Answers - U of L Class Index
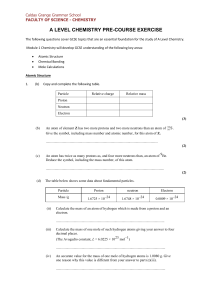
... lithium)? As part of your answer, write a balanced chemical equation (including states of matter) describing the industrial process used to make potassium metal. [2 marks] KCl(l) + Na(l) → K(g) + NaCl(l) Potassium is made by chemical reduction of the K+ in KCl(l) using sodium metal as the reducing a ...
... lithium)? As part of your answer, write a balanced chemical equation (including states of matter) describing the industrial process used to make potassium metal. [2 marks] KCl(l) + Na(l) → K(g) + NaCl(l) Potassium is made by chemical reduction of the K+ in KCl(l) using sodium metal as the reducing a ...
B - eko.olunet.org
... a) Write planar structural formulas for A–D. b) Write spatial structural formulas for (R)- and (S)-isomers of Ibuprofen. ...
... a) Write planar structural formulas for A–D. b) Write spatial structural formulas for (R)- and (S)-isomers of Ibuprofen. ...
Acids and Bases
... all bitter compounds are basic). Caffeine and milk of magnesia (chemical formula Mg(OH)2 ) are two bases that you may have had the opportunity to taste, although the bitterness is generally masked by other flavors when these compounds are consumed. Other common bases are found in a number of cleaning ...
... all bitter compounds are basic). Caffeine and milk of magnesia (chemical formula Mg(OH)2 ) are two bases that you may have had the opportunity to taste, although the bitterness is generally masked by other flavors when these compounds are consumed. Other common bases are found in a number of cleaning ...
Solution
... µm). Two common pharmaceutical coarse dispersions are emulsions (liquid–liquid dispersions) and suspensions (solid–liquid dispersions). A colloidal dispersion represents a system having a particle size intermediate between that of a true solution and a coarse dispersion, roughly 1 to 500 nm. Commonl ...
... µm). Two common pharmaceutical coarse dispersions are emulsions (liquid–liquid dispersions) and suspensions (solid–liquid dispersions). A colloidal dispersion represents a system having a particle size intermediate between that of a true solution and a coarse dispersion, roughly 1 to 500 nm. Commonl ...
ALE 23. Balancing Redox Reactions
... Oxidation-reduction or Redox reactions involve the transfer of one or more electrons from one chemical species to another. Redox reactions are involved in the corrosion of metals, the combustion of fuels, the generation of electricity from batteries and many biological processes including cellular r ...
... Oxidation-reduction or Redox reactions involve the transfer of one or more electrons from one chemical species to another. Redox reactions are involved in the corrosion of metals, the combustion of fuels, the generation of electricity from batteries and many biological processes including cellular r ...
H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, I2
... 3 molecules of hydrogen plus 1 molecule of nitrogen produces 2 molecules of ammonia ...
... 3 molecules of hydrogen plus 1 molecule of nitrogen produces 2 molecules of ammonia ...
answers to part a of the national high school
... The more general form of the fire traingle is needed because there are all sorts of other oxidants apart from oxygen that substances can burn in, e.g. chlorine or nitrogen dioxide. Solid substances such as nitrates or chlorates are also considered to be oxidising substances because they can release ...
... The more general form of the fire traingle is needed because there are all sorts of other oxidants apart from oxygen that substances can burn in, e.g. chlorine or nitrogen dioxide. Solid substances such as nitrates or chlorates are also considered to be oxidising substances because they can release ...
2014_S4_CHM_NORMAL (ALL)
... 53. Element X (atomic number 11) reacts with element Y (atomic number 16) to form an ionic compound. Each atom of X loses one electron and each atom of Y accepts two electrons to form a compound with formula X2Y. 54. Consider the following information: ...
... 53. Element X (atomic number 11) reacts with element Y (atomic number 16) to form an ionic compound. Each atom of X loses one electron and each atom of Y accepts two electrons to form a compound with formula X2Y. 54. Consider the following information: ...
Mr Alasdair Ross at Southpointe Academy
... that electrolytes can also impact the boiling and freezing point of solutions. Consider NaCl and CaCl2 . Both of these substances are strong electrolytes, they dissociate relatively easily in water. As long as the concentration of a solution is low, 1 mole of NaCl forms 2 moles of ions while 1 mole ...
... that electrolytes can also impact the boiling and freezing point of solutions. Consider NaCl and CaCl2 . Both of these substances are strong electrolytes, they dissociate relatively easily in water. As long as the concentration of a solution is low, 1 mole of NaCl forms 2 moles of ions while 1 mole ...
Question 2
... this compound is approximately 140g/mol. What is the empirical formula? What is the molecular formula? ...
... this compound is approximately 140g/mol. What is the empirical formula? What is the molecular formula? ...
Chapter Three PPT
... Acid/Base Chemistry: Summary • Equilibra (Procede in Weak Acid/Base Direction) • Lewis Acidity/Basicity of Organics • pKa Ranges of Common Organic Compounds • Anion Stability (CB) Acid Strength Relationship Know Factors Affecting Anion Stability Resonance, Inductive Effects, etc. ...
... Acid/Base Chemistry: Summary • Equilibra (Procede in Weak Acid/Base Direction) • Lewis Acidity/Basicity of Organics • pKa Ranges of Common Organic Compounds • Anion Stability (CB) Acid Strength Relationship Know Factors Affecting Anion Stability Resonance, Inductive Effects, etc. ...
Lab 1-1 - My eCoach
... On a separate sheet of paper, create a data table and record what you see on the table, then answer the questions below using complete sentences. Questions 1. Sodium hydrogen carbonate is baking soda (NaHCO3). When HCl is added to NaHCO3, carbon dioxide bubbles are formed. What is the chemical formu ...
... On a separate sheet of paper, create a data table and record what you see on the table, then answer the questions below using complete sentences. Questions 1. Sodium hydrogen carbonate is baking soda (NaHCO3). When HCl is added to NaHCO3, carbon dioxide bubbles are formed. What is the chemical formu ...
Review redox reactions
... Do the previous example in a basic solution. Iodide will react with permanganate ions to form iodine and manganese (IV) oxide. ...
... Do the previous example in a basic solution. Iodide will react with permanganate ions to form iodine and manganese (IV) oxide. ...
Measurements/Unit Cancellation/Significant Figures 1. When
... Formula mass: The sum of the atomic masses (atomic weights in amu) of the atomic species as given in the formula of the compound Hydrate: A compound in which a specific number of water molecules are associated with each formula unit. Hydrated ion: An ion in which a specific number of water molecules ...
... Formula mass: The sum of the atomic masses (atomic weights in amu) of the atomic species as given in the formula of the compound Hydrate: A compound in which a specific number of water molecules are associated with each formula unit. Hydrated ion: An ion in which a specific number of water molecules ...
PH

In chemistry, pH (/piːˈeɪtʃ/) is a numeric scale used to specify the acidity or alkalinity of an aqueous solution. It is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the hydrogen ion. Solutions with a pH less than 7 are acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are alkaline or basic. Pure water is neutral, being neither an acid nor a base. Contrary to popular belief, the pH value can be less than 0 or greater than 14 for very strong acids and bases respectively.pH measurements are important in medicine, biology, chemistry, agriculture, forestry, food science, environmental science, oceanography, civil engineering, chemical engineering, nutrition, water treatment & water purification, and many other applications. The pH scale is traceable to a set of standard solutions whose pH is established by international agreement.Primary pH standard values are determined using a concentration cell with transference, by measuring the potential difference between a hydrogen electrode and a standard electrode such as the silver chloride electrode.The pH of aqueous solutions can be measured with a glass electrode and a pH meter, or indicator.pH is the negative of the logarithm to base 10 of the activity of the (solvated) hydronium ion, more often (albeit somewhat inaccurately) expressed as the measure of the hydronium ion concentration.The rest of this article uses the technically correct word ""base"" and its inflections in place of ""alkaline"", which specifically refers to a base dissolved in water, and its inflections.