Experiment 15: Reduction and Oxidation of Organic Compounds
... solutions. The oxidizing agent used in this procedure is hypochlorous acid, the active component of household bleach. Although chromic acid, H2CrO4, is a more commonly used reagent for the oxidation of alcohols, it is a suspected carcinogen and generates hazardous waste. Replacing a harmful and poll ...
... solutions. The oxidizing agent used in this procedure is hypochlorous acid, the active component of household bleach. Although chromic acid, H2CrO4, is a more commonly used reagent for the oxidation of alcohols, it is a suspected carcinogen and generates hazardous waste. Replacing a harmful and poll ...
Document
... hydroxides are called alkalis. The particular salt produced in any reaction between an acid and a base or alkali depends on: ■ the acid used (hydrochloric acid produces chlorides, nitric acid produces nitrates, sulfuric acid produces sulfates) ■ the metal in the base or alkali. Hydrogen ions, H+(aq) ...
... hydroxides are called alkalis. The particular salt produced in any reaction between an acid and a base or alkali depends on: ■ the acid used (hydrochloric acid produces chlorides, nitric acid produces nitrates, sulfuric acid produces sulfates) ■ the metal in the base or alkali. Hydrogen ions, H+(aq) ...
Final Review Sheet Answers (the 6 page packet)
... room. All of the molecules are nonpolar so we can’t easily eliminate anything based on the strength of the IMFs; however, the CO2 molecule does have a dipole moment between the C and O atoms. The dipole cancels in the molecule overall making it nonpolar, but in reality, the oxygens are still slightl ...
... room. All of the molecules are nonpolar so we can’t easily eliminate anything based on the strength of the IMFs; however, the CO2 molecule does have a dipole moment between the C and O atoms. The dipole cancels in the molecule overall making it nonpolar, but in reality, the oxygens are still slightl ...
Biochemistry I Laboratory Chem 4401
... These types of calculations can also be used in reverse, which is most useful when you need to make up solutions of a particular molarity. For example, if a particular experiment requires you to make 1 liter of a 0.25 M solution of NaCl, you know that all you have to do is obtain 0.25 moles of NaCl ...
... These types of calculations can also be used in reverse, which is most useful when you need to make up solutions of a particular molarity. For example, if a particular experiment requires you to make 1 liter of a 0.25 M solution of NaCl, you know that all you have to do is obtain 0.25 moles of NaCl ...
Chapter 4:Chemical Quantities and Aqueous Reactions:
... Homogenous mixtures are called solutions. The major component that keeps its same state is called the solvent. The minor component, the one that may have a change in state, is the solute. Dilute solutions have a small amount of solute, concentrated solutions have a large amount of solute compared to ...
... Homogenous mixtures are called solutions. The major component that keeps its same state is called the solvent. The minor component, the one that may have a change in state, is the solute. Dilute solutions have a small amount of solute, concentrated solutions have a large amount of solute compared to ...
Final Exam - Seattle Central College
... • Identify the type of intermolecular force for a molecule as London/dispersion forces, dipoledipole forces, hydrogen bonding, or ion-diple forces • Know that hydrogen bonds are the strongest type of intermolecular force, dipole-dipole forces are the next strongest, and London forces are generally t ...
... • Identify the type of intermolecular force for a molecule as London/dispersion forces, dipoledipole forces, hydrogen bonding, or ion-diple forces • Know that hydrogen bonds are the strongest type of intermolecular force, dipole-dipole forces are the next strongest, and London forces are generally t ...
Questions - Scheikundeolympiade
... (a) HF boils at a higher temperature than HCl. Y N (b) HBr boils at a lower temperature than HI Y N (c) Pure HI can be produced by reacting concentrated sulfuric acid with KI. Y N (d) Ammonia solutions are buffer solutions because they contain the conjugate pair NH3 – NH4+. Y N (e) Pure water at 80° ...
... (a) HF boils at a higher temperature than HCl. Y N (b) HBr boils at a lower temperature than HI Y N (c) Pure HI can be produced by reacting concentrated sulfuric acid with KI. Y N (d) Ammonia solutions are buffer solutions because they contain the conjugate pair NH3 – NH4+. Y N (e) Pure water at 80° ...
- Kendriya Vidyalaya NKJ Katni
... hydride ‘B’ which is a foul smelling gas and is extensively used in qualitative analysis of salts. When treated with oxygen, ‘B’ forms an oxide ‘C’ which is a colourless, pungent smelling gas. This gas when passed through acidified KMnO4 solution, decolorizes it, ‘C’ gets oxidized to another oxide ‘ ...
... hydride ‘B’ which is a foul smelling gas and is extensively used in qualitative analysis of salts. When treated with oxygen, ‘B’ forms an oxide ‘C’ which is a colourless, pungent smelling gas. This gas when passed through acidified KMnO4 solution, decolorizes it, ‘C’ gets oxidized to another oxide ‘ ...
Types of Chemical Reactions
... Magnesium metal can be used to remove tarnish from silver items. Silver tarnish is the corrosion that occurs when silver metal reacts with substances in the environment, especially those containing sulfur. Why would magnesium remove tarnish from silver? ...
... Magnesium metal can be used to remove tarnish from silver items. Silver tarnish is the corrosion that occurs when silver metal reacts with substances in the environment, especially those containing sulfur. Why would magnesium remove tarnish from silver? ...
AP Chemistry Review Preparing for the AP
... It would be a safe bet to assume that when a metal by itself it placed in acid you will get H2 gas and some aqueous salt and the negative ion is the spectator ion. Cu does not react in HCl, but in AP chemistry it is safe to assume that there is always a reaction. Also groups 1 and group 2 metal by t ...
... It would be a safe bet to assume that when a metal by itself it placed in acid you will get H2 gas and some aqueous salt and the negative ion is the spectator ion. Cu does not react in HCl, but in AP chemistry it is safe to assume that there is always a reaction. Also groups 1 and group 2 metal by t ...
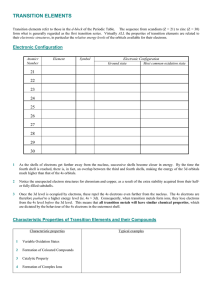
TRANSITION ELEMENTS
... The small, highly charged cations cause greater polarization of associated anions, resulting in the following chemical properties of transition metal compounds compared with those of the s-block metals : their oxides and hydroxides in oxidation states +2 and +3 are less basic and less soluble; their ...
... The small, highly charged cations cause greater polarization of associated anions, resulting in the following chemical properties of transition metal compounds compared with those of the s-block metals : their oxides and hydroxides in oxidation states +2 and +3 are less basic and less soluble; their ...
CHEM 122 - Nmt.edu
... What is the Molarity of this solution? C = / RT = (0.272 atm) / (0.08206 L atm/K mol) (298.15 K) = 0.011 M ...
... What is the Molarity of this solution? C = / RT = (0.272 atm) / (0.08206 L atm/K mol) (298.15 K) = 0.011 M ...
Step 2
... When two or more atoms bond by sharing electrons we call it ____________ BONDING. This type of bonding normally occurs between _______ atoms. It causes the atoms in a molecule to be held together very strongly but there are ____ forces between individual molecules. This is why covalently-bonded mole ...
... When two or more atoms bond by sharing electrons we call it ____________ BONDING. This type of bonding normally occurs between _______ atoms. It causes the atoms in a molecule to be held together very strongly but there are ____ forces between individual molecules. This is why covalently-bonded mole ...
www.xtremepapers.net
... Permission to reproduce items where third-party owned material protected by copyright is included has been sought and cleared where possible. Every reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included ...
... Permission to reproduce items where third-party owned material protected by copyright is included has been sought and cleared where possible. Every reasonable effort has been made by the publisher (UCLES) to trace copyright holders, but if any items requiring clearance have unwittingly been included ...
Exam Review Chapter 18-Equilibrium
... 6. What is the effect of adding more CO2 to the following equilibrium reaction? CO2 + H2O↔ H2CO3 a. More H2CO3 is produced. b. More H2O is produced. c. The equilibrium d. No Change 7. Two opposing reactions (A + B ↔C + D) occurring simultaneously at the same rate is an example of: a. reversibility. ...
... 6. What is the effect of adding more CO2 to the following equilibrium reaction? CO2 + H2O↔ H2CO3 a. More H2CO3 is produced. b. More H2O is produced. c. The equilibrium d. No Change 7. Two opposing reactions (A + B ↔C + D) occurring simultaneously at the same rate is an example of: a. reversibility. ...
The Advanced Placement Examination in Chemistry Part I – Multiple
... (C) Na2O2 (D) SiO2 (E) La2O3 52. Propane gas, C3H8, burns in excess oxygen gas. When the equation for the reaction is correctly balanced and all coefficients are reduced to their lowest whole-number terms, the coefficient for O2 is (A) 4 (B) 5 (C) 7 (D) 10 (E) 22 2 N2H4(g) + N2O4(g) 3 N2(g) + 4 H2 ...
... (C) Na2O2 (D) SiO2 (E) La2O3 52. Propane gas, C3H8, burns in excess oxygen gas. When the equation for the reaction is correctly balanced and all coefficients are reduced to their lowest whole-number terms, the coefficient for O2 is (A) 4 (B) 5 (C) 7 (D) 10 (E) 22 2 N2H4(g) + N2O4(g) 3 N2(g) + 4 H2 ...
Final Exam - Seattle Central College
... Ions that produce basic solutions – anions that are conj. bases of weak acids. – all anions except anions of strong acids – Note: SO42− + H2O → HSO4− + OH− Ions that produce neutral solutions – do not react with H2O to make H+ or OH− Salts with an acidic cation and basic anion – Classify a given sal ...
... Ions that produce basic solutions – anions that are conj. bases of weak acids. – all anions except anions of strong acids – Note: SO42− + H2O → HSO4− + OH− Ions that produce neutral solutions – do not react with H2O to make H+ or OH− Salts with an acidic cation and basic anion – Classify a given sal ...
Solid - Liquid Phase Diagram of a Binary Mixture: The Question of
... (3a) and (3b), crossing with a discontinuity in slope at the eutectic point. Dimer Model: Carboxylic acids are known to have a tendency to form hydrogen - bonded dimers in the solid state and when dissolved in non-polar solvents. There are then two different ways to model the “ideal solution” leadin ...
... (3a) and (3b), crossing with a discontinuity in slope at the eutectic point. Dimer Model: Carboxylic acids are known to have a tendency to form hydrogen - bonded dimers in the solid state and when dissolved in non-polar solvents. There are then two different ways to model the “ideal solution” leadin ...
chemistry — released form
... Light is emitted when relaxation occurs. Relaxation is when an electron goes from a high energy level to a lower energy level. Energy is absorbed when excitation occurs. Excitation is when an electron goes from a low energy level to a higher energy level. ...
... Light is emitted when relaxation occurs. Relaxation is when an electron goes from a high energy level to a lower energy level. Energy is absorbed when excitation occurs. Excitation is when an electron goes from a low energy level to a higher energy level. ...
CHEM230P1_06_2014_Y_P1
... Explain how the composition of A and B will change during this process and also state whether the equilibrium constant, KP, will increase, decrease or stay the same. ...
... Explain how the composition of A and B will change during this process and also state whether the equilibrium constant, KP, will increase, decrease or stay the same. ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.