quarter 1 assessment review
... a) The Expanding Universe - stars and galaxies are moving away from each other as you would expect after and explosion. b) The Red Shift – Stars and galaxies display the red shift of objects moving away from us. c) Background Radiation – the radiation left over from the big bang can still be detecte ...
... a) The Expanding Universe - stars and galaxies are moving away from each other as you would expect after and explosion. b) The Red Shift – Stars and galaxies display the red shift of objects moving away from us. c) Background Radiation – the radiation left over from the big bang can still be detecte ...
Astronomy 1 Is there life in our solar system
... What are the main objects in the Solar System and how were they formed What is the sun and why is it essential to everything in the solar system including our well-being and weather on Earth What are the inner planets and why are they all made of rock? Do the recent space missions answer the questio ...
... What are the main objects in the Solar System and how were they formed What is the sun and why is it essential to everything in the solar system including our well-being and weather on Earth What are the inner planets and why are they all made of rock? Do the recent space missions answer the questio ...
The Inner Planets Mercury Venus Earth Mars WORD BOX
... nearest to the Sun life liquid water atmosphere terrestrial ice ...
... nearest to the Sun life liquid water atmosphere terrestrial ice ...
Outer planets
... • At least 47 moons • Most of the atmosphere is hydrogen and helium • Small mass despite large size • Voyager space probe studied the rings- size range: tiny grains to bulldogs ...
... • At least 47 moons • Most of the atmosphere is hydrogen and helium • Small mass despite large size • Voyager space probe studied the rings- size range: tiny grains to bulldogs ...
Ch. 28.3 Formation of the Solar System
... mass and increased gravity, it attracted a first atmosphere of hydrogen and helium from the surrounding nebula. • This was lost due to weak gravity and the solar wind. • A second atmosphere of mostly CO2 and water vapor came from the earth’s interior due to volcanic eruptions (outgasing). ...
... mass and increased gravity, it attracted a first atmosphere of hydrogen and helium from the surrounding nebula. • This was lost due to weak gravity and the solar wind. • A second atmosphere of mostly CO2 and water vapor came from the earth’s interior due to volcanic eruptions (outgasing). ...
Chapter 28.3
... mass and increased gravity, it attracted a first atmosphere of hydrogen and helium from the surrounding nebula. • This was lost due to weak gravity and the solar wind. • A second atmosphere of mostly CO2 and water vapor came from the earth’s interior due to volcanic eruptions (outgassing). ...
... mass and increased gravity, it attracted a first atmosphere of hydrogen and helium from the surrounding nebula. • This was lost due to weak gravity and the solar wind. • A second atmosphere of mostly CO2 and water vapor came from the earth’s interior due to volcanic eruptions (outgassing). ...
comets-what they are - Interactive Science Teacher
... ___________ is what sends some into the inner solar system among the planets. Copyright © 2011 InteractiveScienceLessons.com™ ...
... ___________ is what sends some into the inner solar system among the planets. Copyright © 2011 InteractiveScienceLessons.com™ ...
Chart_set_4
... 4. planetesimals collide and stick, enhanced by their gravity 5. a few large planets result ...
... 4. planetesimals collide and stick, enhanced by their gravity 5. a few large planets result ...
Guided Notes Section 18.3 Day 2 (Planets)
... 9. All of the gaseous outer planets have __________ and _____________. a. Galileo was the first to use a _______________ to look at the planets and he found 4 ____________ orbiting _____________. b. These were the first __________ to be seen orbiting a planet other than _________. c. Satellite: any ...
... 9. All of the gaseous outer planets have __________ and _____________. a. Galileo was the first to use a _______________ to look at the planets and he found 4 ____________ orbiting _____________. b. These were the first __________ to be seen orbiting a planet other than _________. c. Satellite: any ...
The Role of Comets in the Late Heavy Bombardment
... • The Earth acquired a total of M ≈ 3x1019 kg, much less than the ocean mass • Mars acquired a total of M ≈ 7x1018 kg • This is about 10 m Global Equivalent Layer of water (20%), ...
... • The Earth acquired a total of M ≈ 3x1019 kg, much less than the ocean mass • Mars acquired a total of M ≈ 7x1018 kg • This is about 10 m Global Equivalent Layer of water (20%), ...
Some Slides from the Space Studies Institute
... Using Soil for Protection - Lunar soil or "regolith" will be piled up over the modules. This will protect the inhabitants from both cosmic rays and micrometeoroids, as well as reduce temperature swings. As it happens, dust in a vacuum is excellent insulation. ...
... Using Soil for Protection - Lunar soil or "regolith" will be piled up over the modules. This will protect the inhabitants from both cosmic rays and micrometeoroids, as well as reduce temperature swings. As it happens, dust in a vacuum is excellent insulation. ...
DeKalb Middle School Weekly Lesson Plan Teacher: Angela
... Define gas giant. (a planet that has a ...
... Define gas giant. (a planet that has a ...
Quiz # 5
... 5. The Earth has an average density of 5.5 g/cm3 although the density of rock on its surface is about 3.0 g/cm3. What conclusion can be reached about the Earth's core from this observation? A) It consists of lower density material than surface rock. B) It must be composed of material with density a ...
... 5. The Earth has an average density of 5.5 g/cm3 although the density of rock on its surface is about 3.0 g/cm3. What conclusion can be reached about the Earth's core from this observation? A) It consists of lower density material than surface rock. B) It must be composed of material with density a ...
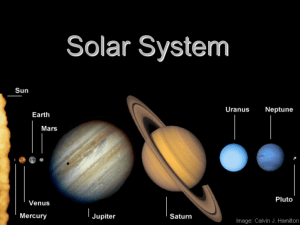
The Solar System
... Has two moons and the largest volcano in the solar system Red planet because the soil is dark reddish brown Has dust storms that last months There is no liquid water now but scientists suspect there may have been once because of the valleys and sedimentary rock. ...
... Has two moons and the largest volcano in the solar system Red planet because the soil is dark reddish brown Has dust storms that last months There is no liquid water now but scientists suspect there may have been once because of the valleys and sedimentary rock. ...
Chapter 18: Inner and Outer Planets Name: 1. What is the study of
... Saturn: has a ring system that orbits the planet Neptune: smallest of the gas giants Uranus: the only planet that rotates on its side ...
... Saturn: has a ring system that orbits the planet Neptune: smallest of the gas giants Uranus: the only planet that rotates on its side ...
Apophis - OSIRIS
... Journey with us through the alphabet as we learn about Earth’s rocky neighbors – the asteroids! There are interesting asteroid characters in our solar system, including an asteroid that has its own moon and even one that is shaped like a dog bone! For each letter of the alphabet, we will showcase an ...
... Journey with us through the alphabet as we learn about Earth’s rocky neighbors – the asteroids! There are interesting asteroid characters in our solar system, including an asteroid that has its own moon and even one that is shaped like a dog bone! For each letter of the alphabet, we will showcase an ...
Solar System Unit Objectives
... List planets in order from the sun, rank their relative sizes, and approx. distances from the sun in rounded AUs From a scale model, give the planets distances and sizes in AUs and km From data giving planet sizes and distances from the sun construct a scale model of the solar system Identify unique ...
... List planets in order from the sun, rank their relative sizes, and approx. distances from the sun in rounded AUs From a scale model, give the planets distances and sizes in AUs and km From data giving planet sizes and distances from the sun construct a scale model of the solar system Identify unique ...
File
... Unit 7 Study Guide 1. Which shape describes a planet’s orbit? Circular 2. Why is Venus hotter than Mercury? The atmosphere traps solar energy 3. How are the out planets similar? They are known as the “Gas Giants” because they are made of gases found on Earth 4. What is Pluto known as? Dwarf Planet 5 ...
... Unit 7 Study Guide 1. Which shape describes a planet’s orbit? Circular 2. Why is Venus hotter than Mercury? The atmosphere traps solar energy 3. How are the out planets similar? They are known as the “Gas Giants” because they are made of gases found on Earth 4. What is Pluto known as? Dwarf Planet 5 ...
Find the Planet Facts column for each of the planets: Mercury: Venus
... ___ Mercury has lots of craters and smooth lava plains like our moon, and a huge ocean under the surface like our Earth’s oceans. ...
... ___ Mercury has lots of craters and smooth lava plains like our moon, and a huge ocean under the surface like our Earth’s oceans. ...
Late Heavy Bombardment

The Late Heavy Bombardment (abbreviated LHB and also known as the lunar cataclysm) is a hypothetical event thought to have occurred approximately 4.1 to 3.8 billion years (Ga) ago, corresponding to the Neohadean and Eoarchean eras on Earth. During this interval, a disproportionately large number of asteroids apparently collided with the early terrestrial planets in the inner Solar System, including Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. The LHB happened after the Earth and other rocky planets had formed and accreted most of their mass, but still quite early in Earth's history.Evidence for the LHB derives from lunar samples brought back by the Apollo astronauts. Isotopic dating of Moon rocks implies that most impact melts occurred in a rather narrow interval of time. Several hypotheses are now offered to explain the apparent spike in the flux of impactors (i.e. asteroids and comets) in the inner Solar System, but no consensus yet exists. The Nice model is popular among planetary scientists; it postulates that the gas giant planets underwent orbital migration and scattered objects in the asteroid and/or Kuiper belts into eccentric orbits, and thereby into the path of the terrestrial planets. Other researchers argue that the lunar sample data do not require a cataclysmic cratering event near 3.9 Ga, and that the apparent clustering of impact melt ages near this time is an artifact of sampling materials retrieved from a single large impact basin. They also note that the rate of impact cratering could be significantly different between the outer and inner zones of the Solar System.