The most important questions to study for the exam
... 9. When a planet is at conjunction, it will • be at the farthest position from the Sun in the sky, as seen from the Earth. • rise as the Sun is setting. • set at the same time as the Sun. 10. When a planet is at superior conjunction, • the planet is between the Earth and the Sun. • the Earth is betw ...
... 9. When a planet is at conjunction, it will • be at the farthest position from the Sun in the sky, as seen from the Earth. • rise as the Sun is setting. • set at the same time as the Sun. 10. When a planet is at superior conjunction, • the planet is between the Earth and the Sun. • the Earth is betw ...
Planetarium Lab 1
... 2. What is the direction, roughly eastward or westward, for direct and retrograde motions? Answer this question below by filling in the two blanks: • Direct motion is ___eastward___________ against the background of fixed stars. • Retrograde motion is ___westward___________ against the background of ...
... 2. What is the direction, roughly eastward or westward, for direct and retrograde motions? Answer this question below by filling in the two blanks: • Direct motion is ___eastward___________ against the background of fixed stars. • Retrograde motion is ___westward___________ against the background of ...
I. Comparing the Sizes of the Sun, Earth, Moon and Jupiter
... II. Comparing Earth size to other Universe Components When examining universe components and their sizes, scientists use the Earth size as a frame of reference instead of the sun due to its enormous size. Scientists question how many times bigger or smaller is a given object in space when compared t ...
... II. Comparing Earth size to other Universe Components When examining universe components and their sizes, scientists use the Earth size as a frame of reference instead of the sun due to its enormous size. Scientists question how many times bigger or smaller is a given object in space when compared t ...
Chapter 27 Quiz Name
... G The orbit of Mars is outside that of the Earth’s orbit. _ H Mars is too small to be seen against the backdrop of the sun. J Mars shines too brightly to be visible against the sun. ...
... G The orbit of Mars is outside that of the Earth’s orbit. _ H Mars is too small to be seen against the backdrop of the sun. J Mars shines too brightly to be visible against the sun. ...
Our Solar System - superscientists5456
... 23 hours and 56 min=1 Earth day (rotation) 365 days =1 Earth year (revolution) Axis tilted 23.5 degrees (causes seasons) Earth is warm enough to keep most of its water from freezing and cold enough to keep it’s water from boiling • Temperature is between –13 degrees Celsius and 37 degrees Celsius • ...
... 23 hours and 56 min=1 Earth day (rotation) 365 days =1 Earth year (revolution) Axis tilted 23.5 degrees (causes seasons) Earth is warm enough to keep most of its water from freezing and cold enough to keep it’s water from boiling • Temperature is between –13 degrees Celsius and 37 degrees Celsius • ...
solar eclipse
... Friday 20th March 2015 Solar and Lunar Eclipses WALT: To explain how eclipses happen To describe the different types of solar eclipse To look at ancient explanations of eclipses ...
... Friday 20th March 2015 Solar and Lunar Eclipses WALT: To explain how eclipses happen To describe the different types of solar eclipse To look at ancient explanations of eclipses ...
The Passage of Time Moon, Moonth, Month Sidereal (Star) Time
... the solar day. You will need to show the motion of the Earth/where it is in its orbit for • (1) when a star crosses the meridian to the next crossing • (2) when the sun crosses the meridian to the next crossing ...
... the solar day. You will need to show the motion of the Earth/where it is in its orbit for • (1) when a star crosses the meridian to the next crossing • (2) when the sun crosses the meridian to the next crossing ...
HELP
... Copy and complete the sentences below, using the names of the objects. You must use all the names. a Some objects are non-luminous. Examples are ... They are non-luminous because ... b Other objects are luminous. Examples are ... They are luminous because ... 2 When the Moon is in the sky at night i ...
... Copy and complete the sentences below, using the names of the objects. You must use all the names. a Some objects are non-luminous. Examples are ... They are non-luminous because ... b Other objects are luminous. Examples are ... They are luminous because ... 2 When the Moon is in the sky at night i ...
Our local neighbourhood – The Solar System (PPT file, 6.12 MB)
... Venus is a similar size to the Earth. It atmosphere is mainly Carbon dioxide and Nitrogen. Its very hot there due to the ‘Green house effect’ a whopping 462C. ...
... Venus is a similar size to the Earth. It atmosphere is mainly Carbon dioxide and Nitrogen. Its very hot there due to the ‘Green house effect’ a whopping 462C. ...
What Makes Up Our Solar System
... steady state. One sixth of an estimated six trillion icy objects or comets are in the outer region with the remainder in the relatively dense core. The Oort cloud is the source of long-period comets and possibly higher-inclination intermediate comets that were pulled into shorter period orbits by th ...
... steady state. One sixth of an estimated six trillion icy objects or comets are in the outer region with the remainder in the relatively dense core. The Oort cloud is the source of long-period comets and possibly higher-inclination intermediate comets that were pulled into shorter period orbits by th ...
Homework # 2 1. For each of the following, make a sketch showing
... 3. Page 74 #16. Two Kinds of Planets. In words a friend would understand, explain why the jovian planets differ from the terrestrial planets in each of the following aspects: composition, size, density, distance from the Sun, and number of moons. The nebular theory of the formation of the solar syst ...
... 3. Page 74 #16. Two Kinds of Planets. In words a friend would understand, explain why the jovian planets differ from the terrestrial planets in each of the following aspects: composition, size, density, distance from the Sun, and number of moons. The nebular theory of the formation of the solar syst ...
Quiz on Solar System study guide with key
... 11. This planet has surface temperatures of 460 ˚C due to an extreme greenhouse effect and has a surface pressure 90 times greater than Earth’s. 12. This planet’s axis is tilted about 90˚ so it looks like it is on its side and was the first new planet to be discovered since ancient times. 13. This p ...
... 11. This planet has surface temperatures of 460 ˚C due to an extreme greenhouse effect and has a surface pressure 90 times greater than Earth’s. 12. This planet’s axis is tilted about 90˚ so it looks like it is on its side and was the first new planet to be discovered since ancient times. 13. This p ...
Kepler`s Laws - Harnett County High Schools Wiki
... 1543 Polish scientist Nicolaus Copernicus suggested Sun was center of solar system First time a sun-centered or “heliocentric” model was proposed In a heliocentric model, the inner planets move faster in their orbits than the outer planets do; as Earth bypasses a slower moving outer planet it appear ...
... 1543 Polish scientist Nicolaus Copernicus suggested Sun was center of solar system First time a sun-centered or “heliocentric” model was proposed In a heliocentric model, the inner planets move faster in their orbits than the outer planets do; as Earth bypasses a slower moving outer planet it appear ...
Chart_set_4
... Solar system formed out of a "whirlpool" in a "universal fluid". Planets formed out of eddies in the fluid. Sun formed at center. Planets in cooler regions. Cloud called "Solar Nebula". This is pre-Newton and modern science. But basic idea correct, and the theory evolved as science advanced, as we'l ...
... Solar system formed out of a "whirlpool" in a "universal fluid". Planets formed out of eddies in the fluid. Sun formed at center. Planets in cooler regions. Cloud called "Solar Nebula". This is pre-Newton and modern science. But basic idea correct, and the theory evolved as science advanced, as we'l ...
Solar system
... compare your results to the actual density. Volume of a sphere = 4/3πr3 (1000 m)3 = (1 km)3 2) Use your density to determine what your planet is made of. Ice = ~1000 kg/m3; Gases < ...
... compare your results to the actual density. Volume of a sphere = 4/3πr3 (1000 m)3 = (1 km)3 2) Use your density to determine what your planet is made of. Ice = ~1000 kg/m3; Gases < ...
PHYS 390 Lecture 6 - A tour of the planets 6 - 1 Lecture 6
... Jupiter’s, a mass of 0.7 Jupiter’s (density = 300-500 kg/m3) but an orbital radius of 0.047 AU, astonishingly small. The mass distribution is (2008 data from http://exoplanet.eu) 0 - 2 Jupiter masses: 63% 2 - 4 Jupiter masses: 17% 4 - 6 Jupiter masses: 7% Issues: • The conventional model of our sola ...
... Jupiter’s, a mass of 0.7 Jupiter’s (density = 300-500 kg/m3) but an orbital radius of 0.047 AU, astonishingly small. The mass distribution is (2008 data from http://exoplanet.eu) 0 - 2 Jupiter masses: 63% 2 - 4 Jupiter masses: 17% 4 - 6 Jupiter masses: 7% Issues: • The conventional model of our sola ...
Astronomy
... because of the type and temperature of the gases and the escape velocity from the planet or moon. The velocity of a gas molecule depends on its mass according to the MaxwellBoltzmann distribution. The distribution has a a very long tail. Heavier molecules like O2, H2O, N2 have less of a tail than He ...
... because of the type and temperature of the gases and the escape velocity from the planet or moon. The velocity of a gas molecule depends on its mass according to the MaxwellBoltzmann distribution. The distribution has a a very long tail. Heavier molecules like O2, H2O, N2 have less of a tail than He ...
Gas Giant Sun-Catcher - Lunar and Planetary Institute
... the planets on the Gas Giant template. Use double-sided tape to attach one square’s clear (non-sticky) side to the planet on the template, and remove the backing from the contact paper. Place the pieces of different colors of tissue paper onto the adhesive side of the contact paper so that the tissu ...
... the planets on the Gas Giant template. Use double-sided tape to attach one square’s clear (non-sticky) side to the planet on the template, and remove the backing from the contact paper. Place the pieces of different colors of tissue paper onto the adhesive side of the contact paper so that the tissu ...
7.1 Space Flight to the Stars
... cosmology, astrophysics, celestial mechanics, planetary science, etc. -These sub disciplines are studied to give humans a specific look at certain parts of the universe and its properties. ...
... cosmology, astrophysics, celestial mechanics, planetary science, etc. -These sub disciplines are studied to give humans a specific look at certain parts of the universe and its properties. ...
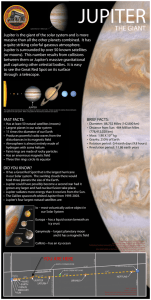
jupiter interpretive sign - Town of Cumberland, Indiana
... JUPITER The image above illustrates the size of each planet in relation to each other. It does not give the relative distance between each planet in the solar system. Refer to map below for the distances between each planet. ...
... JUPITER The image above illustrates the size of each planet in relation to each other. It does not give the relative distance between each planet in the solar system. Refer to map below for the distances between each planet. ...
Orrery

An orrery is a mechanical model of the solar system that illustrates or predicts the relative positions and motions of the planets and moons, usually according to the heliocentric model. It may also represent the relative sizes of these bodies; but since accurate scaling is often not practical due to the actual large ratio differences, a subdued approximation may be used instead. Though the Greeks had working planetaria, the first orrery that was a planetarium of the modern era was produced in 1704, and one was presented to Charles Boyle, 4th Earl of Orrery — whence came the name. They are typically driven by a clockwork mechanism with a globe representing the Sun at the centre, and with a planet at the end of each of the arms.