases: _________________ ...
... o pH is an indication of the ________________________________________ in a solution o the higher the concentration of H+ ions the stronger the acid, the higher the pH acids: _________________ neutral _________________ bases: _________________ ...
14.1 Redox equations
... Work out formulae of the species before and after the change; balance if required Work out oxidation state of the element before and after the change Add electrons to one side of the equation so that the oxidation states balance If the charges on the species (ions and electrons) on either side of th ...
... Work out formulae of the species before and after the change; balance if required Work out oxidation state of the element before and after the change Add electrons to one side of the equation so that the oxidation states balance If the charges on the species (ions and electrons) on either side of th ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.