Astronomy Unit Study Guide
... **What causes the seasons? What are the characteristics of each season? What is the tilt of Earth’s axis? **When does the Northern Hemisphere get the most/least direct sunlight? **When does the Southern Hemisphere get the most/least direct sunlight? **What is the difference between a solst ...
... **What causes the seasons? What are the characteristics of each season? What is the tilt of Earth’s axis? **When does the Northern Hemisphere get the most/least direct sunlight? **When does the Southern Hemisphere get the most/least direct sunlight? **What is the difference between a solst ...
Studying Space
... timeline indicating date, astronomer/object and significant contributions. 15 mins to complete for a grade – NEAT and ACCURATE ...
... timeline indicating date, astronomer/object and significant contributions. 15 mins to complete for a grade – NEAT and ACCURATE ...
Rotation and Revolution of the Earth-PPT
... around the Sun. The Earth makes one complete rotation every 24 hours. The Earth is both rotating and revolving all the time. ...
... around the Sun. The Earth makes one complete rotation every 24 hours. The Earth is both rotating and revolving all the time. ...
Almost three-quarters of the Earth is covered with
... • To our knowledge, the Earth is the only planet in the Solar System with an environment that is suitable for living things • The Earth provides us with the materials and conditions to live comfortably • However the Earth is fragile because it can be damaged by human activities, such as pollution an ...
... • To our knowledge, the Earth is the only planet in the Solar System with an environment that is suitable for living things • The Earth provides us with the materials and conditions to live comfortably • However the Earth is fragile because it can be damaged by human activities, such as pollution an ...
Name _________ Science - 7th period Date: The Universe: Objects
... Name ______________________________________ Science - 7th period ...
... Name ______________________________________ Science - 7th period ...
Labs/Teacher Notes Solar System to Scale Outside
... Sun. Outside I then have the students stand at the appropriate places and say the rotation and revolution rate for each planet. 4. I also demonstrate with a student moving between the Sun and Neptune, the approximate orbit of Halley’s Comet. It moves faster going toward the sun and slowing down movi ...
... Sun. Outside I then have the students stand at the appropriate places and say the rotation and revolution rate for each planet. 4. I also demonstrate with a student moving between the Sun and Neptune, the approximate orbit of Halley’s Comet. It moves faster going toward the sun and slowing down movi ...
Solar System Study Guide Key
... correct answers. 1. Orbit: Earth’s curved path that it follows around the sun 2. Rotation: Planet spinning on an axis; takes the Earth 24 hours or 1 day to complete one rotation 3. Revolution: Earth’s yearly orbit around the sun; about 365 days to complete once 4. Axis: imaginary vertical line that ...
... correct answers. 1. Orbit: Earth’s curved path that it follows around the sun 2. Rotation: Planet spinning on an axis; takes the Earth 24 hours or 1 day to complete one rotation 3. Revolution: Earth’s yearly orbit around the sun; about 365 days to complete once 4. Axis: imaginary vertical line that ...
Solar System Outline
... SUN • 75% hydrogen and 25% helium by mass • Sun converts hydrogen to helium in its core • Differential rotation – equator the surface rotates once every 25.4 days – near the poles it's as much as 36 days ...
... SUN • 75% hydrogen and 25% helium by mass • Sun converts hydrogen to helium in its core • Differential rotation – equator the surface rotates once every 25.4 days – near the poles it's as much as 36 days ...
ExampleQuestions
... Some Fundamental Questions - Planet Earth and Plate Tectonics 1. Compared to other planets in the solar system how is the Earth different? Why? ...
... Some Fundamental Questions - Planet Earth and Plate Tectonics 1. Compared to other planets in the solar system how is the Earth different? Why? ...
AN INTRODUCTION TO ASTRONOMY Dr. Uri Griv Department of Physics, Ben-Gurion University
... Origin of the Moon: A Disk Instability or a Megaimpact? Peculiar Composition and Unconventional Dynamical Features of the Moon • The fraction of iron in the Moon is 10% • This is lower by a factor of 3 than the iron content of the Earth and Venus, lower by a factor of 2.5 than that of Mars • The lu ...
... Origin of the Moon: A Disk Instability or a Megaimpact? Peculiar Composition and Unconventional Dynamical Features of the Moon • The fraction of iron in the Moon is 10% • This is lower by a factor of 3 than the iron content of the Earth and Venus, lower by a factor of 2.5 than that of Mars • The lu ...
Why do we have seasons?
... The earth moves around the sun in an elliptical orbit. Earth is closest to the sun at Perihelion Earth is farthest from the sun at Aphelion Is being close to the sun what causes the seasons? The northern and southern hemisphere should have the same season, not opposite season like we have. • No. Nor ...
... The earth moves around the sun in an elliptical orbit. Earth is closest to the sun at Perihelion Earth is farthest from the sun at Aphelion Is being close to the sun what causes the seasons? The northern and southern hemisphere should have the same season, not opposite season like we have. • No. Nor ...
Our Solar System Notes Geocentric Theory
... C. Meteoroids-Little chunks of rock and debris in space are called meteoroids. • They become meteors -- or shooting stars -- when they fall through a planet's atmosphere • Pieces that survive the journey and hit the ground are called meteorites. Kuipier Belt - is a disc-shaped region of icy objects ...
... C. Meteoroids-Little chunks of rock and debris in space are called meteoroids. • They become meteors -- or shooting stars -- when they fall through a planet's atmosphere • Pieces that survive the journey and hit the ground are called meteorites. Kuipier Belt - is a disc-shaped region of icy objects ...
Solar system notes
... C. Meteoroids-Little chunks of rock and debris in space are called meteoroids. • They become meteors -- or shooting stars -- when they fall through a planet's atmosphere • Pieces that survive the journey and hit the ground are called meteorites. Kuipier Belt - is a disc-shaped region of icy objects ...
... C. Meteoroids-Little chunks of rock and debris in space are called meteoroids. • They become meteors -- or shooting stars -- when they fall through a planet's atmosphere • Pieces that survive the journey and hit the ground are called meteorites. Kuipier Belt - is a disc-shaped region of icy objects ...
Our Solar System
... Earth • 23 hours and 56 min=1 Earth day (rotation) • 365 days =1 Earth year (revolution) • Earth is warm enough to keep most of its water from freezing and cold enough to keep it’s water from boiling • Temperature is between –13 degrees Celsius and 37 degrees Celsius ...
... Earth • 23 hours and 56 min=1 Earth day (rotation) • 365 days =1 Earth year (revolution) • Earth is warm enough to keep most of its water from freezing and cold enough to keep it’s water from boiling • Temperature is between –13 degrees Celsius and 37 degrees Celsius ...
Spinning Earth and gravity
... produce a centripetal force on the object to keep it moving in a circle with the Earth as the Earth spins. This means that its effective weight is slightly less than if the earth were not spinning. So if the earth stopped spinning the measured weight of a body would increase – but ever so slightly! ...
... produce a centripetal force on the object to keep it moving in a circle with the Earth as the Earth spins. This means that its effective weight is slightly less than if the earth were not spinning. So if the earth stopped spinning the measured weight of a body would increase – but ever so slightly! ...
• Keep chat on topic!
... The Earth, the Sun, and the seven other planets that are in orbit around the Sun are part of a solar system. The planets in our solar system are: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Our solar system also contains all of the meteoroids, asteroids, and comets that are in ...
... The Earth, the Sun, and the seven other planets that are in orbit around the Sun are part of a solar system. The planets in our solar system are: Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. Our solar system also contains all of the meteoroids, asteroids, and comets that are in ...
Mass of Jupiter
... When the Planets Align Some authors seeking public attention have suggested that when many planets are “aligned” (i.e., are close together in the sky) their gravitational pull on the earth all acting together might produce earthquakes and other disasters. To get an idea of whether this is plausible, ...
... When the Planets Align Some authors seeking public attention have suggested that when many planets are “aligned” (i.e., are close together in the sky) their gravitational pull on the earth all acting together might produce earthquakes and other disasters. To get an idea of whether this is plausible, ...
axis – the imaginary line on which the Earth spins Apollo Missions
... NASA – National Aeronautics and Space Administration orbit – the path an object in space follows as it revolves around another object phases of the moon – a pattern that repeats itself every 29 1/3 days revolution – one full orbit (circle) around another object rotation – the spinning motion of an o ...
... NASA – National Aeronautics and Space Administration orbit – the path an object in space follows as it revolves around another object phases of the moon – a pattern that repeats itself every 29 1/3 days revolution – one full orbit (circle) around another object rotation – the spinning motion of an o ...
Solar System
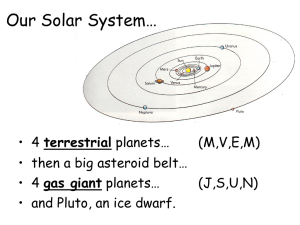
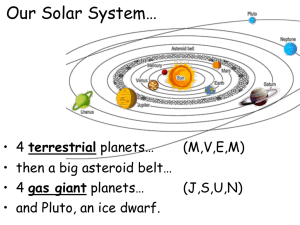
... The four planets closer to the Sun are called rocky, or terrestrial, inner planets. They are small in size and similar to Earth in composition. They have no rings, and only two of them (Earth and Mars) have moons. The four outer planets, called gas giants, are much larger than the rocky planets. The ...
... The four planets closer to the Sun are called rocky, or terrestrial, inner planets. They are small in size and similar to Earth in composition. They have no rings, and only two of them (Earth and Mars) have moons. The four outer planets, called gas giants, are much larger than the rocky planets. The ...
here
... Nebular Hypothesis: States that the planets of our Solar System were formed by the “accretion” of materials from a cloud of gas and dust called a solar “nebula”. Collapse of the nebula under its own gravity formed a rotating disk around a dense, central core of material. This core ...
... Nebular Hypothesis: States that the planets of our Solar System were formed by the “accretion” of materials from a cloud of gas and dust called a solar “nebula”. Collapse of the nebula under its own gravity formed a rotating disk around a dense, central core of material. This core ...
Name_____________________________ Today`s
... _____ 14. During Earth’s formation, materials such as nickel and iron sank to the a. mantle. c. crust. b. core. d. All of the above ...
... _____ 14. During Earth’s formation, materials such as nickel and iron sank to the a. mantle. c. crust. b. core. d. All of the above ...
These are the four largest moons of Jupiter
... rock. They are orbiting the sun, but are too small to be considered planets. ...
... rock. They are orbiting the sun, but are too small to be considered planets. ...
This presentation
... rock. They are orbiting the sun, but are too small to be considered planets. ...
... rock. They are orbiting the sun, but are too small to be considered planets. ...
Epicycles and retrograde motion
... The planets were thought to travel round the Earth on the small circle called an EPICYCLE whose centre moved round the large circle. The combined motions of P and D accounted for the backward or retrograde motion of the planet P which an observer on Earth would see. As the motions of the planets wer ...
... The planets were thought to travel round the Earth on the small circle called an EPICYCLE whose centre moved round the large circle. The combined motions of P and D accounted for the backward or retrograde motion of the planet P which an observer on Earth would see. As the motions of the planets wer ...
Earth's rotation

Earth's rotation is the rotation of the planet Earth around its own axis. The Earth rotates from the west towards east. As viewed from North Star or polestar Polaris, the Earth turns counter-clockwise.The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is the point in the Northern Hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. This point is distinct from the Earth's North Magnetic Pole. The South Pole is the other point where the Earth's axis of rotation intersects its surface, in Antarctica.The Earth rotates once in about 24 hours with respect to the sun and once every 23 hours 56 minutes and 4 seconds with respect to the stars (see below). Earth's rotation is slowing slightly with time; thus, a day was shorter in the past. This is due to the tidal effects the Moon has on Earth's rotation. Atomic clocks show that a modern-day is longer by about 1.7 milliseconds than a century ago, slowly increasing the rate at which UTC is adjusted by leap seconds.










![jeeparty_space_part_one[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008593156_1-4c29b52d83e9b40fb662dc9c07ff2464-300x300.png)