Summaries of Learning Theories and Models
... In the early twentieth century, Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov did Nobel prize-winning work on digestion. While studying the role of saliva in dogs’ digestive processes, he stumbled upon a phenomenon he labeled “psychic reflexes.” While an accidental discovery, he had the foresight to see the impo ...
... In the early twentieth century, Russian physiologist Ivan Pavlov did Nobel prize-winning work on digestion. While studying the role of saliva in dogs’ digestive processes, he stumbled upon a phenomenon he labeled “psychic reflexes.” While an accidental discovery, he had the foresight to see the impo ...
A Judge`s Ethical Dilemma: Assessing a Child`s Capacity to Choose
... obeyed. They know, however, that enforcing orders that conflict with a child's desires is difficult. For example, older children may just run away from the home or hospital in which the judge places them. When judges refuse to permit abortions without parental consent or notification, children may s ...
... obeyed. They know, however, that enforcing orders that conflict with a child's desires is difficult. For example, older children may just run away from the home or hospital in which the judge places them. When judges refuse to permit abortions without parental consent or notification, children may s ...
The influence of pre and neonatal exposure to sodium fluoride on
... neurons and glia which results in the impairment of cognitive functions. Epidemiological studies have shown that children who live in geographical regions in which drinking water is contaminated with fluoride, have a statistically significant decreased level of intelligence in comparison to children ...
... neurons and glia which results in the impairment of cognitive functions. Epidemiological studies have shown that children who live in geographical regions in which drinking water is contaminated with fluoride, have a statistically significant decreased level of intelligence in comparison to children ...
Sociocultural Perspectives on Foreign Language Learning
... mediations. Lauria (1979) believes that mind is not the result of the activity occurring in the brain but a functional system shaped as the brain‘s electro-chemical processes come under control of our cultural artifacts, the most important of which is language. In line with Luria (1979), Lantolf (20 ...
... mediations. Lauria (1979) believes that mind is not the result of the activity occurring in the brain but a functional system shaped as the brain‘s electro-chemical processes come under control of our cultural artifacts, the most important of which is language. In line with Luria (1979), Lantolf (20 ...
is function OF - Association for Contextual Behavioral Science
... Interacting with cognitive psychology can help you achieve the aims of functional psychology (and thus become a better functional psychologist) Interacting with functional psychology can help you achieve the aims of cognitive psychology (and thus become a better cognitive psychologist) Provided th ...
... Interacting with cognitive psychology can help you achieve the aims of functional psychology (and thus become a better functional psychologist) Interacting with functional psychology can help you achieve the aims of cognitive psychology (and thus become a better cognitive psychologist) Provided th ...
9/3 Class
... Cognitive appraisal of event determines our emotions But, our culture provides the context through which we interpret the emotion-eliciting event ...
... Cognitive appraisal of event determines our emotions But, our culture provides the context through which we interpret the emotion-eliciting event ...
`Learning`?
... Learning is usually defined as a relatively permanent change in behaviour or behaviour potential that occurs through experience. However, it does not refer to behavioural changes that can be explained by temporary states of maturation. Learning is the acquisition and development of memories and beha ...
... Learning is usually defined as a relatively permanent change in behaviour or behaviour potential that occurs through experience. However, it does not refer to behavioural changes that can be explained by temporary states of maturation. Learning is the acquisition and development of memories and beha ...
CHAPTER 5 - Suffolk County Community College
... • similar to a running record, but more detailed and precise • used by researchers who are not part of the classroom • researchers may later code observation information to analyze the findings ...
... • similar to a running record, but more detailed and precise • used by researchers who are not part of the classroom • researchers may later code observation information to analyze the findings ...
SG-Ch 7 ANSWERS
... rattling sound with the food. Rattling is therefore a conditioned, or learned, stimulus, and salivation in response to this rattling is a learned, or conditioned, response. 15. acquisition; one-half second 16. does not 17. survive; reproduce 18. neutral; conditioned; higher-order conditioning 19. ex ...
... rattling sound with the food. Rattling is therefore a conditioned, or learned, stimulus, and salivation in response to this rattling is a learned, or conditioned, response. 15. acquisition; one-half second 16. does not 17. survive; reproduce 18. neutral; conditioned; higher-order conditioning 19. ex ...
Rodolphe Gouin - Hal-SHS
... heuristics and other psychological explanations are based on conjectures. Nobody has never seen any of them. They are only inferred from the results they pretend to explain. These theories just provide us with circular explanations. According to Boudon, as far as social sciences are concerned, real ...
... heuristics and other psychological explanations are based on conjectures. Nobody has never seen any of them. They are only inferred from the results they pretend to explain. These theories just provide us with circular explanations. According to Boudon, as far as social sciences are concerned, real ...
Courtney
... something in a footnote about the ability to do this) How do we scale up from the neuronby-neuron account to explain abstract concepts? (There is also an explanation of this in the paper, but I do not fully understand it). Presentation two: Moving beyond the metaphors Historically, there are three p ...
... something in a footnote about the ability to do this) How do we scale up from the neuronby-neuron account to explain abstract concepts? (There is also an explanation of this in the paper, but I do not fully understand it). Presentation two: Moving beyond the metaphors Historically, there are three p ...
Paper titles and abstracts Dan Arnold: "Perception and the
... precisely contrary thesis about the priority of language, that linguistic and conceptual ability pervades perceptual experience. Even a person who is absorbed in walking across a meadow, he says, and I will return to his example in the next section, will be sufficiently aware of the grass and the cl ...
... precisely contrary thesis about the priority of language, that linguistic and conceptual ability pervades perceptual experience. Even a person who is absorbed in walking across a meadow, he says, and I will return to his example in the next section, will be sufficiently aware of the grass and the cl ...
COGNITIVE CONTROL AND LANGUAGE COMPREHENSION 2 The
... automatic yet incorrect language interpretations. A previous study by Novick, Trueswell, and Thompson-Schill (2005) indicated that children’s difficulties in overriding automatic interpretations might be due to an immature cognitive control system. Choi and Trueswell note, however, that this study d ...
... automatic yet incorrect language interpretations. A previous study by Novick, Trueswell, and Thompson-Schill (2005) indicated that children’s difficulties in overriding automatic interpretations might be due to an immature cognitive control system. Choi and Trueswell note, however, that this study d ...
Study Guide 7 Learning
... 2. What does it mean that we learn by association? 3. Associative Learning: 4. What is the difference between Classical and Operant Conditioning? ...
... 2. What does it mean that we learn by association? 3. Associative Learning: 4. What is the difference between Classical and Operant Conditioning? ...
Social Situatedness: Vygotsky and Beyond
... imitation and learning to the zone of proximal development. He argued that a child merely can imitate what is within its zone of proximal development, and if a caregiver presents a too advanced solution to a problem, the child could not grasp the solution, even if the solution was presented repeated ...
... imitation and learning to the zone of proximal development. He argued that a child merely can imitate what is within its zone of proximal development, and if a caregiver presents a too advanced solution to a problem, the child could not grasp the solution, even if the solution was presented repeated ...
What is optimal about perception?
... models of perception, memory and learning Decision theory: describes optimal use of information for action relies on utility/loss functions models of decision making and motor control Bayesian Decision Theory = information theory + decision theory ...
... models of perception, memory and learning Decision theory: describes optimal use of information for action relies on utility/loss functions models of decision making and motor control Bayesian Decision Theory = information theory + decision theory ...
File
... Cognitive Learning – involves mental process and may involve observation and imitation • Cognitive Map – mental picture of a place ...
... Cognitive Learning – involves mental process and may involve observation and imitation • Cognitive Map – mental picture of a place ...
Integrating Neuroscience into Domestic Violence Intervention with
... and salience; self-other distinction Cognitive: no state matching; self-other distinction; perspective-taking (theory of mind) Contagion: state-matching; no self-other distinction; AKA vicarious emotional transfer (vicarious trauma) Sympathy: feeling sorry for other’s situation, not necessarily thei ...
... and salience; self-other distinction Cognitive: no state matching; self-other distinction; perspective-taking (theory of mind) Contagion: state-matching; no self-other distinction; AKA vicarious emotional transfer (vicarious trauma) Sympathy: feeling sorry for other’s situation, not necessarily thei ...
File
... Leon G. Schiffman & Leslie Lazar Kanuk “Consumer Behavior” 8 th edition, Prentice Hall – 2006 ...
... Leon G. Schiffman & Leslie Lazar Kanuk “Consumer Behavior” 8 th edition, Prentice Hall – 2006 ...
Slide 1
... If you decide that time out is an appropriate form of punishment for your child between the ages of 2 and 12, follow these rules for best effectiveness: 1. The time-out area should be easily accessible, and in such a location that the child can be easily monitored while in time-out. 2. Place the ch ...
... If you decide that time out is an appropriate form of punishment for your child between the ages of 2 and 12, follow these rules for best effectiveness: 1. The time-out area should be easily accessible, and in such a location that the child can be easily monitored while in time-out. 2. Place the ch ...
Cognitive Approach
... • An individual may stop at any given stage and at any age. • Moral development fits with Kohlberg’s stage-pattern theory. • There is a cultural universality of sequence of stages. • Middle-class and working-class children move through the same sequence but middle-class children move faster and furt ...
... • An individual may stop at any given stage and at any age. • Moral development fits with Kohlberg’s stage-pattern theory. • There is a cultural universality of sequence of stages. • Middle-class and working-class children move through the same sequence but middle-class children move faster and furt ...
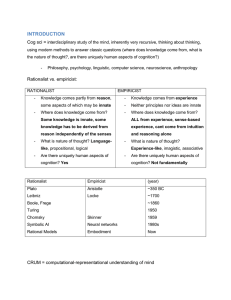
alphabet of human thought
... BEHAVIORISM: Watson, behavior > mind, mind does not exist, black box, NO introspection o role of environment in explaining behavior o behavior > mental states o no substantial difference b/w humans & animals o purely objective o EMPIRICIST (knowledge from experience, knowledge is experience like, no ...
... BEHAVIORISM: Watson, behavior > mind, mind does not exist, black box, NO introspection o role of environment in explaining behavior o behavior > mental states o no substantial difference b/w humans & animals o purely objective o EMPIRICIST (knowledge from experience, knowledge is experience like, no ...
Psychology by Course - University of Dayton
... o Olfactory cells/chemoreceptors that detect specific chemicals o Pheromones o Olfactory pathways in the brain Kinesthetic sense Vestibular sense Perception Perception o Bottom-up/Top-down processing o Perceptual organization (e.g., depth, form, motion, constancy) o Gestalt principles Attentio ...
... o Olfactory cells/chemoreceptors that detect specific chemicals o Pheromones o Olfactory pathways in the brain Kinesthetic sense Vestibular sense Perception Perception o Bottom-up/Top-down processing o Perceptual organization (e.g., depth, form, motion, constancy) o Gestalt principles Attentio ...