Chapter 4: Reactions in Aqueous Solution
... 64. Which of the following represents an acid-base neutralization reaction? A) 2Al(s) + 3H2SO4(aq) Al2(SO4)3(aq) + 3H2(g) B) SO2(g) + H2O(l) H2SO3(g) C) LiOH(aq) + HNO3(aq) LiNO3(aq) + H2O(l) D) 2KBr(aq) + Cl2(g) 2KCl(aq) + Br2(l) E) CaBr2(aq) + H2SO4(aq) CaSO4(s) + 2HBr(g) Ans: C Category ...
... 64. Which of the following represents an acid-base neutralization reaction? A) 2Al(s) + 3H2SO4(aq) Al2(SO4)3(aq) + 3H2(g) B) SO2(g) + H2O(l) H2SO3(g) C) LiOH(aq) + HNO3(aq) LiNO3(aq) + H2O(l) D) 2KBr(aq) + Cl2(g) 2KCl(aq) + Br2(l) E) CaBr2(aq) + H2SO4(aq) CaSO4(s) + 2HBr(g) Ans: C Category ...
Lab - SMC Homepages - Santa Monica College
... to make special arrangements for students who are absent. In addition, the majority of study should NOT be performed immediately before an exam. It is strongly recommended that students schedule a minimum of twenty (20) to thirty (30) hours per week for study. This means that students should READ TH ...
... to make special arrangements for students who are absent. In addition, the majority of study should NOT be performed immediately before an exam. It is strongly recommended that students schedule a minimum of twenty (20) to thirty (30) hours per week for study. This means that students should READ TH ...
Document
... Reaction Enthalpies Calorimetry is an accurate technique for determining enthalpy changes, but how do chemists deal with chemical systems that cannot be analyzed using this technique? For example, the rusting of iron (Figure 1) is extremely slow and, therefore, the resulting temperature change would ...
... Reaction Enthalpies Calorimetry is an accurate technique for determining enthalpy changes, but how do chemists deal with chemical systems that cannot be analyzed using this technique? For example, the rusting of iron (Figure 1) is extremely slow and, therefore, the resulting temperature change would ...
Modern inorganic chemistry
... Chemistry which is intended to replace the book by Wood and Holliday. This new book, like its predecessor, should also be of value in first-year tertiary level chemistry courses. The new syllabuses have made it possible to go much further in systematising and explaining the facts of inorganic chemis ...
... Chemistry which is intended to replace the book by Wood and Holliday. This new book, like its predecessor, should also be of value in first-year tertiary level chemistry courses. The new syllabuses have made it possible to go much further in systematising and explaining the facts of inorganic chemis ...
Chem12 SM Unit 5 Review final ok
... 42. (a) In P2O5, the oxidation number of O is –2 and the oxidation number of P is +5. (b) In NO2, the oxidation number of O is –2 and the oxidation number of N is +4. (c) In Na2SO4, the oxidation number of Na is +1, the oxidation number of O is –2, and the oxidation number of S is +6. (d) In Cu(NO3) ...
... 42. (a) In P2O5, the oxidation number of O is –2 and the oxidation number of P is +5. (b) In NO2, the oxidation number of O is –2 and the oxidation number of N is +4. (c) In Na2SO4, the oxidation number of Na is +1, the oxidation number of O is –2, and the oxidation number of S is +6. (d) In Cu(NO3) ...
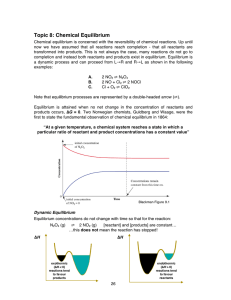
Topic 8: Chemical Equilibrium
... A. Q gets smaller, so the equilibrium shifts to produce more product If concentration increases, the system acts to consume some of it If concentration decreases, the system acts to produce some of it 2. Change in pressure The pressure of a system can be changed in three ways: • Add or remove a gase ...
... A. Q gets smaller, so the equilibrium shifts to produce more product If concentration increases, the system acts to consume some of it If concentration decreases, the system acts to produce some of it 2. Change in pressure The pressure of a system can be changed in three ways: • Add or remove a gase ...
The Mole Concept
... How many moles of water are in a liter of water? Assume 1 liter = 1 kilogram water 1. Calculate the formula weight(mass) for water, H2O. Look up the atomic weights in the periodic table for H and O. The atomic weight for hydrogen is 1 The atomic weight for oxygen is 16 2. Add up the masses from all ...
... How many moles of water are in a liter of water? Assume 1 liter = 1 kilogram water 1. Calculate the formula weight(mass) for water, H2O. Look up the atomic weights in the periodic table for H and O. The atomic weight for hydrogen is 1 The atomic weight for oxygen is 16 2. Add up the masses from all ...
APPENDIX 2 1 ASSESSMENT OF STUDENT LEARNING BROAD
... What are the units for each of these types of solutions? Do all these units apply to solutions made from either dilution of stronger solutions or from the solid? Molarity and normality can be done for either type of solution, but % is for solutions prepared from solids only and 10x is for dilutions ...
... What are the units for each of these types of solutions? Do all these units apply to solutions made from either dilution of stronger solutions or from the solid? Molarity and normality can be done for either type of solution, but % is for solutions prepared from solids only and 10x is for dilutions ...
Chaptr 4 HW PacketAK - Summit Academy High School
... Ba(OH)2 – strong base d) HCl – strong acid e) NH3 – weak base You should have memorized the six “strong” acids—those that can completely dissociate in water—memorizing these six means that anything ...
... Ba(OH)2 – strong base d) HCl – strong acid e) NH3 – weak base You should have memorized the six “strong” acids—those that can completely dissociate in water—memorizing these six means that anything ...
SELECTED ANSWERS
... 2. The distance between the floor and a typical doorknob is about one meter. A penny weighs about three grams. ...
... 2. The distance between the floor and a typical doorknob is about one meter. A penny weighs about three grams. ...
Chapter 17 lecture notes on Chemical Equilibria
... A few points to make about Kc: 1. Temperature dependence. The value is obtained for a specific temperature. This is not surprising since K is a thermodynamic constant and all thermodynamic constants are strongly dependent upon T. Once again, a standard temperature has to be selected for recording v ...
... A few points to make about Kc: 1. Temperature dependence. The value is obtained for a specific temperature. This is not surprising since K is a thermodynamic constant and all thermodynamic constants are strongly dependent upon T. Once again, a standard temperature has to be selected for recording v ...
WA AP Chem gas law IMF MC Set C
... with a high dipole-dipole moment and is capable of forming hydrogen bonds, and these forces of attraction between molecules enable the water to be adhesive to the manometer, and resist the pressures of the gas and the atmosphere. B. The manometer containing water, because water is less dense than me ...
... with a high dipole-dipole moment and is capable of forming hydrogen bonds, and these forces of attraction between molecules enable the water to be adhesive to the manometer, and resist the pressures of the gas and the atmosphere. B. The manometer containing water, because water is less dense than me ...
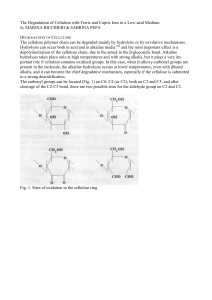
The Degradation of Cellulose with Ferric and Cupric Ions in a Low
... As a reducing agent it is possible to use borohydrides11, which specifically react with two types of carbonyls, aldehydes and ketones, reducing them back to alcohol (Fig. 6). Several investigations12-16 on tetramethylammoniun, tetraethylammoniun and sodium borohydrides have been reported in the lit ...
... As a reducing agent it is possible to use borohydrides11, which specifically react with two types of carbonyls, aldehydes and ketones, reducing them back to alcohol (Fig. 6). Several investigations12-16 on tetramethylammoniun, tetraethylammoniun and sodium borohydrides have been reported in the lit ...
IIT-JEE (Advanced) - Brilliant Public School Sitamarhi
... Silver salt method : (for organic acids) Basicity of an acid : No. of replacable H+ atoms in an acid (H contained to more electronegative atom is acidic) Procedure : Some known amount of silver salt (w1 gm) is heated to obtain w2 gm of while shining residue of silver. Then if the basicity of acid is ...
... Silver salt method : (for organic acids) Basicity of an acid : No. of replacable H+ atoms in an acid (H contained to more electronegative atom is acidic) Procedure : Some known amount of silver salt (w1 gm) is heated to obtain w2 gm of while shining residue of silver. Then if the basicity of acid is ...
exercise on Chapter 13 - Louisiana Tech University
... 5) Increasing temperature of exothermic (Hrxn = negative, shift (left)) or endothermic (Hrxn = positive, shift (right)) and vise versa. 6) Increasing pressure affect a reaction if there is change stoichiometric coefficients (n) of gaseous reactants and products: (n) = 0, no change; (n) = +, shi ...
... 5) Increasing temperature of exothermic (Hrxn = negative, shift (left)) or endothermic (Hrxn = positive, shift (right)) and vise versa. 6) Increasing pressure affect a reaction if there is change stoichiometric coefficients (n) of gaseous reactants and products: (n) = 0, no change; (n) = +, shi ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.