Question Bank for Pre Board Exam(XII Chemistry)
... 2. Why urea has a sharp melting point but glass does not have? 3. A NaCl crystal is found to have Cs Cl structure. Guess how it might have happened? 4. Why is Frenkel defect not found in pure alkali metal halides? 5. NaCl and Cs Cl have similar formula. Then why they have different structures? 6. No ...
... 2. Why urea has a sharp melting point but glass does not have? 3. A NaCl crystal is found to have Cs Cl structure. Guess how it might have happened? 4. Why is Frenkel defect not found in pure alkali metal halides? 5. NaCl and Cs Cl have similar formula. Then why they have different structures? 6. No ...
Module 29: General Chemistry Instructor Guide – Answer Key
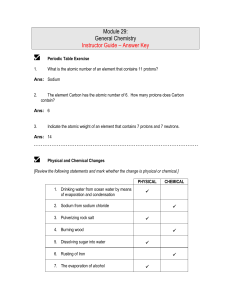
... Ans: Element – a substance that cannot be decomposed into simpler substances by any chemical reaction. Compound – a substance that is composed of two or more elements that are chemically combined in fixed proportions. Mixture – a material that can be separated by physical means into two or more subs ...
... Ans: Element – a substance that cannot be decomposed into simpler substances by any chemical reaction. Compound – a substance that is composed of two or more elements that are chemically combined in fixed proportions. Mixture – a material that can be separated by physical means into two or more subs ...
syllabus - WordPress.com
... Since separation of charge is a seat of potential, the charges of opposite signs on the fixed and diffused parts of the double layeraround the colloidal particle results in a difference in potential between these layers. This potential difference between the fixed layer and the diffused layer of opp ...
... Since separation of charge is a seat of potential, the charges of opposite signs on the fixed and diffused parts of the double layeraround the colloidal particle results in a difference in potential between these layers. This potential difference between the fixed layer and the diffused layer of opp ...
Chapter 7 Plasma Basics
... rate is mainly determined by electron energy in plasma, which is in turn controlled by the applied power. Also related to pressure, electrode spacing, gas species and chamber design. In most plasma processing chambers, the ionization rate is less than 0.01%. The ionization rate of high density p ...
... rate is mainly determined by electron energy in plasma, which is in turn controlled by the applied power. Also related to pressure, electrode spacing, gas species and chamber design. In most plasma processing chambers, the ionization rate is less than 0.01%. The ionization rate of high density p ...
Module 1 Predictor Questions
... Pay special attention to the unit factors provided as they are what will be used in converting one unit to another. Note that each unit factor may be written in two equivalent ways. The one you use depends on what units you are trying to cancel in a dimensional analysis problem (see examples below). ...
... Pay special attention to the unit factors provided as they are what will be used in converting one unit to another. Note that each unit factor may be written in two equivalent ways. The one you use depends on what units you are trying to cancel in a dimensional analysis problem (see examples below). ...
Determination of Equilibrium Constants for Reactions between Nitric
... with about 5% oxygen. Moreover, the main byproducts were nitrite and nitrate, which are sources of fertilizers. Thus, the hexamminecobalt(II) solution can be considered as an ideal absorbent for wet flue gas treatment (FGT) technology. A series of step equilibria exist in solutions containing ammonia ...
... with about 5% oxygen. Moreover, the main byproducts were nitrite and nitrate, which are sources of fertilizers. Thus, the hexamminecobalt(II) solution can be considered as an ideal absorbent for wet flue gas treatment (FGT) technology. A series of step equilibria exist in solutions containing ammonia ...
Answers - logo Pre-U Chemistry Textbook
... Two electrons would have to go into an antibonding molecular orbital. This is energetically unfavourable because the increase in energy of the antibonding orbital is greater than the decrease in energy of the bonding orbital. Helium molecules do not form because they would be at higher energy than t ...
... Two electrons would have to go into an antibonding molecular orbital. This is energetically unfavourable because the increase in energy of the antibonding orbital is greater than the decrease in energy of the bonding orbital. Helium molecules do not form because they would be at higher energy than t ...
A)€€€€ The Formula For The Chemical Compound Magnesium
... Use these relative atomic masses: H = 1; O = 16; Ca = 40 to calculate the relative formula mass (M r) of quicklime CaO ........................................................................................................... slaked lime Ca(OH)2 ..................................................... ...
... Use these relative atomic masses: H = 1; O = 16; Ca = 40 to calculate the relative formula mass (M r) of quicklime CaO ........................................................................................................... slaked lime Ca(OH)2 ..................................................... ...
3 ON THE THERMODYNAMICS OF FATTY ACID OXIDATION
... 1) and decrease with each double bond (Figure 2). Measurements of fH0(FA) for saturated FAs were obtained from seven different sources and it is clear that there is good agreement, whether in the liquid or condensed state (Figure 1). The values for methanoic acid (for which n = 1) are very similar, ...
... 1) and decrease with each double bond (Figure 2). Measurements of fH0(FA) for saturated FAs were obtained from seven different sources and it is clear that there is good agreement, whether in the liquid or condensed state (Figure 1). The values for methanoic acid (for which n = 1) are very similar, ...
Balancing Chemical Reactions
... Characteristics of Chemical Equations, continued Word and Formula Equations, continued • To complete the process of writing a correct equation, the law of conservation of mass must be taken into account. • The relative amounts of reactants and products represented in the equation must be adjusted so ...
... Characteristics of Chemical Equations, continued Word and Formula Equations, continued • To complete the process of writing a correct equation, the law of conservation of mass must be taken into account. • The relative amounts of reactants and products represented in the equation must be adjusted so ...
Ans:- (i) Gluconic acid - Kendriya Vidyalaya No.2, Kribhco, Surat
... Ans. The construction of normal hydrogen electrode is explained below : ...
... Ans. The construction of normal hydrogen electrode is explained below : ...
CHAPTER 20 METALLURGY AND THE CHEMISTRY OF METALS
... electrons in bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals: that is, (σns ) 2 (σ ns ) . The bond order is zero, and such dimers would not be expected to exist. ...
... electrons in bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals: that is, (σns ) 2 (σ ns ) . The bond order is zero, and such dimers would not be expected to exist. ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.