Chapter 24 Genetics and Genomics Genotype and
... • each son with one recessive allele will have the disease • each son has no allele on the Y chromosome to mask the recessive allele • each daughter has a 50% chance of receiving the recessive allele from the ...
... • each son with one recessive allele will have the disease • each son has no allele on the Y chromosome to mask the recessive allele • each daughter has a 50% chance of receiving the recessive allele from the ...
Patterns of Inheritance
... • Gregor Mendel tried his hand at several pursuits, including health care and teaching. • He studied botany and mathematics among other subjects. This training proved crucial to his later experiments, which were the foundation for the modern science of genetics. ...
... • Gregor Mendel tried his hand at several pursuits, including health care and teaching. • He studied botany and mathematics among other subjects. This training proved crucial to his later experiments, which were the foundation for the modern science of genetics. ...
Exercise week 10, with answers File
... b. the lack of blood platelets in female mice lacking one copy of Gata1 c. targeted deletion of a hematopoietic cell-specific enhancer in the Gata1 regulatory region d. promoter bashing studies showing that a fragment of the Gata1 regulatory region can direct lacZ expression in megakaryocytes b) is ...
... b. the lack of blood platelets in female mice lacking one copy of Gata1 c. targeted deletion of a hematopoietic cell-specific enhancer in the Gata1 regulatory region d. promoter bashing studies showing that a fragment of the Gata1 regulatory region can direct lacZ expression in megakaryocytes b) is ...
No Slide Title
... and assortative mating) – Population is large (if appropriately chosen!) – No mutation (but there is) – No migration (but migration occurs) – No selection (but there can be selection) ...
... and assortative mating) – Population is large (if appropriately chosen!) – No mutation (but there is) – No migration (but migration occurs) – No selection (but there can be selection) ...
Lecture #6 Date ______ - Pomp
... be improperly grouped into codons that will likely produce a non- functional protein ...
... be improperly grouped into codons that will likely produce a non- functional protein ...
Active GE relation
... • Many behavioral genotypes reflect polygenic inheritance, which involves many genes • Behavioral geneticists rely upon twin studies and adoption studies • Cognitive abilities, psychological disorders, substance abuse, and personality are all affected by heredity ...
... • Many behavioral genotypes reflect polygenic inheritance, which involves many genes • Behavioral geneticists rely upon twin studies and adoption studies • Cognitive abilities, psychological disorders, substance abuse, and personality are all affected by heredity ...
probability and genetics
... - can be disrupted because of crossing over Recombination patterns - the closer the loci of two genes, the greater the tendency that they will be inherited together Human inheritance - difficult to study - why? - Pedigrees – chart that shows genetic connections among individuals - Analysis of family ...
... - can be disrupted because of crossing over Recombination patterns - the closer the loci of two genes, the greater the tendency that they will be inherited together Human inheritance - difficult to study - why? - Pedigrees – chart that shows genetic connections among individuals - Analysis of family ...
Genetics Quiz Study Guide
... Phenotype. The observable traits or properties of an organism. Refers to both genetic and non-genetic traits. Often used to refer to a single trait. For example: "My phenotype is hairy knuckles and my genotype is Hh." Population. A local group of individuals belonging to the same species, which are ...
... Phenotype. The observable traits or properties of an organism. Refers to both genetic and non-genetic traits. Often used to refer to a single trait. For example: "My phenotype is hairy knuckles and my genotype is Hh." Population. A local group of individuals belonging to the same species, which are ...
Dr Price 2nd lecture
... many times and often widely distributed over the genome. Eg. (AT)n, (GAT)n, ...
... many times and often widely distributed over the genome. Eg. (AT)n, (GAT)n, ...
Genetic Variation I
... mutations in DNA sequence. These forms are called alleles. Property of having different forms is called polymorphism • Normal human body cells (“somatic” cells) are diploid: 23 pairs of chromosomes: – Numbers 1-22 (autosomes) – X and Y (sex chromosomes) – XX in females, XY in males ...
... mutations in DNA sequence. These forms are called alleles. Property of having different forms is called polymorphism • Normal human body cells (“somatic” cells) are diploid: 23 pairs of chromosomes: – Numbers 1-22 (autosomes) – X and Y (sex chromosomes) – XX in females, XY in males ...
Pedigrees - Cloudfront.net
... Pedigrees are used to: – Determine whether a trait is inherited – Show how a trait is passed from one generation to the next – To determine if an allele is dominant or recessive ...
... Pedigrees are used to: – Determine whether a trait is inherited – Show how a trait is passed from one generation to the next – To determine if an allele is dominant or recessive ...
Document
... She first analyzed many octads with regard to their requirement for pyridoxine. Out of 246 octads, two of them had an aberrant ratio in which two spores were pdx-1 and six were pdx-1+. These same spores were then analyzed with regard to the other two genes. In both cases, the aberrant asci gave a no ...
... She first analyzed many octads with regard to their requirement for pyridoxine. Out of 246 octads, two of them had an aberrant ratio in which two spores were pdx-1 and six were pdx-1+. These same spores were then analyzed with regard to the other two genes. In both cases, the aberrant asci gave a no ...
Chapter 11 Notes
... o Each daughter cell contains half the number of chromosomes as the original cell Although they sound the same, meiosis and mitosis are different. Mitosis makes two identical cells. These cells are exactly like the parent cell. Meiosis, however, forms four cells. Each cell has only half the number o ...
... o Each daughter cell contains half the number of chromosomes as the original cell Although they sound the same, meiosis and mitosis are different. Mitosis makes two identical cells. These cells are exactly like the parent cell. Meiosis, however, forms four cells. Each cell has only half the number o ...
ch 15 chrom Genetics
... are far apart on the same chromosome should be separated more often than genes that are close together. Morgan was able to calculate mathematically how close or far apart each particular gene pair seemed to be based on the frequency of crossing over. map? ...
... are far apart on the same chromosome should be separated more often than genes that are close together. Morgan was able to calculate mathematically how close or far apart each particular gene pair seemed to be based on the frequency of crossing over. map? ...
EE150a – Genomic Signal and Information Processing
... • Genome is the part of DNA that encodes proteins: – …AACTCGCATCGAACTCTAAGTC… genetics.gsk.com/ graphics/dna-big.gif ...
... • Genome is the part of DNA that encodes proteins: – …AACTCGCATCGAACTCTAAGTC… genetics.gsk.com/ graphics/dna-big.gif ...
Pros Cons Man has been doing selective breeding since agriculture
... that nature could never do. This will pose unexpected consequences. GE makes use of pathogenic organisms such as viruses and bacteria as vectors of the gene that is being transferred. These pathogens could spread into the environment with unpredictable and dangerous consequences. GE is potentially d ...
... that nature could never do. This will pose unexpected consequences. GE makes use of pathogenic organisms such as viruses and bacteria as vectors of the gene that is being transferred. These pathogens could spread into the environment with unpredictable and dangerous consequences. GE is potentially d ...
Recitation 4 - MIT OpenCourseWare
... Meiosis has two divisions; meiosis 1 looks different from mitosis, but meiosis II looks similar to mitosis. The result of meiosis is the production of haploid gamete cells such as eggs or sperm, each of which has half the number of chromosomes as a diploid somatic cell. Recombination and crossing ov ...
... Meiosis has two divisions; meiosis 1 looks different from mitosis, but meiosis II looks similar to mitosis. The result of meiosis is the production of haploid gamete cells such as eggs or sperm, each of which has half the number of chromosomes as a diploid somatic cell. Recombination and crossing ov ...
The influence of genomic imprinting on brain
... placental growth, suckling, neonatal behavior, appetite, nutrient metabolism, and postnatal growth rate. They also predicted increased expression of maternal alleles at a second set of loci, important in tissue functioning but not resource acquisition, that would function to decrease the costs assoc ...
... placental growth, suckling, neonatal behavior, appetite, nutrient metabolism, and postnatal growth rate. They also predicted increased expression of maternal alleles at a second set of loci, important in tissue functioning but not resource acquisition, that would function to decrease the costs assoc ...
Biology 11.3 Genetic Engineering in Agriculture
... cloned calves were born in March 2001, only to die a month later from immune system failure. ...
... cloned calves were born in March 2001, only to die a month later from immune system failure. ...
Supplementary Information (docx 341K)
... the chromosome section, containing the banding patterns of the 6 Mb chromosome region surrounding the breakpoint (red arrowhead). The second row includes genes present in that section of the chromosome (green rectangles). The third row corresponds to predicted HI genes (red rectangles). The fourth r ...
... the chromosome section, containing the banding patterns of the 6 Mb chromosome region surrounding the breakpoint (red arrowhead). The second row includes genes present in that section of the chromosome (green rectangles). The third row corresponds to predicted HI genes (red rectangles). The fourth r ...
lecture24_RnaInterfe.. - University of Alberta
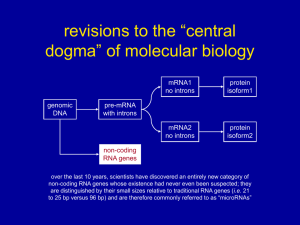
... revisions to the “central dogma” of molecular biology ...
... revisions to the “central dogma” of molecular biology ...