CHEMISTRY – Summer Assignment Solutions 2013
... Naming – always name the ions not the formulas (cation then anion). Name tells the type of ions involved not how many of each ion cations: name the element; if more than one oxidation state is possible (d-block) follow with the charge in Roman numerals in parentheses anions: if monatomic then use ...
... Naming – always name the ions not the formulas (cation then anion). Name tells the type of ions involved not how many of each ion cations: name the element; if more than one oxidation state is possible (d-block) follow with the charge in Roman numerals in parentheses anions: if monatomic then use ...
Ch 11 Review - mvhs
... 10. E – The negative tests suggest that the unknown is a covalent network, metallic, or nonsolubility ionic compound. However, since it is highly volatile, this implies weak IMFs, which contradicts the first tests. ...
... 10. E – The negative tests suggest that the unknown is a covalent network, metallic, or nonsolubility ionic compound. However, since it is highly volatile, this implies weak IMFs, which contradicts the first tests. ...
Chapter 6 Chemical Reactions: An Introduction
... • Count atoms of each element – Polyatomic ions may be counted as one “element” if they do not change in the reaction. Al + FeSO4 → Al2(SO4)3 + Fe 1 SO4 3 – If an element appears in more than one compound on the same side, count each element separately and add. CO + O2 → CO2 1 + 2 O 2 ...
... • Count atoms of each element – Polyatomic ions may be counted as one “element” if they do not change in the reaction. Al + FeSO4 → Al2(SO4)3 + Fe 1 SO4 3 – If an element appears in more than one compound on the same side, count each element separately and add. CO + O2 → CO2 1 + 2 O 2 ...
Chemical Equilibrium
... Changing the volume of a reactant container changes the concentration of gaseous reactants and therefore their partial pressures Equilibrium position will therefore move The value of Kc or Kp does NOT change Changing pressure by adding more of an inert gas has no effect of the equilibrium position - ...
... Changing the volume of a reactant container changes the concentration of gaseous reactants and therefore their partial pressures Equilibrium position will therefore move The value of Kc or Kp does NOT change Changing pressure by adding more of an inert gas has no effect of the equilibrium position - ...
SCH4U Exam Review
... 8. The equilibrium constant for the reaction: SO3 (g) + NO(g) NO2 (g) + SO2 (g) was found to be 0.500 at a certain temperature. If 0.300 mol of SO3 and 0.300 mol of NO were placed in a 2.00 L container and allowed to react, what would be the equilibrium concentration of each gas? ANS: 0.0621 M, 0. ...
... 8. The equilibrium constant for the reaction: SO3 (g) + NO(g) NO2 (g) + SO2 (g) was found to be 0.500 at a certain temperature. If 0.300 mol of SO3 and 0.300 mol of NO were placed in a 2.00 L container and allowed to react, what would be the equilibrium concentration of each gas? ANS: 0.0621 M, 0. ...
Chapter 4 Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... The solubility of a substance at a particular temperature is the amount of that substance that can be dissolved in a given quantity of solvent at that temperature. • A substance with a solubility of less than 0.01 mol/L is regarded as being insoluble. Aqueous Reactions ...
... The solubility of a substance at a particular temperature is the amount of that substance that can be dissolved in a given quantity of solvent at that temperature. • A substance with a solubility of less than 0.01 mol/L is regarded as being insoluble. Aqueous Reactions ...
ws-8-14-2
... _____ 4. (T/F) For the reaction aA bB, the rate remains constant over time. Reactant A is therefore a first order reactant. _____ 5. (T/F) Zero order reactions often have their rate controlled (limited) by a factor other than reactant concentrations, such as a catalyst or adsorption surface. 6. Th ...
... _____ 4. (T/F) For the reaction aA bB, the rate remains constant over time. Reactant A is therefore a first order reactant. _____ 5. (T/F) Zero order reactions often have their rate controlled (limited) by a factor other than reactant concentrations, such as a catalyst or adsorption surface. 6. Th ...
Regents Chemistry Topic Review Packet
... 4. A physical change results in the rearrangement of existing particles in a substance; no new types of particles result from this type of change. A chemical change results in the formation of different particles with changed properties. Distinguish between chemical and physical changes based on w ...
... 4. A physical change results in the rearrangement of existing particles in a substance; no new types of particles result from this type of change. A chemical change results in the formation of different particles with changed properties. Distinguish between chemical and physical changes based on w ...
Electrochemistry
... How to draw a Galvanic Cell The oxidation reaction occurs at the anode. The reduction reaction occurs at the cathode. You will be give the unbalanced net ionic reaction or a list of the substances present (line notation). From the information given you need to decide what half reactions occur in ea ...
... How to draw a Galvanic Cell The oxidation reaction occurs at the anode. The reduction reaction occurs at the cathode. You will be give the unbalanced net ionic reaction or a list of the substances present (line notation). From the information given you need to decide what half reactions occur in ea ...
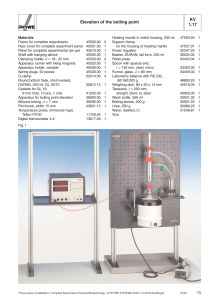
KV 1.17 Elevation of the boiling point
... set-up or procedure. For details on this, refer to the technical literature and the operating instructions for the “Apparatus for boiling point elevation”. From the results of the measurement example, seven values are given, between 55.32 g/mole and 64.70 g/mole. The average of these gives a molar m ...
... set-up or procedure. For details on this, refer to the technical literature and the operating instructions for the “Apparatus for boiling point elevation”. From the results of the measurement example, seven values are given, between 55.32 g/mole and 64.70 g/mole. The average of these gives a molar m ...
Class_X–Science__term_I
... i) Reaction with Metals - Certain reactive metals such as Zinc, Aluminium, and Tin react with alkali solutions on heating and evolve hydrogen gas. 2NaOH + Zn Na2ZnO2 +H2 ii) Reaction with acids -Bases react with acids to form salt and water. KOH +HCl KCl +H2O iii) Reaction with Non -metallic ox ...
... i) Reaction with Metals - Certain reactive metals such as Zinc, Aluminium, and Tin react with alkali solutions on heating and evolve hydrogen gas. 2NaOH + Zn Na2ZnO2 +H2 ii) Reaction with acids -Bases react with acids to form salt and water. KOH +HCl KCl +H2O iii) Reaction with Non -metallic ox ...
Chemical fractionation at environmental interfaces
... interfacial depth of the NaBr and NaI solutions is observed to be greater than that of neat water, NaF, and NaCl solution, implying that there are concentration gradients of the various species that extend the interfacial region several layers into what was the bulk. 1.2.4 Hofmeister effects ...
... interfacial depth of the NaBr and NaI solutions is observed to be greater than that of neat water, NaF, and NaCl solution, implying that there are concentration gradients of the various species that extend the interfacial region several layers into what was the bulk. 1.2.4 Hofmeister effects ...
ExamView - 1999 AP Chemistry Exam.tst
... NH4NO3(s) → N2O(g) + 2 H2O(g) A 0.03 mol sample of NH4NO3(s) is placed in a 1 L evacuated flask, which is then sealed and heated. The NH4NO3(s) decomposes completely according to the balanced equation above. The total pressure in the flask measured at 400 K is closest to which of the following? ( Th ...
... NH4NO3(s) → N2O(g) + 2 H2O(g) A 0.03 mol sample of NH4NO3(s) is placed in a 1 L evacuated flask, which is then sealed and heated. The NH4NO3(s) decomposes completely according to the balanced equation above. The total pressure in the flask measured at 400 K is closest to which of the following? ( Th ...
Unit 3: Bonding and Nomenclature Content Outline: Chemical
... ii. The fewer Hydrogen bonds, the lower the boiling point usually. iii. A single water molecule has 4 simultaneous Hydrogen bonds, so it requires a high temperature to boil, which is good since water covers 2/3rds of Earth and makes up 90% of your body. d. Hydrogen bonds are represented by dotted li ...
... ii. The fewer Hydrogen bonds, the lower the boiling point usually. iii. A single water molecule has 4 simultaneous Hydrogen bonds, so it requires a high temperature to boil, which is good since water covers 2/3rds of Earth and makes up 90% of your body. d. Hydrogen bonds are represented by dotted li ...
C:\SUBJECTS\SUBJECTS\Chemistry
... oxygen gas in an eudiometer at 373K (100oC) and 1 at atmosphere. The resulting mixture is cooled to 298 K (25oC) and passed over calcium chloride. The volume of the residual gas is A. 40cm3 B. 20cm3 ...
... oxygen gas in an eudiometer at 373K (100oC) and 1 at atmosphere. The resulting mixture is cooled to 298 K (25oC) and passed over calcium chloride. The volume of the residual gas is A. 40cm3 B. 20cm3 ...
About writing chemical equations ppt
... 3. Conditions required to carry out the reaction may be placed above or below the arrow. A delta indicates heat is applied. 4. Coefficients 2 H2O are placed in front to balance the equation. One is never placed there, it is just understood. ...
... 3. Conditions required to carry out the reaction may be placed above or below the arrow. A delta indicates heat is applied. 4. Coefficients 2 H2O are placed in front to balance the equation. One is never placed there, it is just understood. ...
Equilibrium
... Indicator: Discuss why most chemical reactions do not proceed to completion Some chemical reactions proceed to completion: CH4 + O2 ---> CO2 + H2O Combustion reaction goes until all of the reactant is converted to product Most reactions do not go to completion: ...
... Indicator: Discuss why most chemical reactions do not proceed to completion Some chemical reactions proceed to completion: CH4 + O2 ---> CO2 + H2O Combustion reaction goes until all of the reactant is converted to product Most reactions do not go to completion: ...
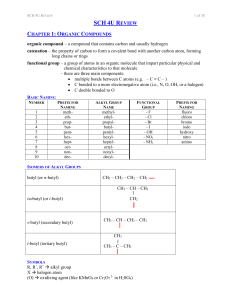
SCH 4U REVIEW Notes
... a compound with a structure based on benzene (a ring of six carbons) consider the benzene ring to be the parent molecule alkyl groups are named to give the lowest combination of numbers, with no particular starting carbon (as it is a ring) when it is easier to consider the benzene ring as an alk ...
... a compound with a structure based on benzene (a ring of six carbons) consider the benzene ring to be the parent molecule alkyl groups are named to give the lowest combination of numbers, with no particular starting carbon (as it is a ring) when it is easier to consider the benzene ring as an alk ...
chemistry-subject test5 w. solutions
... dispersion forces (in the order of decreasing strength). For the ideal gas law to give an accurate prediction of the volume, then, we are looking for gases that do not have ahttp://doc.guandang.net/bbca35c11081d34250955e480.html strong dipole moment. Methane, CH4, does not have a dipole moment: What ...
... dispersion forces (in the order of decreasing strength). For the ideal gas law to give an accurate prediction of the volume, then, we are looking for gases that do not have ahttp://doc.guandang.net/bbca35c11081d34250955e480.html strong dipole moment. Methane, CH4, does not have a dipole moment: What ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.