Worksheet 13.3
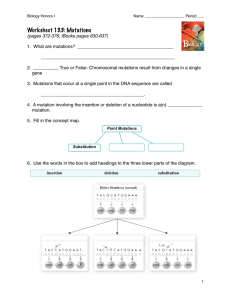
... 2. __________ True or False: Chromosomal mutations result from changes in a single gene 3. Mutations that occur at a single point in the DNA sequence are called ...
... 2. __________ True or False: Chromosomal mutations result from changes in a single gene 3. Mutations that occur at a single point in the DNA sequence are called ...
The relation of genetics to physiology and medicine
... RELATION OF GENETICS TO PHYSIOLOGY/MEDICINE ...
... RELATION OF GENETICS TO PHYSIOLOGY/MEDICINE ...
Lesson 13: Polygenic Inheritance student notes
... While it is over-simplistic to say that each gene responsible for the genetic control of a polygenic trait works equally to all other genes controlling that trait, polygenic inheritance is already complicated enough if we start there. And generally it is true that the genes controlling polygenic tra ...
... While it is over-simplistic to say that each gene responsible for the genetic control of a polygenic trait works equally to all other genes controlling that trait, polygenic inheritance is already complicated enough if we start there. And generally it is true that the genes controlling polygenic tra ...
Patterns of Inheritance DNA Chromosome(s) Gene(s) Character(s
... • Specific locations for certain DNA within chromosomes. • 1 gene is one unit of DNA out of all DNA. • There can be many genes within a chromosome. • Chemicals that control the characters of an organism. ...
... • Specific locations for certain DNA within chromosomes. • 1 gene is one unit of DNA out of all DNA. • There can be many genes within a chromosome. • Chemicals that control the characters of an organism. ...
Heredity
... We still don’t know it all. • Just when people thought they had it down, along came chromosome 15 deletions. – Prader-Willi syndrome if mutations is inherited from the father • obesity, mental retardation, short stature. (abbreviated PWS) ...
... We still don’t know it all. • Just when people thought they had it down, along came chromosome 15 deletions. – Prader-Willi syndrome if mutations is inherited from the father • obesity, mental retardation, short stature. (abbreviated PWS) ...
Horizontal Gene transfer
... genes encoding enzymes required for synthesis of AA, nucleotides, substances not added to minimal media ...
... genes encoding enzymes required for synthesis of AA, nucleotides, substances not added to minimal media ...
Methodology for Pattern Discovery, Validation, and Hypothesis
... http://dbserv2.informatik.uni-leipzig.de:8080/dsggs/?analysis http://pattaran.umiacs.umd.edu ...
... http://dbserv2.informatik.uni-leipzig.de:8080/dsggs/?analysis http://pattaran.umiacs.umd.edu ...
A primer on the structure and function of genes
... element of DNA, as it suggests that most, if not all, of the information required to obtain the functional protein is contained in the local DNA sequence. A consequence of this view was that most functional and structural diversity arose via local changes in the DNA sequence of genes. The determinis ...
... element of DNA, as it suggests that most, if not all, of the information required to obtain the functional protein is contained in the local DNA sequence. A consequence of this view was that most functional and structural diversity arose via local changes in the DNA sequence of genes. The determinis ...
Nerve activates contraction
... genes depend on whether they were inherited from the mother or the father (imprinting) • For most genes it is a reasonable assumption that a specific allele will have the same effect regardless of whether it was inherited from the mother or father. • However, for some traits in mammals, it does depe ...
... genes depend on whether they were inherited from the mother or the father (imprinting) • For most genes it is a reasonable assumption that a specific allele will have the same effect regardless of whether it was inherited from the mother or father. • However, for some traits in mammals, it does depe ...
Whose got Genes?
... fruits that would result from crossbreeding two plants in his father’s garden Picture taken from biography.com Baker 2003/2004 ...
... fruits that would result from crossbreeding two plants in his father’s garden Picture taken from biography.com Baker 2003/2004 ...
Mendelian Genetics Mono and Dihybrid Crosses, Sex
... Do a Punnett Square: determine genotypic and phenotypic ratios. ...
... Do a Punnett Square: determine genotypic and phenotypic ratios. ...
Chapter 15 Assignment - kyoussef-mci
... linked (i.e. on the same chromosome). Why do the alleles for seed colour and seed shape always segregate and assort independently? Hint: look at the picture of the chromosome on the right. Why are b and C genes almost always inherited together, while A is almost always inherited separately from b an ...
... linked (i.e. on the same chromosome). Why do the alleles for seed colour and seed shape always segregate and assort independently? Hint: look at the picture of the chromosome on the right. Why are b and C genes almost always inherited together, while A is almost always inherited separately from b an ...
Human Biology
... - The structure of DNA is called a “double helix” - The DNA contains instructions on how the cell should work - Genes control the development of characteristics (“it’s in the genes”) by issuing instructions to the cell to produce certain proteins - These proteins are either structural (used for cell ...
... - The structure of DNA is called a “double helix” - The DNA contains instructions on how the cell should work - Genes control the development of characteristics (“it’s in the genes”) by issuing instructions to the cell to produce certain proteins - These proteins are either structural (used for cell ...
File
... What happens to the chromosome # in mitosis? What happens to the chromosome # in meiosis? What is the abbreviation for the steps in mitosis? What’s the abbreviation for the steps in meiosis? Draw a picture showing difference between mitosis & ...
... What happens to the chromosome # in mitosis? What happens to the chromosome # in meiosis? What is the abbreviation for the steps in mitosis? What’s the abbreviation for the steps in meiosis? Draw a picture showing difference between mitosis & ...
genes - Computational Diagnostics Group
... A common idea behind all models ... All models confine the set of possible signatures a priori; however, they do it in different ways. Gene selection aims for few genes in the signature SVM go for large margins between data points and the separating hyper-plane. PC-Regression confine the signature ...
... A common idea behind all models ... All models confine the set of possible signatures a priori; however, they do it in different ways. Gene selection aims for few genes in the signature SVM go for large margins between data points and the separating hyper-plane. PC-Regression confine the signature ...
Sex-Limited, Linked, and Influenced Traits Some traits are carried on
... Some traits are carried on the sex chromosomes, X and Y. Most traits carried are present on only the X-chromosome. The Y-chromosome is smaller, and so, very few genes are located on this chromosome. Sex traits can be categorized into three types of inheritance: sex-limited, sex-linked, and sexinflue ...
... Some traits are carried on the sex chromosomes, X and Y. Most traits carried are present on only the X-chromosome. The Y-chromosome is smaller, and so, very few genes are located on this chromosome. Sex traits can be categorized into three types of inheritance: sex-limited, sex-linked, and sexinflue ...
pdffile - UCI Math
... gametes by half, so that when fertilization occurs the normal number of chromosomes is restored. For example, in humans the gametes produced by meiosis are haploid—they have just one copy of each of the 23 chromosomes. Besides preventing the number of chromosomes from doubling with each successive g ...
... gametes by half, so that when fertilization occurs the normal number of chromosomes is restored. For example, in humans the gametes produced by meiosis are haploid—they have just one copy of each of the 23 chromosomes. Besides preventing the number of chromosomes from doubling with each successive g ...
The mouse that roared
... are reported on page 520 of this issue. Why is this so important? It is because there can scarcely be a major area of mammalian biology or medicine to which mouse studies have not contributed in some way, often as surrogates for human studies. For genetics and development, for immunology and pharmac ...
... are reported on page 520 of this issue. Why is this so important? It is because there can scarcely be a major area of mammalian biology or medicine to which mouse studies have not contributed in some way, often as surrogates for human studies. For genetics and development, for immunology and pharmac ...
Genomics and Bioinformatics KEY CONCEPT Entire genomes are
... – Study of entire genomes – can include the sequencing of the genome – Compare genomes within & across species to find similarities & differences among different organisms ...
... – Study of entire genomes – can include the sequencing of the genome – Compare genomes within & across species to find similarities & differences among different organisms ...
7.2 D: Genes and Alleles
... The chromosomes in body cells are in pairs. One chromosome in each pair comes from the father. The other chromosome in the pair comes from the mother. The chromosomes carry genes from parents to offspring. This is related to the pairs of alleles for each trait. One set of alleles comes from the moth ...
... The chromosomes in body cells are in pairs. One chromosome in each pair comes from the father. The other chromosome in the pair comes from the mother. The chromosomes carry genes from parents to offspring. This is related to the pairs of alleles for each trait. One set of alleles comes from the moth ...
Clinical Next Generation Sequencing (From Bench to Clinitions)
... of the genome are isolated and sequenced. Targeted approaches using next-generation sequencing (NGS) allow researchers to focus time, expenses, and data analysis on specific areas of interest. Such targeted analysis can include the exome (the protein-coding portion of the genome), specific genes of ...
... of the genome are isolated and sequenced. Targeted approaches using next-generation sequencing (NGS) allow researchers to focus time, expenses, and data analysis on specific areas of interest. Such targeted analysis can include the exome (the protein-coding portion of the genome), specific genes of ...
Chapter 18 Genes and Medical Genetics
... • there are dominant and recessive alleles (e.g. tall versus short) • if tall is dominant (T) over short (t), the phenotype of an individual with TT will be tall (both dominant alleles) • the phenotype of an individual with tt will be short (both recessive alleles • both TT or tt are called homozygo ...
... • there are dominant and recessive alleles (e.g. tall versus short) • if tall is dominant (T) over short (t), the phenotype of an individual with TT will be tall (both dominant alleles) • the phenotype of an individual with tt will be short (both recessive alleles • both TT or tt are called homozygo ...
Biol115_2014_Lecture 12_Eukaryotic Gene Regulation
... egg gives rise to many different cell types" • Cell types are organised successively into tissues, organs, organ systems, and the whole organism" • Gene expression orchestrates the developmental programs of animals" Biol115_2014_Lecture 11" ...
... egg gives rise to many different cell types" • Cell types are organised successively into tissues, organs, organ systems, and the whole organism" • Gene expression orchestrates the developmental programs of animals" Biol115_2014_Lecture 11" ...
Genetics
... What if there was no crossing-over in any organism? Gene Mapping Distance between genes (alleles) determines how often crossing over occurs. The farther apart- the more likely genes are to cross-over. This distance helps to “map” a chromosome and tell the probable place to find a certain gene on th ...
... What if there was no crossing-over in any organism? Gene Mapping Distance between genes (alleles) determines how often crossing over occurs. The farther apart- the more likely genes are to cross-over. This distance helps to “map” a chromosome and tell the probable place to find a certain gene on th ...























