D. mel - Biology Courses Server
... GENOMIC IMPRINGITNG Lions live in prides led by several adult males. The lionesses mate with each of those males. Each male wants his offspring to be the ones to survive, but the female's genes want multiple offspring to survive. The father's genes promote size of the offspring to ensure that his of ...
... GENOMIC IMPRINGITNG Lions live in prides led by several adult males. The lionesses mate with each of those males. Each male wants his offspring to be the ones to survive, but the female's genes want multiple offspring to survive. The father's genes promote size of the offspring to ensure that his of ...
1. Which genetic concept was proposed by Mendel?
... but are not identical to, either of their parents. Explain why they resemble their parents but are not identical to either parent. ...
... but are not identical to, either of their parents. Explain why they resemble their parents but are not identical to either parent. ...
FanBLM2
... dataset with disease labels(thus we may find pathways relevant to specific disease). Using ICA to finding hidden variables(hidden layers) and check its consistency with bayes network learning ...
... dataset with disease labels(thus we may find pathways relevant to specific disease). Using ICA to finding hidden variables(hidden layers) and check its consistency with bayes network learning ...
I - Angelfire
... i. In mammals, certain genes are imprinted with the sex of the individual they are inherited from. a. In gamete producing cells, the maternal and paternal imprints are erased, and replaced with those that correspond to the sex of the individual they currently reside in. b. Imprints are believed to c ...
... i. In mammals, certain genes are imprinted with the sex of the individual they are inherited from. a. In gamete producing cells, the maternal and paternal imprints are erased, and replaced with those that correspond to the sex of the individual they currently reside in. b. Imprints are believed to c ...
Zoo/Bot 3333
... 2. A single crossover within the inverted region yields four viable gametes. a) 1 and 2; b) 1 and 3; c) 2 and 4; d) 1 and 4; e) none of the above. 3. A single crossover involving the inverted region on one chromosome and the homologous region on the other chromosome would yield an acentric fragment. ...
... 2. A single crossover within the inverted region yields four viable gametes. a) 1 and 2; b) 1 and 3; c) 2 and 4; d) 1 and 4; e) none of the above. 3. A single crossover involving the inverted region on one chromosome and the homologous region on the other chromosome would yield an acentric fragment. ...
Smchd1 regulates a subset of autosomal genes subject to
... Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. ...
... Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/2.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. ...
Slide 1
... they will be separated during meiosis by crossing over Genes close together usually don’t separate and are called linked genes ...
... they will be separated during meiosis by crossing over Genes close together usually don’t separate and are called linked genes ...
HMIVT
... chromatids. Non-sister chromatids exchange segments at cross over site. Crossing over breaks up old combinations of alleles and puts new ones together in homologous chromosomes, mixes up maternal and paternal information about traits. ...
... chromatids. Non-sister chromatids exchange segments at cross over site. Crossing over breaks up old combinations of alleles and puts new ones together in homologous chromosomes, mixes up maternal and paternal information about traits. ...
AP Biology – PowerPoint Notes – Chapter 11 & 12 ‐ Patterns of Heredity and Human Genetics
... 2. Fetal testing ‐ methods for testing a fetus in utero to determine if it carries genetic disorders a. Amniocentesis ‐ a small sample of amniotic fluid is withdrawn and the fetal cells it contains are cultured for a few weeks. The cells can then be tested for genetic disorders. This pro ...
... 2. Fetal testing ‐ methods for testing a fetus in utero to determine if it carries genetic disorders a. Amniocentesis ‐ a small sample of amniotic fluid is withdrawn and the fetal cells it contains are cultured for a few weeks. The cells can then be tested for genetic disorders. This pro ...
Giant chromosomes and mendl`s Laws
... The probable answer: gene amplification. Having multiple copies of genes permits a high level of gene expression; that is, abundant transcription and translation to produce the gene products. This would account of polyteny being associated with large, metabolically active cells (like salivary glan ...
... The probable answer: gene amplification. Having multiple copies of genes permits a high level of gene expression; that is, abundant transcription and translation to produce the gene products. This would account of polyteny being associated with large, metabolically active cells (like salivary glan ...
Genetics - Easy Plan Book
... 1851 – worked with pea plants to study the effects of crossing plants with certain traits with others. Came up with a couple of rules, and ideas of how heredity works. ...
... 1851 – worked with pea plants to study the effects of crossing plants with certain traits with others. Came up with a couple of rules, and ideas of how heredity works. ...
Introduction to Next-Generation Sequence analysis
... • Population genetics – The study of inherited variation in populations of individuals – Forces, such as environment, that result in changing gene frequencies over generations ...
... • Population genetics – The study of inherited variation in populations of individuals – Forces, such as environment, that result in changing gene frequencies over generations ...
Document
... ◦ a. Families with alkaptonuria often have several affected members. ◦ b.Alkaptonuria is much more common in firstcousin marriages than marriages with unrelated partners. ...
... ◦ a. Families with alkaptonuria often have several affected members. ◦ b.Alkaptonuria is much more common in firstcousin marriages than marriages with unrelated partners. ...
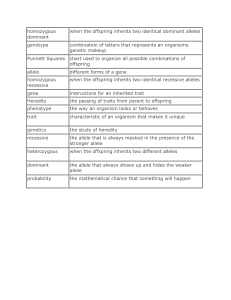
Terms and Definitions 2017 File
... An alternative/different form of a particular gene eg a recessive form or a dominant form. Two different alleles present e.g. Bb The genes an organism possesses How the genes are expressed, i.e. what an organism looks like An allele that shows up in the phenotype if it is present in the genotype An ...
... An alternative/different form of a particular gene eg a recessive form or a dominant form. Two different alleles present e.g. Bb The genes an organism possesses How the genes are expressed, i.e. what an organism looks like An allele that shows up in the phenotype if it is present in the genotype An ...
Chapter 6
... • Gregor Mendel was the first person to apply statistical methods to the study of inheritance. Mendel observed that heterozygotes do not express recessive traits, but can pass on these traits to their offspring. • Mendel’s law of segregation states that all individuals have two copies of each factor ...
... • Gregor Mendel was the first person to apply statistical methods to the study of inheritance. Mendel observed that heterozygotes do not express recessive traits, but can pass on these traits to their offspring. • Mendel’s law of segregation states that all individuals have two copies of each factor ...
Speciation Genes (How does one species become two?)
... GENOMIC IMPRINGITNG Lions live in prides led by several adult males. The lionesses mate with each of those males. Each male wants his offspring to be the ones to survive, but the female's genes want multiple offspring to survive. The father's genes promote size of the offspring to ensure that his of ...
... GENOMIC IMPRINGITNG Lions live in prides led by several adult males. The lionesses mate with each of those males. Each male wants his offspring to be the ones to survive, but the female's genes want multiple offspring to survive. The father's genes promote size of the offspring to ensure that his of ...
Ch 18 Notes - FacStaff Home Page for CBU
... Differential Gene Expression leads to Different Cell Types During embryonic development, a fertilized egg gives rise to many different cell types. Cell types are organized successively into tissues, organs, organ systems, and the whole organism. Gene expression orchestrates the developmental program ...
... Differential Gene Expression leads to Different Cell Types During embryonic development, a fertilized egg gives rise to many different cell types. Cell types are organized successively into tissues, organs, organ systems, and the whole organism. Gene expression orchestrates the developmental program ...