Controlling the genes
... Across the board • Bacterial cells exhibit control of gene expression - not all the enzymes needed for metabolism are expressed at all times - just those for the nutrients present in the environment at that time • Multicellular organisms exhibit even more elaborate gene expression - we have brain c ...
... Across the board • Bacterial cells exhibit control of gene expression - not all the enzymes needed for metabolism are expressed at all times - just those for the nutrients present in the environment at that time • Multicellular organisms exhibit even more elaborate gene expression - we have brain c ...
The entire human genome consists of 23 pairs of chromosomes
... healthy individuals with a database that reveals which genetic elements are active during prenatal brain development. They used this to identify a set of exons that are highly expressed in the brain but rarely vary from person to person. MUTATION RATE HIGH ...
... healthy individuals with a database that reveals which genetic elements are active during prenatal brain development. They used this to identify a set of exons that are highly expressed in the brain but rarely vary from person to person. MUTATION RATE HIGH ...
Παρουσίαση του PowerPoint
... We have previously analyzed the gene expression profile in urinary bladder cancer and determined the differentially expressed (DE) genes between cancer and healthy tissue. It is reasonable to assume that genes with similar expression profiles are regulated by the same set of transcription factors. I ...
... We have previously analyzed the gene expression profile in urinary bladder cancer and determined the differentially expressed (DE) genes between cancer and healthy tissue. It is reasonable to assume that genes with similar expression profiles are regulated by the same set of transcription factors. I ...
Biologic
... identical form). Here is one difference that might produce a genetic drive: closely related genes may operate in a different way to produce different outcomes as a result of this type of change. However, perhaps more significant, in one major respect, is that some genes have altered their function a ...
... identical form). Here is one difference that might produce a genetic drive: closely related genes may operate in a different way to produce different outcomes as a result of this type of change. However, perhaps more significant, in one major respect, is that some genes have altered their function a ...
punnett square guidelines
... Phenotype: refers to the appearance/what the offspring looks like. EX: Black hair is dominant. A purebred black haired cat is crossed with a hybrid male who also carries a gene for white hair. ...
... Phenotype: refers to the appearance/what the offspring looks like. EX: Black hair is dominant. A purebred black haired cat is crossed with a hybrid male who also carries a gene for white hair. ...
Document
... Nondisjunction of sex chromosomes produces a variety of aneuploid conditions Klinefelter syndrome is the result of an extra chromosome in a male, producing ______ individuals The most common symptom is infertility. Other symptoms may include: o Abnormal body proportions (long legs, short trunk ...
... Nondisjunction of sex chromosomes produces a variety of aneuploid conditions Klinefelter syndrome is the result of an extra chromosome in a male, producing ______ individuals The most common symptom is infertility. Other symptoms may include: o Abnormal body proportions (long legs, short trunk ...
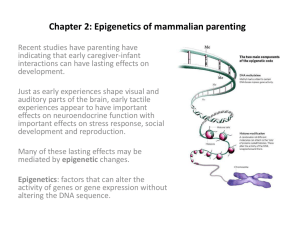
Chapter 2: Epigenetics of mammalian parenting
... auditory parts of the brain, early tactile experiences appear to have important effects on neuroendocrine function with important effects on stress response, social development and reproduction. Many of these lasting effects may be mediated by epigenetic changes. Epigenetics: factors that can alter ...
... auditory parts of the brain, early tactile experiences appear to have important effects on neuroendocrine function with important effects on stress response, social development and reproduction. Many of these lasting effects may be mediated by epigenetic changes. Epigenetics: factors that can alter ...
MENDEL Fundamentals of Genetics _1_
... Example: Tallness vs. Shortness T = tall gene t = short gene ...
... Example: Tallness vs. Shortness T = tall gene t = short gene ...
(part of a “developmental reprogramming”). The roots of evolutionary
... As in Drosophila, they act along the developing embryo in the same sequence that they occupy on the chromosome. All the genes in the mammalian Hox clusters show some sequence homology to each other (especially in their homeobox) but very strong sequence homology to the equivalent genes in Drosophila ...
... As in Drosophila, they act along the developing embryo in the same sequence that they occupy on the chromosome. All the genes in the mammalian Hox clusters show some sequence homology to each other (especially in their homeobox) but very strong sequence homology to the equivalent genes in Drosophila ...
Genome Annotation - Virginia Commonwealth University
... Placing the genes on the genome (where are they?) ...
... Placing the genes on the genome (where are they?) ...
CH-14 Sect 14
... Match the labels to the parts of the pedigree chart shown below. Some of the parts of the pedigree chart may be used more than once. ...
... Match the labels to the parts of the pedigree chart shown below. Some of the parts of the pedigree chart may be used more than once. ...
The Genetic Basis of Development
... animals: movements of cells & tissues are necessary for transformation plants: morphogenesis & growth are not limited to embryonic and juvenile periods because they have perpetually embryonic regions called apical meristems ...
... animals: movements of cells & tissues are necessary for transformation plants: morphogenesis & growth are not limited to embryonic and juvenile periods because they have perpetually embryonic regions called apical meristems ...
Ch. 13 Meiosis
... organism’s inherited traits. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... organism’s inherited traits. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Nuclear genome 1
... • Using transposon mutagenesis, ~150 of the 517 genes could be knocked out; ~ 300 genes deemed essential (under lab conditions), which included: – ~100 of unknown function – Genes for glycolysis & ATP synthesis – ABC transporters – Genes for DNA replication, transcription and translation ...
... • Using transposon mutagenesis, ~150 of the 517 genes could be knocked out; ~ 300 genes deemed essential (under lab conditions), which included: – ~100 of unknown function – Genes for glycolysis & ATP synthesis – ABC transporters – Genes for DNA replication, transcription and translation ...
Notes The Work of Gregor Mendel Mendel studied 7 different pea
... Mendel studied 7 different pea plant traits. A trait is a characteristic that varies from one individual to the next, i.e. plant height. Each trait had 2 contrasting forms, i.e. tall or short. Today, scientists call the chemical factors that determine traits genes. The different forms of the gene ar ...
... Mendel studied 7 different pea plant traits. A trait is a characteristic that varies from one individual to the next, i.e. plant height. Each trait had 2 contrasting forms, i.e. tall or short. Today, scientists call the chemical factors that determine traits genes. The different forms of the gene ar ...
Genetic Disorders in Culture and Art
... Many different model organisms have been used ranging from bacteria to plants to insects to humans. We will discuss how scientists study genes in each chapter of this course and so a discussion of this ...
... Many different model organisms have been used ranging from bacteria to plants to insects to humans. We will discuss how scientists study genes in each chapter of this course and so a discussion of this ...
A Perspective on Human Genetics
... Many different model organisms have been used ranging from bacteria to plants to insects to humans. We will discuss how scientists study genes in each chapter of this course and so a discussion of this ...
... Many different model organisms have been used ranging from bacteria to plants to insects to humans. We will discuss how scientists study genes in each chapter of this course and so a discussion of this ...
word - The Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology at
... observed in lions and in some primates. A male may kill infants that he did not father, providing him the opportunity to essentially substitute his own genes (or at least half of his own genes) by mating with the mother of the infant. This behavior would appear to be detrimental to the group (and pr ...
... observed in lions and in some primates. A male may kill infants that he did not father, providing him the opportunity to essentially substitute his own genes (or at least half of his own genes) by mating with the mother of the infant. This behavior would appear to be detrimental to the group (and pr ...
genes - Brookwood High School
... a. self-pollinators meaning inherit all characteristics from the original plant or identical: true-breeding. ...
... a. self-pollinators meaning inherit all characteristics from the original plant or identical: true-breeding. ...
Notes - marric
... Why Does Crossing Over Occur? To provide genetic variation during meiosis Its Why You and I Don’t Look Alike Crossing Over ensures a ____________________ of the maternal and paternal genes we inherited The History of Crossing Over ...
... Why Does Crossing Over Occur? To provide genetic variation during meiosis Its Why You and I Don’t Look Alike Crossing Over ensures a ____________________ of the maternal and paternal genes we inherited The History of Crossing Over ...
Identification of func
... With ~10 million single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) occurring at >1% in humans, identifying the functionally important SNP can be likened to “finding a needle in a haystack”. It is thus not practical to investigate every SNP for their functionality or disease/drug response association. Our appro ...
... With ~10 million single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) occurring at >1% in humans, identifying the functionally important SNP can be likened to “finding a needle in a haystack”. It is thus not practical to investigate every SNP for their functionality or disease/drug response association. Our appro ...