Risk And Return - Thunderbird Trust
... Interest rates affect the price of most fixed income securities, especially bonds Interest rates (yields) go up and down, depending on what is happening in the economy; generally the better the economy, the higher the interest rate ...
... Interest rates affect the price of most fixed income securities, especially bonds Interest rates (yields) go up and down, depending on what is happening in the economy; generally the better the economy, the higher the interest rate ...
Week10.2 Stocks - B-K
... P/E – Price/earnings ratio = price / EPS – The higher the P/E, the more the market thinks the company’s profits will grow ...
... P/E – Price/earnings ratio = price / EPS – The higher the P/E, the more the market thinks the company’s profits will grow ...
CHAPTER 5 ANSWERS TO "DO YOU UNDERSTAND?" TEXT
... 1. When a bond’s coupon rate is less than the prevailing market rate on interest on similar bonds, will the bond sell at par, a discount, or a premium? Explain. Answer: The bond will sell at a discount because buyers in the secondary market will bid the price down until the bond yields the market ra ...
... 1. When a bond’s coupon rate is less than the prevailing market rate on interest on similar bonds, will the bond sell at par, a discount, or a premium? Explain. Answer: The bond will sell at a discount because buyers in the secondary market will bid the price down until the bond yields the market ra ...
Sample Questions - U of L Class Index
... 36- Dividend reinvestment plans: a. enable investors to earn money market rates on their dividend income. b. enable investors to directly purchase shares from corporations, thereby eliminating brokerage commissions. c. are provided by full-service brokerage houses only. d. are provided by corporatio ...
... 36- Dividend reinvestment plans: a. enable investors to earn money market rates on their dividend income. b. enable investors to directly purchase shares from corporations, thereby eliminating brokerage commissions. c. are provided by full-service brokerage houses only. d. are provided by corporatio ...
Emerging Market Carry Trades - FMT-HANU
... • Both central banks, in an effort to maintain high levels of liquidity and support fragile commercial banking systems, have kept interest rates at near-zero levels. • Now global investors, those who see opportunities for profit in an anemic global economy, are using those same low-cost funds in the ...
... • Both central banks, in an effort to maintain high levels of liquidity and support fragile commercial banking systems, have kept interest rates at near-zero levels. • Now global investors, those who see opportunities for profit in an anemic global economy, are using those same low-cost funds in the ...
Chapter 5
... purchase price for securities Margin account: Investor borrows part of the purchase price from the broker ...
... purchase price for securities Margin account: Investor borrows part of the purchase price from the broker ...
Chapter1
... *If Ingrid at Chase posts a quote of 125.00-.10 and is called by Taka at Sumitomo who wants to “hit her ask” and have her buy his yen for her dollars, she may wonder if Taka knows something she doesn’t *what private information could Taka have? order flow his bank receives from customers early infor ...
... *If Ingrid at Chase posts a quote of 125.00-.10 and is called by Taka at Sumitomo who wants to “hit her ask” and have her buy his yen for her dollars, she may wonder if Taka knows something she doesn’t *what private information could Taka have? order flow his bank receives from customers early infor ...
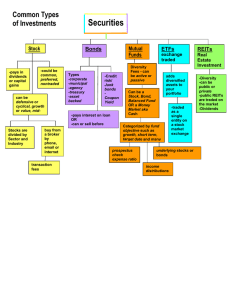
Securities
... Types of stock include Market Capitalization (indicates the size of a company, small-cap is less than one billion, mid-cap is one to 5 billion, large-cap-over is over 5 billion), Defensive (stocks with a stable demand such as groceries, health care or electricity), Cyclical (less stable, often fluct ...
... Types of stock include Market Capitalization (indicates the size of a company, small-cap is less than one billion, mid-cap is one to 5 billion, large-cap-over is over 5 billion), Defensive (stocks with a stable demand such as groceries, health care or electricity), Cyclical (less stable, often fluct ...
Chris Diaz Commentary - Snowden Lane Partners
... fruit. We believe debt lower in the capital structure of these firms is attractive as deleveraging remains a top priority ahead of the European stress tests later this fall. Meanwhile, we favor select names in Europe’s automotive industry as they could continue to register improvement in the euro zo ...
... fruit. We believe debt lower in the capital structure of these firms is attractive as deleveraging remains a top priority ahead of the European stress tests later this fall. Meanwhile, we favor select names in Europe’s automotive industry as they could continue to register improvement in the euro zo ...
rainbow trading corporation spyglass trading. lp
... • Event risks, e.g. mergers or crises • Substantial directional moved based on skewed market psychology • Lost profit when directional bias is correct • Potential loss in any given position can significantly exceed potential gain • Highly intense, requires constant monitoring, and may generate highe ...
... • Event risks, e.g. mergers or crises • Substantial directional moved based on skewed market psychology • Lost profit when directional bias is correct • Potential loss in any given position can significantly exceed potential gain • Highly intense, requires constant monitoring, and may generate highe ...
Ch. 15: Financial Markets
... maturity value will be paid to the bond holder. Bond maturity dates when issued generally range from 3 months up to 30 years. Coupon rate • Between the date of issuance and the maturity date, the bond-holder receives an annual interest payment equal to the coupon rate times the maturity value. Yield ...
... maturity value will be paid to the bond holder. Bond maturity dates when issued generally range from 3 months up to 30 years. Coupon rate • Between the date of issuance and the maturity date, the bond-holder receives an annual interest payment equal to the coupon rate times the maturity value. Yield ...
Government Securities
... Government securities for financing the internal deficit: o Treasury Bills with maturity within one year o Treasury Bills with maturity within 5 years o Treasury Bonds with maturity of 5 years or more Government bonds for financing structural deficits in the financial sector: o ZUNK bonds (long term ...
... Government securities for financing the internal deficit: o Treasury Bills with maturity within one year o Treasury Bills with maturity within 5 years o Treasury Bonds with maturity of 5 years or more Government bonds for financing structural deficits in the financial sector: o ZUNK bonds (long term ...
What if Interest Rates Rise and Nobody Does Anything?
... After more than six years of keeping the fed funds rate near zero, most experts agree: The Federal Reserve will soon raise interest rates. Why? Because interest rates are one of the Fed’s best tools for accomplishing its main goals: Full employment and price stability. Low interest rates encourage p ...
... After more than six years of keeping the fed funds rate near zero, most experts agree: The Federal Reserve will soon raise interest rates. Why? Because interest rates are one of the Fed’s best tools for accomplishing its main goals: Full employment and price stability. Low interest rates encourage p ...
Chapter 11 Securities Markets
... “Buying on margin” means to use some of your money (equity) and some borrowed funds to purchase a security Margin: investor’s equity position Margin requirements: minimum percentage of the purchase price that the investor must pay from his/her funds ...
... “Buying on margin” means to use some of your money (equity) and some borrowed funds to purchase a security Margin: investor’s equity position Margin requirements: minimum percentage of the purchase price that the investor must pay from his/her funds ...