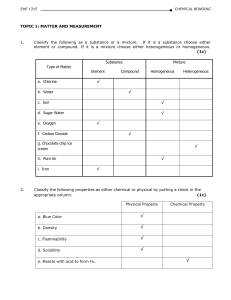
Stoichiometry Notes
... A) How many grams of carbon are found in 33 grams of CO2? B) How many grams of hydrogen are found in 36 grams of H2O? C) If a sample that contains only C, H, & O is originally 30 grams and is found to have 12 grams of carbon and 2 grams of hydrogen. How many grams are oxygen and what is the e ...
... A) How many grams of carbon are found in 33 grams of CO2? B) How many grams of hydrogen are found in 36 grams of H2O? C) If a sample that contains only C, H, & O is originally 30 grams and is found to have 12 grams of carbon and 2 grams of hydrogen. How many grams are oxygen and what is the e ...
Chapter 3: Formulae, Equations and Moles (Ch3 Chang, Ch3
... Chapter 3: Formulae, Equations and Moles (Ch3 Chang, Ch3 Jespersen) Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions Atomic mass (or weight) is the mass of an atom in atomic mass units. Molecular weight is the mass of the molecule in atomic mass units. ...
... Chapter 3: Formulae, Equations and Moles (Ch3 Chang, Ch3 Jespersen) Mass Relationships in Chemical Reactions Atomic mass (or weight) is the mass of an atom in atomic mass units. Molecular weight is the mass of the molecule in atomic mass units. ...
2015 International Practice Exam: Chemistry
... never discuss these specific multiple-choice questions at any time in any form with anyone, including your teacher and other students. If you disclose these questions through any means, your AP Exam score will be canceled. . . . You must complete the answer sheet using a No. 2 pencil only. Mark all ...
... never discuss these specific multiple-choice questions at any time in any form with anyone, including your teacher and other students. If you disclose these questions through any means, your AP Exam score will be canceled. . . . You must complete the answer sheet using a No. 2 pencil only. Mark all ...
Industrial Zinc Plating Processes
... ii. E0 = constant characteristic of material of electrode. Standard electrode potential iii. R = gas constant = 8.3143 J/kmol iv. T = absolute temperature in Kelvins v. F = faraday vi. N = valence change vii. A = activity of the metal E0 = -0.76 volts for zinc without complex Zn2+ + 4(CN)- → [Zn(CN) ...
... ii. E0 = constant characteristic of material of electrode. Standard electrode potential iii. R = gas constant = 8.3143 J/kmol iv. T = absolute temperature in Kelvins v. F = faraday vi. N = valence change vii. A = activity of the metal E0 = -0.76 volts for zinc without complex Zn2+ + 4(CN)- → [Zn(CN) ...
Chemical Reactions
... 1. Give the student the formula of barium hydroxide and sulfuric acid and ask them to predict the product of the reaction. 2. To a 250-mL beaker add 30 mL of 0.1 M sulfuric acid. 3. To the beaker add 50 mL of water and 2 drops of phenolphthalein. 4. Ask the student for their opinion as why the water ...
... 1. Give the student the formula of barium hydroxide and sulfuric acid and ask them to predict the product of the reaction. 2. To a 250-mL beaker add 30 mL of 0.1 M sulfuric acid. 3. To the beaker add 50 mL of water and 2 drops of phenolphthalein. 4. Ask the student for their opinion as why the water ...
DEPARTMENT OF CHEMISTRY, CFS, IIUM
... variety of matter is recognized is called a property. A characteristic that depends upon the amount of matter in the sample is called an extensive property. A characteristic that does not depend upon the amount of matter is called an intensive property. A characteristic that can be observed without ...
... variety of matter is recognized is called a property. A characteristic that depends upon the amount of matter in the sample is called an extensive property. A characteristic that does not depend upon the amount of matter is called an intensive property. A characteristic that can be observed without ...
Chapter 4 Alcohols and Alkyl Halides
... Thus, although the difluoride CH3CHF2 boils at a higher temperature than CH3CH2F, the trifluoride CH3CF3 boils at a lower temperature than either of them. Even more striking is the observation that the hexafluoride CF3CF3 is the lowest boiling of any of the fluorinated derivatives of ethane. The boi ...
... Thus, although the difluoride CH3CHF2 boils at a higher temperature than CH3CH2F, the trifluoride CH3CF3 boils at a lower temperature than either of them. Even more striking is the observation that the hexafluoride CF3CF3 is the lowest boiling of any of the fluorinated derivatives of ethane. The boi ...
CHAPTER 23 THE TRANSITION ELEMENTS AND THEIR
... a) The cation is tetramminezinc ion. The tetraammine indicate four NH3 ligands. Zinc has an oxidation state of +2, so the charge on the cation is +2. The anion is SO42-. Only one sulfate is needed to make a neutral salt. The formula of the compound is [Zn(NH3)4]SO4. b) The cation is pentaamminechlor ...
... a) The cation is tetramminezinc ion. The tetraammine indicate four NH3 ligands. Zinc has an oxidation state of +2, so the charge on the cation is +2. The anion is SO42-. Only one sulfate is needed to make a neutral salt. The formula of the compound is [Zn(NH3)4]SO4. b) The cation is pentaamminechlor ...
4-Pres-Feb-08
... Chemical Equation • C2H5OH + 3 O2 2 CO2 + 3 H2O The equation is balanced and the reaction can be completely stated as: ...
... Chemical Equation • C2H5OH + 3 O2 2 CO2 + 3 H2O The equation is balanced and the reaction can be completely stated as: ...
concentration 0.100 mol dm -3
... Individual students may use the material at home for revision purposes or it may be used for classroom teaching if an interactive white board is available. Accompanying notes on this, and the full range of AS and A2 topics, are available from the KNOCKHARDY SCIENCE WEBSITE at... ...
... Individual students may use the material at home for revision purposes or it may be used for classroom teaching if an interactive white board is available. Accompanying notes on this, and the full range of AS and A2 topics, are available from the KNOCKHARDY SCIENCE WEBSITE at... ...
Chemistry of METALS
... II. Chemical processes. Rock salt/ solid sodium chloride is heated to molten state in a chamber lined with fire bricks on the outside. Sodium chloride has a melting point of about 800oC. A little calcium (II) chloride is added to lower the melting point of the electrolyte to about 600oC. The molten ...
... II. Chemical processes. Rock salt/ solid sodium chloride is heated to molten state in a chamber lined with fire bricks on the outside. Sodium chloride has a melting point of about 800oC. A little calcium (II) chloride is added to lower the melting point of the electrolyte to about 600oC. The molten ...
Critical Assessment of the Formation of Ionic-Liquid - PATh
... [C4mim]Cl, and distinct inorganic salts. The authors6 have shown that ATPS with [C4mim]Cl can be formed by the adequate addition of alkaline aqueous solutions of the following salts: K3PO4, KOH, K2HPO4, NaOH, K2CO3, and Na2HPO4. Nevertheless, when using acidic or neutral salts, such as KH2PO4, (NH4) ...
... [C4mim]Cl, and distinct inorganic salts. The authors6 have shown that ATPS with [C4mim]Cl can be formed by the adequate addition of alkaline aqueous solutions of the following salts: K3PO4, KOH, K2HPO4, NaOH, K2CO3, and Na2HPO4. Nevertheless, when using acidic or neutral salts, such as KH2PO4, (NH4) ...
Stoichiometry File
... combustion simultaneously, reacting with oxygen from the air. As you might imagine, an accurate description of the combustion of such a complex mixture of compounds would be quite a challenge. So for our present purposes, it will be helpful to use a simplifying model. The simplest possible model is ...
... combustion simultaneously, reacting with oxygen from the air. As you might imagine, an accurate description of the combustion of such a complex mixture of compounds would be quite a challenge. So for our present purposes, it will be helpful to use a simplifying model. The simplest possible model is ...
Production of materials
... communication. Increasing affluence and the importance placed upon material possessions and mobility have increased incentives to develop alternative materials and energy sources. 'Chemists and chemical engineers continue to play a pivotal role in the search for new sources of traditional materials ...
... communication. Increasing affluence and the importance placed upon material possessions and mobility have increased incentives to develop alternative materials and energy sources. 'Chemists and chemical engineers continue to play a pivotal role in the search for new sources of traditional materials ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.