III. High Power Density
... research activities in improving the efficiency of high power bi-directional chopper circuits. C-Bridge switch shown in Figure 2(a) was proposed in [19] for high power application (8 kW) and 96.0 % efficiency at 25 kHz was obtained. Later on, Quasiresonant Regenerating Active Snubber (QRAS) was prop ...
... research activities in improving the efficiency of high power bi-directional chopper circuits. C-Bridge switch shown in Figure 2(a) was proposed in [19] for high power application (8 kW) and 96.0 % efficiency at 25 kHz was obtained. Later on, Quasiresonant Regenerating Active Snubber (QRAS) was prop ...
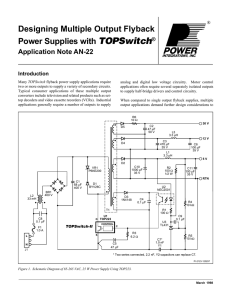
Power Supplies with TOPSwitch - Power Integrations - AC
... Table 1 gives an outline specification for a 25 W power supply with three outputs. Note that the 5 V output has the highest current and the tightest regulation, but the 12 V output delivers the highest power. The techniques presented here can be extended to any number of outputs. Some specific consi ...
... Table 1 gives an outline specification for a 25 W power supply with three outputs. Note that the 5 V output has the highest current and the tightest regulation, but the 12 V output delivers the highest power. The techniques presented here can be extended to any number of outputs. Some specific consi ...
ADG719 数据手册DataSheet下载
... switch on resistance is small, this zero usually occurs at high frequencies. The bandwidth is a function of the switch output capacitance combined with CDS and the load capacitance. The frequency pole corresponding to these capacitances appears in the denominator of A(s). ...
... switch on resistance is small, this zero usually occurs at high frequencies. The bandwidth is a function of the switch output capacitance combined with CDS and the load capacitance. The frequency pole corresponding to these capacitances appears in the denominator of A(s). ...
Application Note for an LLC Resonant Converter Using
... switch turns off at time t0 and the resonant current firstly discharges the parasitic capacitor and then flows through the body diode of S1. The output rectifier diode, D1, continues to deliver energy to the load. Cr and Lr resonate because the voltage across Lm is clamped at the reflected output vo ...
... switch turns off at time t0 and the resonant current firstly discharges the parasitic capacitor and then flows through the body diode of S1. The output rectifier diode, D1, continues to deliver energy to the load. Cr and Lr resonate because the voltage across Lm is clamped at the reflected output vo ...
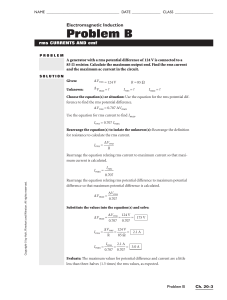
Problem B - Geneva Area City Schools
... 9. A wind turbine is built to service farmers in England. The turbine is connected to a generator, which can supply a rms current of 1.3 A on a 12 kΩ load. If the rms potential difference is 15.6 kV, find the maximum output emf provided by the wind turbine. Calculate the maximum ac current. How much ...
... 9. A wind turbine is built to service farmers in England. The turbine is connected to a generator, which can supply a rms current of 1.3 A on a 12 kΩ load. If the rms potential difference is 15.6 kV, find the maximum output emf provided by the wind turbine. Calculate the maximum ac current. How much ...
extending lifetime on t5 fluorescent lamp using an electronic ballast
... of the coating is eroded from the electrodes each time the lamp is started, additional evaporation and erosion also occurs during lamp operation. Electrode temperature directly affects the evaporation and erosion of the emitting material, and so affects lamp life. Because electrode temperature is di ...
... of the coating is eroded from the electrodes each time the lamp is started, additional evaporation and erosion also occurs during lamp operation. Electrode temperature directly affects the evaporation and erosion of the emitting material, and so affects lamp life. Because electrode temperature is di ...
Electrical Surge-Protection Devices for Industrial
... Electrical surges have been studied since the 1960s [1]; however, during the last decade, the issue of surge protection for electronic equipment is receiving more attention. Semiconductor integrated circuits are much more vulnerable to failure by overstresses compared to earlier electronic circuits. ...
... Electrical surges have been studied since the 1960s [1]; however, during the last decade, the issue of surge protection for electronic equipment is receiving more attention. Semiconductor integrated circuits are much more vulnerable to failure by overstresses compared to earlier electronic circuits. ...
Transponder power supply, a transponder and a method for
... age of the transponder input signal 102 may be limited to 5 V. However it has been found that medium voltage capacitors may be typically charged up to about 7 V. Therefore the charging circuit 104 may charge the emergency capacitor 105 to 7 V, even if the maximum voltage of the antenna input signal ...
... age of the transponder input signal 102 may be limited to 5 V. However it has been found that medium voltage capacitors may be typically charged up to about 7 V. Therefore the charging circuit 104 may charge the emergency capacitor 105 to 7 V, even if the maximum voltage of the antenna input signal ...
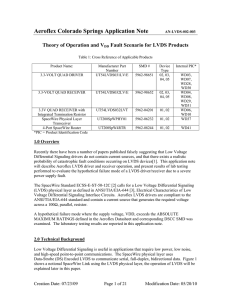
Theory of Operation and VDD Fault Scenario
... using LVDS is the resulting low power consumption. An example of LVDS power can be easily calculated using P=I*V where P = Power, V = Voltage, and I = Current. PowerLVDS=3.5mA * 350mV = 1.225mW at any frequency and loading. As compared to a single ended CMOS signal is very dependant upon loading cap ...
... using LVDS is the resulting low power consumption. An example of LVDS power can be easily calculated using P=I*V where P = Power, V = Voltage, and I = Current. PowerLVDS=3.5mA * 350mV = 1.225mW at any frequency and loading. As compared to a single ended CMOS signal is very dependant upon loading cap ...
AN10721 Logic level VGS ratings for NXP power MOSFETs
... gate bias life testing can be performed at a value of 100 % of the absolute maximum rating. However, there are some instances where this is not possible. When logic level devices were first introduced they were designed to interface directly to 5 V logic. The devices were designed so that a guarante ...
... gate bias life testing can be performed at a value of 100 % of the absolute maximum rating. However, there are some instances where this is not possible. When logic level devices were first introduced they were designed to interface directly to 5 V logic. The devices were designed so that a guarante ...
GE 0106 Basic Engineering II
... The voltage across an element is denoted as E or V. The current through the element is I. Conductor is used to carry current. When a voltage is applied across a conductor, current flows through the conductor. If the applied voltage is increased, the current also increases. The voltage current relati ...
... The voltage across an element is denoted as E or V. The current through the element is I. Conductor is used to carry current. When a voltage is applied across a conductor, current flows through the conductor. If the applied voltage is increased, the current also increases. The voltage current relati ...
PTC Thermistor (POSISTOR®)
... The POSISTOR® can be used as a constant temperature heater with an automatic temperature adjustment function and can maintain constant wattage, even over voltage fluctuation, if the current through the POSISTOR is maintained above its maximum current point. The POSISTOR can provide over-current prot ...
... The POSISTOR® can be used as a constant temperature heater with an automatic temperature adjustment function and can maintain constant wattage, even over voltage fluctuation, if the current through the POSISTOR is maintained above its maximum current point. The POSISTOR can provide over-current prot ...
Landscape Lighting PowerPoint
... composed of three basic parts: the power pack, the electric cables, and the fixtures. – When designing a low voltage lighting system, it is important that the proper size cable is used (usually 10 or 12 gauge). – Always choose the least number of lights to achieve the desired lighting effect. Too ma ...
... composed of three basic parts: the power pack, the electric cables, and the fixtures. – When designing a low voltage lighting system, it is important that the proper size cable is used (usually 10 or 12 gauge). – Always choose the least number of lights to achieve the desired lighting effect. Too ma ...
Rectifier

A rectifier is an electrical device that converts alternating current (AC), which periodically reverses direction, to direct current (DC), which flows in only one direction. The process is known as rectification. Physically, rectifiers take a number of forms, including vacuum tube diodes, mercury-arc valves, copper and selenium oxide rectifiers, semiconductor diodes, silicon-controlled rectifiers and other silicon-based semiconductor switches. Historically, even synchronous electromechanical switches and motors have been used. Early radio receivers, called crystal radios, used a ""cat's whisker"" of fine wire pressing on a crystal of galena (lead sulfide) to serve as a point-contact rectifier or ""crystal detector"".Rectifiers have many uses, but are often found serving as components of DC power supplies and high-voltage direct current power transmission systems. Rectification may serve in roles other than to generate direct current for use as a source of power. As noted, detectors of radio signals serve as rectifiers. In gas heating systems flame rectification is used to detect presence of a flame.Because of the alternating nature of the input AC sine wave, the process of rectification alone produces a DC current that, though unidirectional, consists of pulses of current. Many applications of rectifiers, such as power supplies for radio, television and computer equipment, require a steady constant DC current (as would be produced by a battery). In these applications the output of the rectifier is smoothed by an electronic filter (usually a capacitor) to produce a steady current.More complex circuitry that performs the opposite function, converting DC to AC, is called an inverter.