~Crowfoot
... a) arises from the Balmer γ transition. b) is due to preferential scattering of blue light as in Earth’s sky. c) is the light from an embedded blue star. 3)2 The “Pillars of Creation” on this image Eagle Nebula a) show the destruction of a nebula by a supernova explosion b) are the jets from a young ...
... a) arises from the Balmer γ transition. b) is due to preferential scattering of blue light as in Earth’s sky. c) is the light from an embedded blue star. 3)2 The “Pillars of Creation” on this image Eagle Nebula a) show the destruction of a nebula by a supernova explosion b) are the jets from a young ...
The Life of a Star
... atmosphere will be blown off into space: our blue green planet will become a scorched lifeless ball of rock. Of course the new fuel (helium) will not last forever either and the core will go through a series of collapses; each resulting in the creation of new heavier elements and new thermonuclear r ...
... atmosphere will be blown off into space: our blue green planet will become a scorched lifeless ball of rock. Of course the new fuel (helium) will not last forever either and the core will go through a series of collapses; each resulting in the creation of new heavier elements and new thermonuclear r ...
Supernova and Supernova Remnants lec 1-2
... Type II supernovae - implosion-explosion events of a massive star. They show a characteristic plateau in their light curves a few months after explosion . This plateau is reproduced by models which assume that the energy comes from the expansion and cooling of the star's outer envelope as it is blow ...
... Type II supernovae - implosion-explosion events of a massive star. They show a characteristic plateau in their light curves a few months after explosion . This plateau is reproduced by models which assume that the energy comes from the expansion and cooling of the star's outer envelope as it is blow ...
Chapter 25 Study guide Answer Key
... Compare and contrast apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude. Apparent is how bright a star appears to us and absolute is how bright it actually is. ...
... Compare and contrast apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude. Apparent is how bright a star appears to us and absolute is how bright it actually is. ...
What are stars? - Manhasset Schools
... the collapsing core reaches 10 billion K and atomic nuclei are split into neutrons and protons. Protons merge with electrons to form neutrons, and the collapsing core becomes a neutron star. A typical neutron star is the size of a major city on Earth, but has a mass greater than the Sun’s. ...
... the collapsing core reaches 10 billion K and atomic nuclei are split into neutrons and protons. Protons merge with electrons to form neutrons, and the collapsing core becomes a neutron star. A typical neutron star is the size of a major city on Earth, but has a mass greater than the Sun’s. ...
What The Star of Bethlehem Was Not
... This theory has been championed, in various guises, by Patrick Moore. He suggests that the magi saw a bright meteor, or possibly two bright meteors – one to tell them when Jesus was born, the other to tell them that they had arrived at their destination. An alternative which he has proposed is a "Cy ...
... This theory has been championed, in various guises, by Patrick Moore. He suggests that the magi saw a bright meteor, or possibly two bright meteors – one to tell them when Jesus was born, the other to tell them that they had arrived at their destination. An alternative which he has proposed is a "Cy ...
Chapter 27 Review Guide// ESS
... 3. How do astronomers determine a star’s composition and temperature? 4. What are the two types of stellar motion? a. What causes the stars to “move” westward across the night sky? b. Why do we see different stars at different times of the year? ...
... 3. How do astronomers determine a star’s composition and temperature? 4. What are the two types of stellar motion? a. What causes the stars to “move” westward across the night sky? b. Why do we see different stars at different times of the year? ...
White Dwarf Stars - University of California Observatories
... • The heat generated by viscosity (friction) in this high speed gas produces X-rays. Some of the gas is ultimately swallowed by the black hole. ...
... • The heat generated by viscosity (friction) in this high speed gas produces X-rays. Some of the gas is ultimately swallowed by the black hole. ...
A Study of the Nature and Representative Features of Supernova
... (Galactic) supernovae remnants exist, with a few dozen other heavily suspected. For a listing and summary see Green D.A. 2001. The remainder of this paper will focus on Galactic SNRs since they are the most accessible and easiest to study. The first extragalactic supernova was not observed until 188 ...
... (Galactic) supernovae remnants exist, with a few dozen other heavily suspected. For a listing and summary see Green D.A. 2001. The remainder of this paper will focus on Galactic SNRs since they are the most accessible and easiest to study. The first extragalactic supernova was not observed until 188 ...
Supernovae and supernova remnants
... Z is the atomic number) existed. This energy gap hindered the creation of elements beyond helium in the first 3-minute after the Big Bang. In contrast, the universe today is abundant in high-Z elements. In the first epoch of the universe, matter was partly clustered and formed into stars. Once the s ...
... Z is the atomic number) existed. This energy gap hindered the creation of elements beyond helium in the first 3-minute after the Big Bang. In contrast, the universe today is abundant in high-Z elements. In the first epoch of the universe, matter was partly clustered and formed into stars. Once the s ...
FSA school wide Science Olympiad 12/8/2007
... hence occulted by the moon at some time or the other. D. All of them lie in the Milky Way band of the sky (the galactic equator) 3. On July 4, 1054, Chinese astronomers (and possibly Native Americans) recorded a supernova explosion taking place in the constellation Taurusso bright that it was even v ...
... hence occulted by the moon at some time or the other. D. All of them lie in the Milky Way band of the sky (the galactic equator) 3. On July 4, 1054, Chinese astronomers (and possibly Native Americans) recorded a supernova explosion taking place in the constellation Taurusso bright that it was even v ...
PPT
... White Dwarfs are supported by electron degeneracy pressure • in a low-mass star, Fusion stops after He -->C and O • Just cools off and fizzles out ...
... White Dwarfs are supported by electron degeneracy pressure • in a low-mass star, Fusion stops after He -->C and O • Just cools off and fizzles out ...
Estimating the Age of Supernova Remnants - Chandra X
... most of the gas in the remnant is not from the star. As the ejected material expands outwards, it encounters and intermingles with the interstellar medium and propels it outward, building up the outer shock wave. The volume through which the remnant has expanded and the density of the interstellar m ...
... most of the gas in the remnant is not from the star. As the ejected material expands outwards, it encounters and intermingles with the interstellar medium and propels it outward, building up the outer shock wave. The volume through which the remnant has expanded and the density of the interstellar m ...
Frantic Finish - Max-Planck
... neutrinos. These nearly massless particles succeed almost effortlessly in penetrating practically anything that gets in their way – like our thumbnail, through which more than 66 billion of these elusive phantoms race every second. That they also play a role in supernovae has been known since the ev ...
... neutrinos. These nearly massless particles succeed almost effortlessly in penetrating practically anything that gets in their way – like our thumbnail, through which more than 66 billion of these elusive phantoms race every second. That they also play a role in supernovae has been known since the ev ...
White Dwarf Stars
... • The heat generated by viscosity (friction) in this high speed gas produces X-rays. Some of the gas is ultimately swallowed by the black hole. ...
... • The heat generated by viscosity (friction) in this high speed gas produces X-rays. Some of the gas is ultimately swallowed by the black hole. ...
Homework #3 10 points Question #1 (2 pts) The brightest star in the
... one massive star that exploded as a core collapse supernova, and in a region of space B we found several white dwarfs that all exploded as thermonuclear supernovae. The number of white dwarfs in the region B is such that in both regions, A and B, exactly the same amounts of carbon and oxygen are pro ...
... one massive star that exploded as a core collapse supernova, and in a region of space B we found several white dwarfs that all exploded as thermonuclear supernovae. The number of white dwarfs in the region B is such that in both regions, A and B, exactly the same amounts of carbon and oxygen are pro ...
Lecture 16 - Yet More Evolution of Stars
... nuclei are converted into neutrons with the emission of neutrinos • Core collapse stops, neutron star is formed • Rest of the star collapses in on the core, but bounces off the new neutron star (also pushed outwards by the neutrinos) ...
... nuclei are converted into neutrons with the emission of neutrinos • Core collapse stops, neutron star is formed • Rest of the star collapses in on the core, but bounces off the new neutron star (also pushed outwards by the neutrinos) ...
Lecture 10 - Concord University
... Do we have all this right? How do we check all this out? (1) Star clusters are perfect because they contain stars in many of the evolutionary phases. Can test timescale, surface temperature and luminosity predictions. After 30 years of testing, it looks like we understand the basic evolution o ...
... Do we have all this right? How do we check all this out? (1) Star clusters are perfect because they contain stars in many of the evolutionary phases. Can test timescale, surface temperature and luminosity predictions. After 30 years of testing, it looks like we understand the basic evolution o ...
14_creationism
... be just right to allow intelligent life. The origin of life. This is such an extraordinary event and “achievement”. Perhaps life is so complex that the origin of life is a lot less likely than we think. This is testable. As we search the universe we may be unlikely to find even primitive life. The o ...
... be just right to allow intelligent life. The origin of life. This is such an extraordinary event and “achievement”. Perhaps life is so complex that the origin of life is a lot less likely than we think. This is testable. As we search the universe we may be unlikely to find even primitive life. The o ...
Life Cycle of a Star
... Heat and pressure begin to build until __________ __________ begins to take place. Inside the core, _____________ atoms smash together and are fused into heavier _____________ atoms. This process generates an enormous amount of ______________ and the star ignites becoming a _________ ______________ ...
... Heat and pressure begin to build until __________ __________ begins to take place. Inside the core, _____________ atoms smash together and are fused into heavier _____________ atoms. This process generates an enormous amount of ______________ and the star ignites becoming a _________ ______________ ...
Absolute magnitude of type Ia supernovae
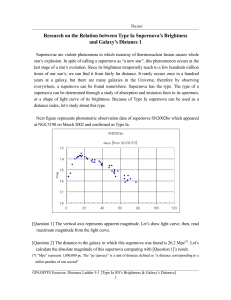
... times of our sun’s, we can find it from fairly far distance. It rarely occurs once in a hundred years at a galaxy, but there are many galaxies in the Universe, therefore by observing everywhere, a supernova can be found somewhere. Supernova has the type. The type of a supernova can be determined thr ...
... times of our sun’s, we can find it from fairly far distance. It rarely occurs once in a hundred years at a galaxy, but there are many galaxies in the Universe, therefore by observing everywhere, a supernova can be found somewhere. Supernova has the type. The type of a supernova can be determined thr ...
Chapter 7 Formation of metal-enriched 2nd generation objects 7.1
... Observations of quasar absorption spectra show that the universe at the present day is uniformly polluted with metals, even at the lowest observed column densities, which correspond to regions of very low overdensity which are know as the Lyman-α forest [84, 85]. The primordial composition of the un ...
... Observations of quasar absorption spectra show that the universe at the present day is uniformly polluted with metals, even at the lowest observed column densities, which correspond to regions of very low overdensity which are know as the Lyman-α forest [84, 85]. The primordial composition of the un ...
ES High mass star life cycle plus black holes
... Now we are going to have a little practice quiz. On Thursday we watched a video about the life cycle of a low mass star. What I would you to attempt is to draw the life cycle of a low mass star. All stars start as a nebula and this is also the ending point for many stars so this a true cycle. Protos ...
... Now we are going to have a little practice quiz. On Thursday we watched a video about the life cycle of a low mass star. What I would you to attempt is to draw the life cycle of a low mass star. All stars start as a nebula and this is also the ending point for many stars so this a true cycle. Protos ...
History of supernova observation

The known history of supernova observation goes back to 185 CE, when, supernova SN 185 appeared, the oldest appearance of a supernova recorded by humankind. Several additional supernovae within the Milky Way galaxy have been recorded since that time, with SN 1604 being the most recent supernova to be observed in this galaxy.Since the development of the telescope, the field of supernova discovery has expanded to other galaxies. These occurrences provide important information on the distances of galaxies. Successful models of supernova behavior have also been developed, and the role of supernovae in the star formation process is now increasingly understood.