ASTRONOMY TEST 1 – STUDY GUIDE The layer of the Sun`s
... C. the Sun’s gravity attracts the tail of the comet D. energy from other planets pulls the tail of the comet There are many meteors that enter Earth’s atmosphere, but very few of them actually land on Earth. Most of the ones that do not strike the Earth _______________. A. turn around and travel bac ...
... C. the Sun’s gravity attracts the tail of the comet D. energy from other planets pulls the tail of the comet There are many meteors that enter Earth’s atmosphere, but very few of them actually land on Earth. Most of the ones that do not strike the Earth _______________. A. turn around and travel bac ...
Astronomy
... The early Greeks astronomers held a geocentric view, believing the Earth was stationary and all known bodies (the moon, sun, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn) were in orbit around the Earth. They believed there existed beyond the planets a transparent, hollow sphere (celestial sphere) o ...
... The early Greeks astronomers held a geocentric view, believing the Earth was stationary and all known bodies (the moon, sun, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter, and Saturn) were in orbit around the Earth. They believed there existed beyond the planets a transparent, hollow sphere (celestial sphere) o ...
“Solar System Study Guide”
... opposite direction and debris left behind in the comets orbit 22. _____________- A piece of rock that is similar to the material that formed our planets 23. _____________- Small pieces of rock that travel through space 24. _____________-A meteoroid that burns up in the earth’s atmosphere 25. _______ ...
... opposite direction and debris left behind in the comets orbit 22. _____________- A piece of rock that is similar to the material that formed our planets 23. _____________- Small pieces of rock that travel through space 24. _____________-A meteoroid that burns up in the earth’s atmosphere 25. _______ ...
The Sun and planets
... i.e. slightly squashed, and almost all on the same plane because of the mechanism with which they were created during the formation of our planetary system. Dwarf planets and minor bodies on the contrary are characterised by more elongated and inclined orbits. All bodies in the Solar System move at ...
... i.e. slightly squashed, and almost all on the same plane because of the mechanism with which they were created during the formation of our planetary system. Dwarf planets and minor bodies on the contrary are characterised by more elongated and inclined orbits. All bodies in the Solar System move at ...
Spring 2013 Final Exam Study Guide
... 42. Which layer of the sun is considered the surface? 43. Which layer of the sun gives it its color? 44. In which layer of the sun does it produce its energy? 45. What is the process called that produces the Sun’s energy? 46. What gas is used to make the energy in the Sun? 47. What gas is produced w ...
... 42. Which layer of the sun is considered the surface? 43. Which layer of the sun gives it its color? 44. In which layer of the sun does it produce its energy? 45. What is the process called that produces the Sun’s energy? 46. What gas is used to make the energy in the Sun? 47. What gas is produced w ...
Day-28
... same amount of radioactive material and that the successive decay produced all the internal heat, then the rate of energy loss is dictated by how much energy there is (volume = 4/3 π R3) and where the planet loses the energy (surface area = 4 π R2) . The amount of energy that could be lost divided ...
... same amount of radioactive material and that the successive decay produced all the internal heat, then the rate of energy loss is dictated by how much energy there is (volume = 4/3 π R3) and where the planet loses the energy (surface area = 4 π R2) . The amount of energy that could be lost divided ...
Nine Planets and Counting
... how others feel about this issue. Each year NASA publishes a free booklet called Space Spin-offs that shows how space technology is used to improve life on Earth. Send for the booklet and share it with students. 8. Many students hear that Neptune and Pluto switch orbits. This is a misconception. Plu ...
... how others feel about this issue. Each year NASA publishes a free booklet called Space Spin-offs that shows how space technology is used to improve life on Earth. Send for the booklet and share it with students. 8. Many students hear that Neptune and Pluto switch orbits. This is a misconception. Plu ...
1 Chapter 2 - University of Minnesota
... rotation axis remains fixed in space, providing us with an invaluably constant frame of reference. 2) The earth’s rotation axis is used to define the north and south celestial poles, and also the celestial equator. 3) The north-south line passing through our location on the earth’s surface, the meri ...
... rotation axis remains fixed in space, providing us with an invaluably constant frame of reference. 2) The earth’s rotation axis is used to define the north and south celestial poles, and also the celestial equator. 3) The north-south line passing through our location on the earth’s surface, the meri ...
File
... 1. _ASTEROIDS__ are found in a belt area marking the division between the inner and outer planets. 2. The universe is believed to be expanding based on light emitted by stars that has been __RED-SHIFTED_. 3. 24 hours in a day is caused by Earth’s _ROTATION_ on its axis. 4. The term to describe Mars’ ...
... 1. _ASTEROIDS__ are found in a belt area marking the division between the inner and outer planets. 2. The universe is believed to be expanding based on light emitted by stars that has been __RED-SHIFTED_. 3. 24 hours in a day is caused by Earth’s _ROTATION_ on its axis. 4. The term to describe Mars’ ...
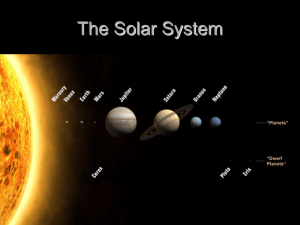
THE SOLAR SYSTEM HAS GOT - 1 star: The Sun - 1 moon
... It’s called the ‘ goldilocks planet ‘, because it’s not too hot and not to cold it is the densest major body in the solar system. This means that it's the most "compact" of all the planets it is 4.5 to 4.6 billion years old 71 % of the Earth's surface is covered with water.. Water is essenti ...
... It’s called the ‘ goldilocks planet ‘, because it’s not too hot and not to cold it is the densest major body in the solar system. This means that it's the most "compact" of all the planets it is 4.5 to 4.6 billion years old 71 % of the Earth's surface is covered with water.. Water is essenti ...
Activity 12: Solar System
... “relating to the sun.” System is defined as: “a set of things or parts forming a whole.” When you consider the meanings of these words, there is indication that the sun plays a major role among this group of celestial bodies we call the “solar system.” The sun is, in fact, at the center of this mass ...
... “relating to the sun.” System is defined as: “a set of things or parts forming a whole.” When you consider the meanings of these words, there is indication that the sun plays a major role among this group of celestial bodies we call the “solar system.” The sun is, in fact, at the center of this mass ...
Planets in the Sky
... About how long does it take the Sun to complete one “trip” around along the ecliptic around the entire sky? ...
... About how long does it take the Sun to complete one “trip” around along the ecliptic around the entire sky? ...
11History
... Copernicus, a Polish astronomer, suggested a dramatically different model of the Solar System, a heliocentric model, with the Sun at the center Copernicus preserved the idea that planets orbited in circular orbits around the Sun ...
... Copernicus, a Polish astronomer, suggested a dramatically different model of the Solar System, a heliocentric model, with the Sun at the center Copernicus preserved the idea that planets orbited in circular orbits around the Sun ...
Chapter 29, Section 2
... Orbit period: the time required for the planet to make one revolution around the Sun. Average distance of a planet to the sun (r) measured in AU. Orbit period (p) measured in Earth years. Law of Periods: r³ = p² (r x r x r = p x p) Which means: the cube of the average distance of a planet from the S ...
... Orbit period: the time required for the planet to make one revolution around the Sun. Average distance of a planet to the sun (r) measured in AU. Orbit period (p) measured in Earth years. Law of Periods: r³ = p² (r x r x r = p x p) Which means: the cube of the average distance of a planet from the S ...
Name - MIT
... A) He wanted the Earth at the center. B) He wanted the Moon to be at the center. C) He did not think Mars was a planet. D) He did not think Jupiter was a planet. E) He wanted all the orbits of the planets to be perfectly circular. 27) Which of these planets travels the slowest around the Sun? A) Nep ...
... A) He wanted the Earth at the center. B) He wanted the Moon to be at the center. C) He did not think Mars was a planet. D) He did not think Jupiter was a planet. E) He wanted all the orbits of the planets to be perfectly circular. 27) Which of these planets travels the slowest around the Sun? A) Nep ...
Meteors - Little Worksheets
... There are lots of objects that we see in the sky. During the day we see the sun. After the sun sets in the evening we see mostly the stars. Not all the lights in the sky that we see are really stars. Of course, we see the moon. Some of the other lights in the sky are planets. Planets revolve around ...
... There are lots of objects that we see in the sky. During the day we see the sun. After the sun sets in the evening we see mostly the stars. Not all the lights in the sky that we see are really stars. Of course, we see the moon. Some of the other lights in the sky are planets. Planets revolve around ...
TOILET PAPER SOLAR SYSTEM
... Mercury is the closest and Neptune is the farthest. We are going to reduce the size of the solar system so that we can represent it using a roll of toilet paper. If you thought the Earth was a long way from the Sun, you may be surprised at how far we go to reach the outer planets. Mercury: about 0.4 ...
... Mercury is the closest and Neptune is the farthest. We are going to reduce the size of the solar system so that we can represent it using a roll of toilet paper. If you thought the Earth was a long way from the Sun, you may be surprised at how far we go to reach the outer planets. Mercury: about 0.4 ...
The Milky Way
... The Solar System is also home to a number of regions populated by smaller objects. The asteroid belt, which lies between Mars and Jupiter, is similar to the terrestrial planets as it is composed mainly of rock and metal. Beyond Neptune's orbit lie the Kuiper belt and scattered disc; linked populati ...
... The Solar System is also home to a number of regions populated by smaller objects. The asteroid belt, which lies between Mars and Jupiter, is similar to the terrestrial planets as it is composed mainly of rock and metal. Beyond Neptune's orbit lie the Kuiper belt and scattered disc; linked populati ...
Chapter 16: The Origin of the Solar System RQ 16
... solids. At these inner orbits, material with lower boiling points (lighter elements) could not be collected, since it still was in its gaseous state. This way the inner planets selectively were made out of heavy elements and thus have now high densities. At greater distance from the center, matter l ...
... solids. At these inner orbits, material with lower boiling points (lighter elements) could not be collected, since it still was in its gaseous state. This way the inner planets selectively were made out of heavy elements and thus have now high densities. At greater distance from the center, matter l ...
Orrery

An orrery is a mechanical model of the solar system that illustrates or predicts the relative positions and motions of the planets and moons, usually according to the heliocentric model. It may also represent the relative sizes of these bodies; but since accurate scaling is often not practical due to the actual large ratio differences, a subdued approximation may be used instead. Though the Greeks had working planetaria, the first orrery that was a planetarium of the modern era was produced in 1704, and one was presented to Charles Boyle, 4th Earl of Orrery — whence came the name. They are typically driven by a clockwork mechanism with a globe representing the Sun at the centre, and with a planet at the end of each of the arms.