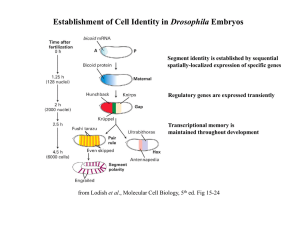
meiosis mitosis Independent orientation of chromosomes in meiosis
... Alternative versions of genes account for variations in inherited characters. ...
... Alternative versions of genes account for variations in inherited characters. ...
Human Genome PPT 2013
... Such disorders manifest only when an individual has got two defective alleles of the same gene, one from each parent. Ex: aa (Albinism, Cvstic fibrosis) Co-dominant alleles: Disorder manifested when two dominant alleles are inherited. Ex: AB (Sickle cell disease) Multi-factorial Genetic Disorders: ...
... Such disorders manifest only when an individual has got two defective alleles of the same gene, one from each parent. Ex: aa (Albinism, Cvstic fibrosis) Co-dominant alleles: Disorder manifested when two dominant alleles are inherited. Ex: AB (Sickle cell disease) Multi-factorial Genetic Disorders: ...
Microarray Data Analysis Normalization
... Gene Expression (TMT) Transcription Factor binding sites Cis-regulatory elements (CisReD) miRNAs (new) ...
... Gene Expression (TMT) Transcription Factor binding sites Cis-regulatory elements (CisReD) miRNAs (new) ...
chapter twelve INHERITANCE PATTERNS AND HUMAN GENETICS
... (sperm or eggs), through the process of MEIOSIS, that have either one or the other of the gene pair in it. ...
... (sperm or eggs), through the process of MEIOSIS, that have either one or the other of the gene pair in it. ...
Lecture_13_2005
... Identifying essential functions that are controlled by redundant genes. • Synthetic lethal screens • Synthetic lethal = when two mutations that are not essential for growth individually are essential when combined. • Done on a genome wide scale for yeast. ...
... Identifying essential functions that are controlled by redundant genes. • Synthetic lethal screens • Synthetic lethal = when two mutations that are not essential for growth individually are essential when combined. • Done on a genome wide scale for yeast. ...
The characterization of floral organ identity gene homologues in
... vesselless wood and lacks perianth, therefore for some time it has been suggested as the most primitive angiosperm. But according to detail morphology, anatomy and molecular phylogenetic analyses, it is widely accepted now that Trochodendron belongs to a more derived group in angiosperms, the basal ...
... vesselless wood and lacks perianth, therefore for some time it has been suggested as the most primitive angiosperm. But according to detail morphology, anatomy and molecular phylogenetic analyses, it is widely accepted now that Trochodendron belongs to a more derived group in angiosperms, the basal ...
Vector - Manhasset Public Schools
... salmon grew at about twice the rate. **It is more difficult to genetically modify animals than plants. ...
... salmon grew at about twice the rate. **It is more difficult to genetically modify animals than plants. ...
Lecture 3: More Transmission Genetics
... The diseased individuals are present in every generation (indicates a dominant disease) and males and females are both about equally affected (indicates autosomal inheritance) ...
... The diseased individuals are present in every generation (indicates a dominant disease) and males and females are both about equally affected (indicates autosomal inheritance) ...
Epigenetics-2015
... DNA Methylation Dynamics During Epigenetic Reprogramming Epigenetic memory must be erased for cells to achieve pleuripotency ...
... DNA Methylation Dynamics During Epigenetic Reprogramming Epigenetic memory must be erased for cells to achieve pleuripotency ...
Gene Maps
... Gene Maps…in other words • Knowing how often crossing over occurs between genes allows us to map positions of genes on chromosomes • Yes, crossing over is random…BUT the distance between two genes determines how often crossing over occurs • Frequency of crossing over: how often crossing over occurs ...
... Gene Maps…in other words • Knowing how often crossing over occurs between genes allows us to map positions of genes on chromosomes • Yes, crossing over is random…BUT the distance between two genes determines how often crossing over occurs • Frequency of crossing over: how often crossing over occurs ...
Inheritance and Adaptations
... pass traits to their offspring in one of the two ways: Asexual reproduction – it produces offspring who are identical to the original; passing of traits by cell division an mitosis ...
... pass traits to their offspring in one of the two ways: Asexual reproduction – it produces offspring who are identical to the original; passing of traits by cell division an mitosis ...
Chapter 5
... Use of cytologically marked chromosomes shows that crossing over involves breakage and reunion of chromosomes ...
... Use of cytologically marked chromosomes shows that crossing over involves breakage and reunion of chromosomes ...
Sex-Influenced Traits
... Genes that are carried on the sex chromosomes are the genes responsible for the sex linked traits. Most sex linked traits are determined by genes found on the X chromosome, not the Y chromosome. This is because the Y chromosome bears very few genes in comparison to the X chromosome which bears a nor ...
... Genes that are carried on the sex chromosomes are the genes responsible for the sex linked traits. Most sex linked traits are determined by genes found on the X chromosome, not the Y chromosome. This is because the Y chromosome bears very few genes in comparison to the X chromosome which bears a nor ...
Checklist unit 15: The Chromosomal Basis of Inheritance
... close proximity of each other (which will, more often than not, be sorted together). The latter are referred to as “linked genes.” Genes found on sex chromosomes have altered inheritance patterns because the paired sex chromosomes, XY, are not homologous in males (in mammals). This can lead to highe ...
... close proximity of each other (which will, more often than not, be sorted together). The latter are referred to as “linked genes.” Genes found on sex chromosomes have altered inheritance patterns because the paired sex chromosomes, XY, are not homologous in males (in mammals). This can lead to highe ...
Blue Biology Review Second Semester
... What is the difference between genotype and phenotype? What information does a pedigree provide? How can we determine your blood type by knowing your parents? Compare a cell, tissue, organ, and an organ system. Each parent contributes one of two genes for a particular trait. The gene pairs are calle ...
... What is the difference between genotype and phenotype? What information does a pedigree provide? How can we determine your blood type by knowing your parents? Compare a cell, tissue, organ, and an organ system. Each parent contributes one of two genes for a particular trait. The gene pairs are calle ...
Chapter 16 Evolution of Populations WORKSHEET 1
... 3. In stabilizing selection, how does the fitness of individuals at the center of the curve differ from the individuals at either end? 4. How does disruptive selection result in two distinct phenotypes? ...
... 3. In stabilizing selection, how does the fitness of individuals at the center of the curve differ from the individuals at either end? 4. How does disruptive selection result in two distinct phenotypes? ...
Biology 6 Practice Genetics Problems (chapter 15)
... chromosomes in gametes and 50% parental chromosomes (as revealed by a test cross). This would be the case only if the genetic loci are at opposite ends of a chromosome, which produces the same basic outcome as with unlinked genes (50% parental genotypes, 50% recombinant genotypes). If recombination ...
... chromosomes in gametes and 50% parental chromosomes (as revealed by a test cross). This would be the case only if the genetic loci are at opposite ends of a chromosome, which produces the same basic outcome as with unlinked genes (50% parental genotypes, 50% recombinant genotypes). If recombination ...
Ch 15b
... Monosomy Xcalled Turner syndrome, produces X0 females, who are sterile; it is the only known viable monosomy in humans ...
... Monosomy Xcalled Turner syndrome, produces X0 females, who are sterile; it is the only known viable monosomy in humans ...