PSC100 Transparant Replacement for Chapter 8 Measurement of
... Measuring the distance to stars is so important that many astronomers spend their entire lives working on this. Even though it is critical to understanding many of the other properties of stars, we can only determine the distance to far away objects in space to about 50% accuracy. ...
... Measuring the distance to stars is so important that many astronomers spend their entire lives working on this. Even though it is critical to understanding many of the other properties of stars, we can only determine the distance to far away objects in space to about 50% accuracy. ...
Death of Massive Stars
... The Earth completely? • Depends on the mass of the Earth and your distance from the center of the Earth. • At Earth’s surface: 25,000 mph (11km/s) • From the top of a 1000 mile high tower, 22,000 mph (10km/s) • From the surface of the Sun? (Mass 1MSUN, radius 700,000km): 1,400,000 mph (620km/s) • Fr ...
... The Earth completely? • Depends on the mass of the Earth and your distance from the center of the Earth. • At Earth’s surface: 25,000 mph (11km/s) • From the top of a 1000 mile high tower, 22,000 mph (10km/s) • From the surface of the Sun? (Mass 1MSUN, radius 700,000km): 1,400,000 mph (620km/s) • Fr ...
Slide 1
... supernova is an exploding star that can become three times as bright as the sun. When a supernova occurs. All the dust particles, gas, and Dupree collect up. Creating a Nebula. These Nebulas can create many stars like our sun. Some stars can be brighter then others. This is an example of a Supernova ...
... supernova is an exploding star that can become three times as bright as the sun. When a supernova occurs. All the dust particles, gas, and Dupree collect up. Creating a Nebula. These Nebulas can create many stars like our sun. Some stars can be brighter then others. This is an example of a Supernova ...
Lecture 9/10 Stellar evolution Ulf Torkelsson 1 Main sequence stars
... gains momentum and continues outward. The shock wave eventually reaches the stellar surface after a few hours, at which time the star appears as a supernova. Typically this will be a type II supernova, which is characterised by a spectrum with strong hydrogen lines. (There are also type I supernovae ...
... gains momentum and continues outward. The shock wave eventually reaches the stellar surface after a few hours, at which time the star appears as a supernova. Typically this will be a type II supernova, which is characterised by a spectrum with strong hydrogen lines. (There are also type I supernovae ...
Steve Holmes - KWFN October 22 2012 speaker
... own right, the night sky also brings much to see, with a truly breathtaking expanse of space and time that far eclipses anything terrestrial. A cosmic vista, viewed on a clear night well away from urban light pollution, can turn anyone into a philosopher. Steve Holmes, a chemist, long-time hobby ast ...
... own right, the night sky also brings much to see, with a truly breathtaking expanse of space and time that far eclipses anything terrestrial. A cosmic vista, viewed on a clear night well away from urban light pollution, can turn anyone into a philosopher. Steve Holmes, a chemist, long-time hobby ast ...
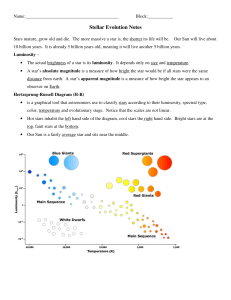
Stellar Evolution Notes
... It takes about 10 billion years for a star with the mass of the Sun to convert all of the hydrogen in its ...
... It takes about 10 billion years for a star with the mass of the Sun to convert all of the hydrogen in its ...
Stellar Evolution Notes
... It takes about 10 billion years for a star with the mass of the Sun to convert all of the hydrogen in its ...
... It takes about 10 billion years for a star with the mass of the Sun to convert all of the hydrogen in its ...
UCLA 2004
... 6. Many other SLRs cannot be produced by spallation, including 60Fe, 107Pd and 182Hf [Gounelle et al. (2001); Leya et al. (2003)] and 63Ni [Leya et al. (2003)] 7. Siting of 26Al must be in small grains, not CAIs: type 6 OCs heated to ~1200 K, must have had abundant 26Al, yet OCs have almost no CAIs ...
... 6. Many other SLRs cannot be produced by spallation, including 60Fe, 107Pd and 182Hf [Gounelle et al. (2001); Leya et al. (2003)] and 63Ni [Leya et al. (2003)] 7. Siting of 26Al must be in small grains, not CAIs: type 6 OCs heated to ~1200 K, must have had abundant 26Al, yet OCs have almost no CAIs ...
Answer Key
... justifications must be in your own words. If you are unsure about a question, make an educated guess, and justify your guess (which can include why you can rule out certain choices from the list). If you get stuck, please seek assistance from your peers, the TA, or the professor. Note: It may be hel ...
... justifications must be in your own words. If you are unsure about a question, make an educated guess, and justify your guess (which can include why you can rule out certain choices from the list). If you get stuck, please seek assistance from your peers, the TA, or the professor. Note: It may be hel ...
What is the net result of the proton-proton chain? a. 2 protons make
... d. It makes the light from stars appear to twinkle e. It ionizes the light and creates emission lines Interstellar gas is composed mainly of: a. Hydrogen b. Helium c. Carbon dioxide d. Methane e. Ammonia Some regions of the Milky Way appear dark because: a. There are no stars there b. Stars in that ...
... d. It makes the light from stars appear to twinkle e. It ionizes the light and creates emission lines Interstellar gas is composed mainly of: a. Hydrogen b. Helium c. Carbon dioxide d. Methane e. Ammonia Some regions of the Milky Way appear dark because: a. There are no stars there b. Stars in that ...
Today`s Powerpoint
... Pulse periods observed from 0.001 sec to 10 seconds - DEMO Explanation: "beamed" radiation from rapidly spinning neutron star. Usually neutron stars are pulsars for 107 years after supernova. ...
... Pulse periods observed from 0.001 sec to 10 seconds - DEMO Explanation: "beamed" radiation from rapidly spinning neutron star. Usually neutron stars are pulsars for 107 years after supernova. ...
Stars
... • Most elements are synthesized in the interior of Stars. • The heaviest, and least abundant, elements are synthesized in supernova. • Our Sun is presently burning H in its core. In 4.5 billion years it will use up the H in the core and collapse. When temperatures are hot enough it will burn carbon. ...
... • Most elements are synthesized in the interior of Stars. • The heaviest, and least abundant, elements are synthesized in supernova. • Our Sun is presently burning H in its core. In 4.5 billion years it will use up the H in the core and collapse. When temperatures are hot enough it will burn carbon. ...
Report Sheet
... 37. Where did the carbon and oxygen in your body originally come from? ____________________________________ 38. What does the Law of Angular Momentum do to a White Dwarf? _____________________________________ 39. Why is Sirius B rotating slower than TYC-2-900-0? _____________________________________ ...
... 37. Where did the carbon and oxygen in your body originally come from? ____________________________________ 38. What does the Law of Angular Momentum do to a White Dwarf? _____________________________________ 39. Why is Sirius B rotating slower than TYC-2-900-0? _____________________________________ ...
Prep Homework Solutions for HW due 10/04/10
... Sequence before its companion, but then it lost significant mass through mass transfer to the companion, so the more massive star is the less massive star now. Note: a couple of you suggested that the paradox could be resolved by supposing that stars in binaries change each other rate of aging or “l ...
... Sequence before its companion, but then it lost significant mass through mass transfer to the companion, so the more massive star is the less massive star now. Note: a couple of you suggested that the paradox could be resolved by supposing that stars in binaries change each other rate of aging or “l ...
Lifecycle of a Star
... Super dense core of a star left over after a supernova. Only 5 to 15 MILES in diameter, but have a mass 1.5 – 2 times that of the Sun. ...
... Super dense core of a star left over after a supernova. Only 5 to 15 MILES in diameter, but have a mass 1.5 – 2 times that of the Sun. ...
Black Hole
... Cygnus X-1’s brightness “flickers” in a thousandth of a second. For something to blink so quickly, it must be very small, less than 200 miles in diameter. In 1971, radio astronomers measured the position of Cygnus X-1 accurately. It coincides with the giant blue star HDE 226868. Such a large star co ...
... Cygnus X-1’s brightness “flickers” in a thousandth of a second. For something to blink so quickly, it must be very small, less than 200 miles in diameter. In 1971, radio astronomers measured the position of Cygnus X-1 accurately. It coincides with the giant blue star HDE 226868. Such a large star co ...
Star Life Cycle Powerpoin
... • When a massive Red Giant fuses all of the helium into carbon, fusion stops and the outer layers collapse on the core. ...
... • When a massive Red Giant fuses all of the helium into carbon, fusion stops and the outer layers collapse on the core. ...
THE CONSTELLATION LUPUS, THE WOLF
... Towards the north of the constellation are globular clusters NGC 5824 and NGC 5986, and close by the dark nebula B 228. To the south are two open clusters, NGC 5822 and NGC 5749, as well as globular cluster NGC 5927 on the eastern border with Norma. On the western border are two spiral galaxies and ...
... Towards the north of the constellation are globular clusters NGC 5824 and NGC 5986, and close by the dark nebula B 228. To the south are two open clusters, NGC 5822 and NGC 5749, as well as globular cluster NGC 5927 on the eastern border with Norma. On the western border are two spiral galaxies and ...
Ancient astronomy Part 8
... Americans as astronomers. Findings at a number of archaeological sites in southwestern USA, an area occupied by the Anasazi, suggest that these native Americans were experienced sky-watchers. A recently discovered site called Penasco Blanco in Chaco Canyon, New Mexico, includes a depiction on a cave ...
... Americans as astronomers. Findings at a number of archaeological sites in southwestern USA, an area occupied by the Anasazi, suggest that these native Americans were experienced sky-watchers. A recently discovered site called Penasco Blanco in Chaco Canyon, New Mexico, includes a depiction on a cave ...
Lives and Deaths of Stars (middle school)
... Surface temperature 6000 K Temperature at the center 14,000,000 K! ...
... Surface temperature 6000 K Temperature at the center 14,000,000 K! ...
Stellar Evolution
... Since Iron doesn’t release energy when it fuses, It needs vast amounts of energy to fuse, so Fusion Stops. The core shrinks rapidly in microseconds. The Outer-layers crash inward superheating the core to billions of degrees. Iron and other elements fuse into heavy metals and The Outer-layer bounce b ...
... Since Iron doesn’t release energy when it fuses, It needs vast amounts of energy to fuse, so Fusion Stops. The core shrinks rapidly in microseconds. The Outer-layers crash inward superheating the core to billions of degrees. Iron and other elements fuse into heavy metals and The Outer-layer bounce b ...
Study Guide: Use your notes and handouts to
... What is a light year? What is it used to measure in space? ...
... What is a light year? What is it used to measure in space? ...
Supernova Neutrinos
... • GZK seem a “guaranteed” source, from cosmic rays colliding with CMB • Wait and see… ...
... • GZK seem a “guaranteed” source, from cosmic rays colliding with CMB • Wait and see… ...
The Astrophysical Origins of the Short
... But they do not produce 129I, 53Mn, or 182Hf. 2. AGB stars are extremely unlikely to be associated with the early Solar System. Kastner & Myers (1994) conservatively calculate ...
... But they do not produce 129I, 53Mn, or 182Hf. 2. AGB stars are extremely unlikely to be associated with the early Solar System. Kastner & Myers (1994) conservatively calculate ...
History of supernova observation

The known history of supernova observation goes back to 185 CE, when, supernova SN 185 appeared, the oldest appearance of a supernova recorded by humankind. Several additional supernovae within the Milky Way galaxy have been recorded since that time, with SN 1604 being the most recent supernova to be observed in this galaxy.Since the development of the telescope, the field of supernova discovery has expanded to other galaxies. These occurrences provide important information on the distances of galaxies. Successful models of supernova behavior have also been developed, and the role of supernovae in the star formation process is now increasingly understood.