Abnormal-Psychology-in-a-Changing-World-7th
... Which of the following is NOT one of the three regions of the mind described by Freud? a. the conscious c. the preconscious b. the superconscious d. the unconscious ...
... Which of the following is NOT one of the three regions of the mind described by Freud? a. the conscious c. the preconscious b. the superconscious d. the unconscious ...
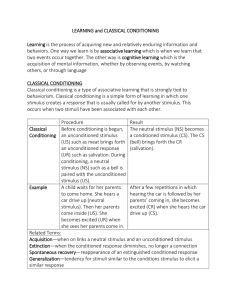
LEARNING and Classical Conditioning
... Learning is the process of acquiring new and relatively enduring information and behaviors. One way we learn is by associative learning which is when we learn that two events occur together. The other way is cognitive learning which is the acquisition of mental information, whether by observing even ...
... Learning is the process of acquiring new and relatively enduring information and behaviors. One way we learn is by associative learning which is when we learn that two events occur together. The other way is cognitive learning which is the acquisition of mental information, whether by observing even ...
Happy Kids Pediatric Dentistry - Happy Kids Pediatrics Dentistry
... This financial agreement is intended to facilitate our ability to provide excellent service to you while minimizing our administrative costs. All charges you incur are your responsibility regardless of your insurance coverage. We must emphasize that as your dental care provider, our relationship is ...
... This financial agreement is intended to facilitate our ability to provide excellent service to you while minimizing our administrative costs. All charges you incur are your responsibility regardless of your insurance coverage. We must emphasize that as your dental care provider, our relationship is ...
full text - Ghent University Academic Bibliography
... which to build a dynamic model of affect serving to challenge current pedagogy and inform and build a new praxis, called neuropedagogy. (Patten in Patten & Campbell, 2011, p. 94) ...
... which to build a dynamic model of affect serving to challenge current pedagogy and inform and build a new praxis, called neuropedagogy. (Patten in Patten & Campbell, 2011, p. 94) ...
PDF - H4H Initiative
... cognition, and provides official recommendations for daily water intake. ...
... cognition, and provides official recommendations for daily water intake. ...
Wrinkles, Wormholes, and Hamlet
... to eradicate (leading to “Cartesian Theatre,” the “software/hardware” understanding of mind and brain, etc.).8 In his introduction to The Foundations of Cognitive Science (2001), João Branquinho points out that, as explored in the chapters of the book, “cognitive science” includes more than the info ...
... to eradicate (leading to “Cartesian Theatre,” the “software/hardware” understanding of mind and brain, etc.).8 In his introduction to The Foundations of Cognitive Science (2001), João Branquinho points out that, as explored in the chapters of the book, “cognitive science” includes more than the info ...
Attitudes - Mrs. Harvey`s Social Psychology Class
... would not reveal even to his friends, but only to himself, and that in secret. But there are other things which a man is afraid to tell even to himself, and every decent man has a number of such ...
... would not reveal even to his friends, but only to himself, and that in secret. But there are other things which a man is afraid to tell even to himself, and every decent man has a number of such ...
Decoding Scientific Text
... When all groups are finished with their part, relocate to your “jigsaw” group. In your new group, share the information from your old group. Answer any clarifying questions. The result: each student has a complete handout for this passage. Prepare for a short quiz (just kidding!). ...
... When all groups are finished with their part, relocate to your “jigsaw” group. In your new group, share the information from your old group. Answer any clarifying questions. The result: each student has a complete handout for this passage. Prepare for a short quiz (just kidding!). ...
People, Places and Things: Leveraging Insights from Distributed
... has been examined in the resources model developed by (Wright, Fields, & Harrison, 2000), and in Walenstein’s analytic RODS framework (2002). Extensions of Dcog (Perry, 1999; Walenstein, 2002; Wright, Fields, & Harrison, 2000) were not applied to our research, but are examples of how Dcog can be use ...
... has been examined in the resources model developed by (Wright, Fields, & Harrison, 2000), and in Walenstein’s analytic RODS framework (2002). Extensions of Dcog (Perry, 1999; Walenstein, 2002; Wright, Fields, & Harrison, 2000) were not applied to our research, but are examples of how Dcog can be use ...
Competencies vs Learning Outcomes by
... identified six levels within the cognitive domain, from the simple recall or recognition of facts (knowledge), as the lowest level, through increasingly more complex and abstract mental levels to the highest level that is classified as evaluation. Here is a table illustrating the different levels of ...
... identified six levels within the cognitive domain, from the simple recall or recognition of facts (knowledge), as the lowest level, through increasingly more complex and abstract mental levels to the highest level that is classified as evaluation. Here is a table illustrating the different levels of ...
To Share or Not to Share: When Do Toddlers Respond to Another's
... snack, but only one of the two trays closest to the recipient was loaded. The child thus chose between the 1/1 snack arrangement (sharing) and the 1/0 arrangement (nonsharing). The 1/1 side (either left or right) was alternated over trials, and the starting side for the 1/1 arrangement (left or righ ...
... snack, but only one of the two trays closest to the recipient was loaded. The child thus chose between the 1/1 snack arrangement (sharing) and the 1/0 arrangement (nonsharing). The 1/1 side (either left or right) was alternated over trials, and the starting side for the 1/1 arrangement (left or righ ...
Consciousness:our awareness of ourselves and our
... Korsakoff’s Syndrome: a disorder that involves a severe B1 deficiency that causes dementia, brought on by alcoholism. Alcoholics tend to drink instead of eat. Barbiturates: a major tranquilizer that depress the activity of the CNS, reducing anxiety but impairing memory and judgment. Benzodiazepin ...
... Korsakoff’s Syndrome: a disorder that involves a severe B1 deficiency that causes dementia, brought on by alcoholism. Alcoholics tend to drink instead of eat. Barbiturates: a major tranquilizer that depress the activity of the CNS, reducing anxiety but impairing memory and judgment. Benzodiazepin ...
Bio-Psycho-Social influences on drug use: States of Consciousness
... 28-day cycles: cycles that occur every month. Ex. a woman’s menstrual cycle. Circadian rhythm: the biological clock; regular bodily rhythms that occur on a 24-hour cycle, such as body temperature or wakefulness. Suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN): a pair of grain-of-rice –sized cell clusters in the hypot ...
... 28-day cycles: cycles that occur every month. Ex. a woman’s menstrual cycle. Circadian rhythm: the biological clock; regular bodily rhythms that occur on a 24-hour cycle, such as body temperature or wakefulness. Suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN): a pair of grain-of-rice –sized cell clusters in the hypot ...
to get the file
... Fundamentals of Cognitive Psychology, 2e by Ronald T. Kellogg ©SAGE Publications, Inc. ...
... Fundamentals of Cognitive Psychology, 2e by Ronald T. Kellogg ©SAGE Publications, Inc. ...
Biological Imitation
... representation is the ability to coordinate multiple models, which represent different situations. ...
... representation is the ability to coordinate multiple models, which represent different situations. ...
Number and Size Matter: Discrete versus continuous
... possess a discrete quantity system that applies to small set sizes, although there is some debate as to whether this system is the same as in adults or if it develops over time (see Carey, 2004). Research has also shown that young children generalize names for objects by shape but by material for su ...
... possess a discrete quantity system that applies to small set sizes, although there is some debate as to whether this system is the same as in adults or if it develops over time (see Carey, 2004). Research has also shown that young children generalize names for objects by shape but by material for su ...
Chapter 4 – wilhelm wundt and the founding of psychology
... Lewin used diagrams like this to describe life spaces ...
... Lewin used diagrams like this to describe life spaces ...
The Behavioral And Brain Sciences (1984) 7:4, pp
... of behavior must face the problem of privacy by dealing with events within the skin in their relation to behavior, without assuming they have a special nature or must be known in a special way. The search for copies of the world within the body (e.g. the sensations and images of conscious content) h ...
... of behavior must face the problem of privacy by dealing with events within the skin in their relation to behavior, without assuming they have a special nature or must be known in a special way. The search for copies of the world within the body (e.g. the sensations and images of conscious content) h ...
Psychological Concepts in Elf
... Intellectualization is the overemphasis on thinking when confronted with an unacceptable impulse, situation or behavior without employing any emotions whatsoever to help mediate and place the thoughts into an emotional, ...
... Intellectualization is the overemphasis on thinking when confronted with an unacceptable impulse, situation or behavior without employing any emotions whatsoever to help mediate and place the thoughts into an emotional, ...
- Academy Test Bank
... seeks treatment now because he is an accomplished musician but cannot perform for an audience. According to behavioral theory, his behavior is an example of which of the following concepts? A) Discrimination B) Modeling C) Generalization D) Shaping Ans: C Feedback: Generalization happens when a cond ...
... seeks treatment now because he is an accomplished musician but cannot perform for an audience. According to behavioral theory, his behavior is an example of which of the following concepts? A) Discrimination B) Modeling C) Generalization D) Shaping Ans: C Feedback: Generalization happens when a cond ...
Social Learning - Ms. Zolpis` Classes
... Reinforcement follows a response and strengthens our tendency to repeat that response in the future. For example, say that there is a bar inside an animal cage, and each time the animal presses the bar, food appears. The behavior of bar pressing is reinforced (strengthened) by the arrival of the foo ...
... Reinforcement follows a response and strengthens our tendency to repeat that response in the future. For example, say that there is a bar inside an animal cage, and each time the animal presses the bar, food appears. The behavior of bar pressing is reinforced (strengthened) by the arrival of the foo ...
Chapter 4 Reading Guide
... Can you think of another example of classical conditioning in your own life? Think about your previous experiences or childhood. What is the UCS? UCR? NS? CS? CR? ...
... Can you think of another example of classical conditioning in your own life? Think about your previous experiences or childhood. What is the UCS? UCR? NS? CS? CR? ...
Chapter 10 - Non-verbal Information and Artistic Expression in the
... writer and the artist and hence both entail a theory of mind, which we will explicate in the next section. Both forms of communication can be used to express emotions. Both require thought and planning although speech and some forms of musical performance tends to be more spontaneous and less planne ...
... writer and the artist and hence both entail a theory of mind, which we will explicate in the next section. Both forms of communication can be used to express emotions. Both require thought and planning although speech and some forms of musical performance tends to be more spontaneous and less planne ...
General Psychology 1
... one or the other…cannot be simultaneously anxious and relaxed Therefore, if you can repeatedly relax someone (see spider example) when they are faced with anxiety-producing stimuli – you will gradually eliminate their anxiety The trick is to proceed gradually ...
... one or the other…cannot be simultaneously anxious and relaxed Therefore, if you can repeatedly relax someone (see spider example) when they are faced with anxiety-producing stimuli – you will gradually eliminate their anxiety The trick is to proceed gradually ...