The Human Genome Project
... body can make many kinds of proteins. (This process is called alternative splicing.) • If a gene is “expressed” that means it is turned on and it will make proteins. ...
... body can make many kinds of proteins. (This process is called alternative splicing.) • If a gene is “expressed” that means it is turned on and it will make proteins. ...
Basic Concepts of Genetic Improvement
... quantitative traits include: 1. Quantitative traits are controlled by possibly hundreds or thousands of gene pairs located on several different chromosome pairs. Some gene pairs will contain additive genes while others can contain nonadditive genes. Most economically important traits are quantitativ ...
... quantitative traits include: 1. Quantitative traits are controlled by possibly hundreds or thousands of gene pairs located on several different chromosome pairs. Some gene pairs will contain additive genes while others can contain nonadditive genes. Most economically important traits are quantitativ ...
30 From Parents to Children – Elements of Genetics
... 3. If a Y bearing sperm fuses with an egg, what will be the sex of the individual developing from the zygote? 4. How many X chromosomes can be found in the cells of (i) a boy, and (ii) a girl. 5. How many molecules of DNA are present in one chromosome? 30.5 INHERITANCE OF BLOOD GROUPS You have alrea ...
... 3. If a Y bearing sperm fuses with an egg, what will be the sex of the individual developing from the zygote? 4. How many X chromosomes can be found in the cells of (i) a boy, and (ii) a girl. 5. How many molecules of DNA are present in one chromosome? 30.5 INHERITANCE OF BLOOD GROUPS You have alrea ...
No Slide Title
... e.g., Bork group - associate pathological conditions with Gene Ontology terms. ...
... e.g., Bork group - associate pathological conditions with Gene Ontology terms. ...
Prioritizing curation of mouse genes by paucity of annotations and
... To maximize the utility of the wealth of experimental data generated by these mouse ciliopathy models, we have initiated a project to comprehensively annotate ciliary genes of the laboratory mouse using Gene Ontology (GO) terms to describe their molecular functions, biological roles, and cellular lo ...
... To maximize the utility of the wealth of experimental data generated by these mouse ciliopathy models, we have initiated a project to comprehensively annotate ciliary genes of the laboratory mouse using Gene Ontology (GO) terms to describe their molecular functions, biological roles, and cellular lo ...
Polygenic Traits
... • Mothers older than 35 have rapidly increasing risk. – 95% of non-disjunctions occur with the ovum. • Most Down syndrome babies are born to women younger than 35 because those are the ages that most women have children. • Dogma: all your oocytes are present at birth; meiosis is arrested in Prophase ...
... • Mothers older than 35 have rapidly increasing risk. – 95% of non-disjunctions occur with the ovum. • Most Down syndrome babies are born to women younger than 35 because those are the ages that most women have children. • Dogma: all your oocytes are present at birth; meiosis is arrested in Prophase ...
Cancer
... Unlike diseases such as cystic fibrosis or muscular dystrophy, wherein mutations in one gene can cause disease, no single gene defect 'causes' cancer. Mammalian cells have multiple safeguards to protect them against the potentially lethal effects of cancer gene mutations, and only when several genes ...
... Unlike diseases such as cystic fibrosis or muscular dystrophy, wherein mutations in one gene can cause disease, no single gene defect 'causes' cancer. Mammalian cells have multiple safeguards to protect them against the potentially lethal effects of cancer gene mutations, and only when several genes ...
Heredity PPT File
... 17.2 Examine the molecular basis of heredity and resulting genetic diversity. ...
... 17.2 Examine the molecular basis of heredity and resulting genetic diversity. ...
Purple flowers
... VII. Human Genetics Inheritance of human traits. Most genetic diseases are recessive. ...
... VII. Human Genetics Inheritance of human traits. Most genetic diseases are recessive. ...
Biclustering of Gene Expression Data using a Two
... condition and each element represents an expression level of a gene under a condition [2][3]. Clustering is one of the most widely used data mining techniques used for gene expression analysis for identifying the genes participating in the same biological process [1]. However clustering has some lim ...
... condition and each element represents an expression level of a gene under a condition [2][3]. Clustering is one of the most widely used data mining techniques used for gene expression analysis for identifying the genes participating in the same biological process [1]. However clustering has some lim ...
File S1
... and substantial changes in expression. We assigned yellow (cerebellum), green (hippocampus), blue (neocortex), and red (hypothalamus). Genes are marked with blue if they are only present in the neocortex list. If one other region has differential expression of that gene, it is marked with the color ...
... and substantial changes in expression. We assigned yellow (cerebellum), green (hippocampus), blue (neocortex), and red (hypothalamus). Genes are marked with blue if they are only present in the neocortex list. If one other region has differential expression of that gene, it is marked with the color ...
Slide 1
... length Markov chains Weighing scheme places less weight on rare k-mers Final probability is the probability of all weighted k-mers Typical and atypical genes ...
... length Markov chains Weighing scheme places less weight on rare k-mers Final probability is the probability of all weighted k-mers Typical and atypical genes ...
Genome-wide RNAi screening in Caenorhabditis elegans
... •1990: Fire & Moerman show antisense RNA can disrupt myofilament protein encoding genes •1995: Guo & Kemphues accidentally discover that sense RNA can is as effective as antisense RNA in gene silencing •1998: Mello & Fire illustrate that dsRNA is the agent that leads to potent and specific genetic i ...
... •1990: Fire & Moerman show antisense RNA can disrupt myofilament protein encoding genes •1995: Guo & Kemphues accidentally discover that sense RNA can is as effective as antisense RNA in gene silencing •1998: Mello & Fire illustrate that dsRNA is the agent that leads to potent and specific genetic i ...
Chapter 9: Patterns of Inheritance
... VII. Human Genetics Inheritance of human traits. Most genetic diseases are recessive. ...
... VII. Human Genetics Inheritance of human traits. Most genetic diseases are recessive. ...
Genetics
... Explain the random process of chromosome segregation and distribution of alleles in gametes. Predict possible combinations of alleles in a zygote from the genetic makeup of the parents. ...
... Explain the random process of chromosome segregation and distribution of alleles in gametes. Predict possible combinations of alleles in a zygote from the genetic makeup of the parents. ...
No Slide Title
... VII. Human Genetics Inheritance of human traits. Most genetic diseases are recessive. ...
... VII. Human Genetics Inheritance of human traits. Most genetic diseases are recessive. ...
The Dismissal of Development Doing Evolution without Development
... Phenotypic response becomes coded in genes. Four conditions for assimilation: 1. The genome must be responsive to environmental inducers. 2. The competence to be induced must be transferred from an external inducer to an internal, embryonic inducer. 3. There has to be cryptic variation within a popu ...
... Phenotypic response becomes coded in genes. Four conditions for assimilation: 1. The genome must be responsive to environmental inducers. 2. The competence to be induced must be transferred from an external inducer to an internal, embryonic inducer. 3. There has to be cryptic variation within a popu ...
Genetics/DNA PowerPoint
... – Means “having many genes” Example: Skin and eye color in humans is controlled by a number of different genes that control these traits. – Different combinations of the alleles yield the enormous range of variation in our skin color. ...
... – Means “having many genes” Example: Skin and eye color in humans is controlled by a number of different genes that control these traits. – Different combinations of the alleles yield the enormous range of variation in our skin color. ...
BiGCaT
... Figure 9-87. Control of the poly-A tail length affects both mRNA stability and mRNA translation. (A) Most translated mRNAs have poly-A tails that exceed a minimum length of about 30 As. The tails on selected mRNAs can be either elongated or rapidly cleaved in the cytosol, and this will have an effe ...
... Figure 9-87. Control of the poly-A tail length affects both mRNA stability and mRNA translation. (A) Most translated mRNAs have poly-A tails that exceed a minimum length of about 30 As. The tails on selected mRNAs can be either elongated or rapidly cleaved in the cytosol, and this will have an effe ...
18. GENETIC REGULATION OF DEVELOPMENT.
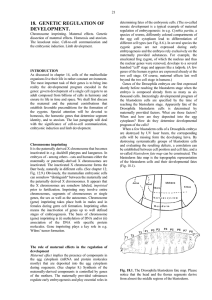
... The zygotic genes If the Bicoid morphogen does indeed control expression of the zygotic genes, function of the regulated zygotic genes can be eliminated by mutations. It may be expected that headless embryos develop in absence of the Bicoid-regulated zygotic gene function. However, the headless phen ...
... The zygotic genes If the Bicoid morphogen does indeed control expression of the zygotic genes, function of the regulated zygotic genes can be eliminated by mutations. It may be expected that headless embryos develop in absence of the Bicoid-regulated zygotic gene function. However, the headless phen ...
Molecular pathology of growth anomalies in Montipora capitata
... expression of MDM2, which regulates the tumor suppressor gene p53, is oaen increased in the presence of neoplasia and we observed no change in expression 10. Similarly, TPK is oaen over-‐expressed under ...
... expression of MDM2, which regulates the tumor suppressor gene p53, is oaen increased in the presence of neoplasia and we observed no change in expression 10. Similarly, TPK is oaen over-‐expressed under ...
Chapter 1: Even fish obey Mendel`s laws
... a cake and is analogous to a genotype. The cake that results, however, depends on the quality of ingredients used, the skill of the baker, and occasionally the barometric pressure or altitude. No two cakes are identical, even though they were products of the same recipe. Some genes very explicitly d ...
... a cake and is analogous to a genotype. The cake that results, however, depends on the quality of ingredients used, the skill of the baker, and occasionally the barometric pressure or altitude. No two cakes are identical, even though they were products of the same recipe. Some genes very explicitly d ...
Word file (37 KB )
... corresponds to a gene. The rows and columns are displayed in the order given by the clustering output trees in the two dimensions. Not all genes are retained in the clustering analysis, only 5,000 significant genes with more than two-fold regulation and significance of regulation p < 0.01 in more th ...
... corresponds to a gene. The rows and columns are displayed in the order given by the clustering output trees in the two dimensions. Not all genes are retained in the clustering analysis, only 5,000 significant genes with more than two-fold regulation and significance of regulation p < 0.01 in more th ...