File
... Whereas novae are small eruptions involving only a tiny fraction of a star’s mass, supernovae involve entire stars. A supernova may appear about as bright as the entire galaxy it is in. ...
... Whereas novae are small eruptions involving only a tiny fraction of a star’s mass, supernovae involve entire stars. A supernova may appear about as bright as the entire galaxy it is in. ...
Stars 3
... This confirms our theoretical ideas that such objects should remain after a supernova explosion. explosion Other supernovae in our galaxy during the last 1000 years occurred in 1006, 1572, and 1604. We observe many such explosions in other galaxies. (Jocelyn Bell was at the controls when the pulses ...
... This confirms our theoretical ideas that such objects should remain after a supernova explosion. explosion Other supernovae in our galaxy during the last 1000 years occurred in 1006, 1572, and 1604. We observe many such explosions in other galaxies. (Jocelyn Bell was at the controls when the pulses ...
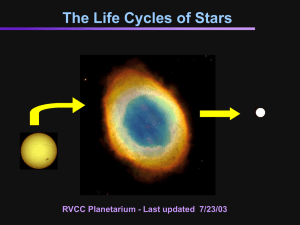
Make one copy for each student on plain paper. Life Cycle of Star
... collapse leading to a massive explosion that can remain visible for months. ...
... collapse leading to a massive explosion that can remain visible for months. ...
Life Cycle of Star Pictures
... collapse leading to a massive explosion that can remain visible for months. ...
... collapse leading to a massive explosion that can remain visible for months. ...
Constellation, Star, and Deep Sky Object
... Parsec = parallax second of arc – distance that a star “jumps” one second of a degree of arc in the sky as a result of the earth’s revolution around the sun. 1 parsec = 3.262 light years Distance in astronomy is measured in light years, parsecs, or astronomical units. Metric prefix for AU and parsec ...
... Parsec = parallax second of arc – distance that a star “jumps” one second of a degree of arc in the sky as a result of the earth’s revolution around the sun. 1 parsec = 3.262 light years Distance in astronomy is measured in light years, parsecs, or astronomical units. Metric prefix for AU and parsec ...
Life Cycles of Stars
... Fate of High Mass Stars • After Helium is exhausted, core collapses again until it becomes hot enough to fuse Carbon into Magnesium or Oxygen. • Through a combination of processes, successively heavier elements are formed and burned. ...
... Fate of High Mass Stars • After Helium is exhausted, core collapses again until it becomes hot enough to fuse Carbon into Magnesium or Oxygen. • Through a combination of processes, successively heavier elements are formed and burned. ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... • 90% of classified stars are on main sequence • Main sequence stars are “young” stars • If a star is leaving the main sequence, it is at the end of its lifespan of burning hydrogen into ...
... • 90% of classified stars are on main sequence • Main sequence stars are “young” stars • If a star is leaving the main sequence, it is at the end of its lifespan of burning hydrogen into ...
Stellar Evolution: the Death of Stars
... • Convection occurs over a larger portion of its volume • It takes heavy elements formed in the star’s interior and distributes them throughout the star • AGB star is also called Carbon Star • AGB star has strong stellar wind, losing mass at very high rate • AGB star enriches interstellar medium wit ...
... • Convection occurs over a larger portion of its volume • It takes heavy elements formed in the star’s interior and distributes them throughout the star • AGB star is also called Carbon Star • AGB star has strong stellar wind, losing mass at very high rate • AGB star enriches interstellar medium wit ...
www.if.ufrgs.br
... "Cosmic x-rays reveal evidence for new form of matter" WWW.msfc.nasa.gov/news ...
... "Cosmic x-rays reveal evidence for new form of matter" WWW.msfc.nasa.gov/news ...
final review sheet
... 10) There are basically two different type of supernovae (SNe): Type Ia and core collapse (which includes both Type II and Type Ib/c). In each case, what is the progenitor star, what produces the SN, and what is left after the explosion. 11) What are sunspots? Why do they appear dark? 12) What is t ...
... 10) There are basically two different type of supernovae (SNe): Type Ia and core collapse (which includes both Type II and Type Ib/c). In each case, what is the progenitor star, what produces the SN, and what is left after the explosion. 11) What are sunspots? Why do they appear dark? 12) What is t ...
Supernovae Gamma-Ray Bursts and and some of their uses
... freshly synthesized heavy elements, and forms what is called a supernova remnant • Supernova remnants may be observed for hundreds of thousands of years as often beautiful, visual objects, but also as emitters of radio waves and X-rays • Close to 150 supernova remnants have been detected in the Milk ...
... freshly synthesized heavy elements, and forms what is called a supernova remnant • Supernova remnants may be observed for hundreds of thousands of years as often beautiful, visual objects, but also as emitters of radio waves and X-rays • Close to 150 supernova remnants have been detected in the Milk ...
Chapter 13 Notes – The Deaths of Stars
... of an ___________ core, happen extremely rapidly: _________ burning only lasts for about _______ day Iron core ultimately _________________, triggering an explosion that destroys the star: A __________________! Several hundreds to ________________ of years later, the ejected material from supern ...
... of an ___________ core, happen extremely rapidly: _________ burning only lasts for about _______ day Iron core ultimately _________________, triggering an explosion that destroys the star: A __________________! Several hundreds to ________________ of years later, the ejected material from supern ...
CH27.2 Stellar Evolution
... Some may have one or more large explosions, causing them to become very bright for a short time(days) ...
... Some may have one or more large explosions, causing them to become very bright for a short time(days) ...
300 MHz - 3 GHz Yes, we`re interested
... • HI wrt young stars: HI outflows, and Zeeman splitting (also OH) - importance of magnetic fields vs. turbulence • Continuum: extragalactic - cosmic magnetism (Faraday rotation). Galactic magnetic fields, cluster magnetic fields, the cosmic web itself? ...
... • HI wrt young stars: HI outflows, and Zeeman splitting (also OH) - importance of magnetic fields vs. turbulence • Continuum: extragalactic - cosmic magnetism (Faraday rotation). Galactic magnetic fields, cluster magnetic fields, the cosmic web itself? ...
Protostar, Initial mass, Main Sequence
... Red dwarf stars with less than half a solar mass do not achieve red giant status they begin to fade as soon as their hydrogen fuel is exhausted. White dwarfs, planetary nebulae Our Sun, and any star with similar mass, will fuse to carbon and, possibly, oxygen and neon before shrinking to become a wh ...
... Red dwarf stars with less than half a solar mass do not achieve red giant status they begin to fade as soon as their hydrogen fuel is exhausted. White dwarfs, planetary nebulae Our Sun, and any star with similar mass, will fuse to carbon and, possibly, oxygen and neon before shrinking to become a wh ...
Volume 20 Number 10 September 2012
... Researchers have released the largest threedimensional map of black holes and massive galaxies, it pinpoints the locations and distances to more than 1 million galaxies, each of which contains more than 100 billion stars, This will enable scientists to retrace the history of the universe for the las ...
... Researchers have released the largest threedimensional map of black holes and massive galaxies, it pinpoints the locations and distances to more than 1 million galaxies, each of which contains more than 100 billion stars, This will enable scientists to retrace the history of the universe for the las ...
PHY 150
... track that the Sun will follow from when it leaves the main sequence to when it becomes a white dwarf. Approximately how much mass will the Sun have when it becomes a white dwarf? Where will the rest of the mass ...
... track that the Sun will follow from when it leaves the main sequence to when it becomes a white dwarf. Approximately how much mass will the Sun have when it becomes a white dwarf? Where will the rest of the mass ...
Lecture 10a Neutron Star and Black Holes (Test 2 overview)
... Supernovas • 10-20 supernovas occur every1000 years in a galaxy the size of the Milky Way (~200 billion stars) with ~15% being type Ia • 8 observed in last 2000 years (185, 386, ...
... Supernovas • 10-20 supernovas occur every1000 years in a galaxy the size of the Milky Way (~200 billion stars) with ~15% being type Ia • 8 observed in last 2000 years (185, 386, ...
Homework 1 - Course Pages of Physics Department
... earth is 235 U/238 U = 0.00725. When were they equal in abundance? The heavy elements were created in supernova explosions and mixed with the interstellar gas and dust, from which the earth was formed. According to supernova calculations the uranium isotopes are produced in ratio 235 U/238 U = 1.3 ± ...
... earth is 235 U/238 U = 0.00725. When were they equal in abundance? The heavy elements were created in supernova explosions and mixed with the interstellar gas and dust, from which the earth was formed. According to supernova calculations the uranium isotopes are produced in ratio 235 U/238 U = 1.3 ± ...
supernova - Michigan State University
... If a stellar core grows beyond its Chandrasekhar mass limit, it will collapse. Typically this will result in a Supernova explosion at least the outer part of a star is blown off into space ...
... If a stellar core grows beyond its Chandrasekhar mass limit, it will collapse. Typically this will result in a Supernova explosion at least the outer part of a star is blown off into space ...
Objects Beyond our Solar System
... when a large sun comes to the end of its life and explodes. The outside of the star is blown outward but the core that is left behind collapses in on itself and creates an incredibly dense mass of material. The core of a neutron star is so dense that one cupful of it would have a mass of millions ...
... when a large sun comes to the end of its life and explodes. The outside of the star is blown outward but the core that is left behind collapses in on itself and creates an incredibly dense mass of material. The core of a neutron star is so dense that one cupful of it would have a mass of millions ...
Death of Stars - Astronomy @ Walton High School
... a city or the human population on Earth fitting inside an area the size of a sugar cube. Neutron stars rotate rapidly after formation, typically spinning between fractions of a second and half a minute. We can detect this because they emit radio pulses, and the ones we detect are known as pulsars. R ...
... a city or the human population on Earth fitting inside an area the size of a sugar cube. Neutron stars rotate rapidly after formation, typically spinning between fractions of a second and half a minute. We can detect this because they emit radio pulses, and the ones we detect are known as pulsars. R ...
History of supernova observation

The known history of supernova observation goes back to 185 CE, when, supernova SN 185 appeared, the oldest appearance of a supernova recorded by humankind. Several additional supernovae within the Milky Way galaxy have been recorded since that time, with SN 1604 being the most recent supernova to be observed in this galaxy.Since the development of the telescope, the field of supernova discovery has expanded to other galaxies. These occurrences provide important information on the distances of galaxies. Successful models of supernova behavior have also been developed, and the role of supernovae in the star formation process is now increasingly understood.