Virtual Science Fair - Dark Matter Alexander Mashaal
... Dark Matter: In cosmology, dark matter has matter particles that cannot be spotted by their releases of radiation but when they are there, they can be taken from gravitational effects on visible matter such as stars and galaxies. Black Holes: A black hole is a part of space that has so much mass con ...
... Dark Matter: In cosmology, dark matter has matter particles that cannot be spotted by their releases of radiation but when they are there, they can be taken from gravitational effects on visible matter such as stars and galaxies. Black Holes: A black hole is a part of space that has so much mass con ...
PH607 – Galaxies
... Another question is why, if all galaxies are mergers of smaller ones, many of them don't look it. Beautiful spiral galaxies, for instance, appear neat and symmetrical, not as though they were formed from violent collisions of multiple smaller galaxies. Merging galaxies look like train wrecks. Maybe ...
... Another question is why, if all galaxies are mergers of smaller ones, many of them don't look it. Beautiful spiral galaxies, for instance, appear neat and symmetrical, not as though they were formed from violent collisions of multiple smaller galaxies. Merging galaxies look like train wrecks. Maybe ...
PPT
... What have we learned? • How do we measure the distances to galaxies? – The distance-measurement chain begins with parallax measurements that build on radar ranging in our solar system – Using parallax and the relationship between luminosity, distance, and brightness, we can calibrate a series of st ...
... What have we learned? • How do we measure the distances to galaxies? – The distance-measurement chain begins with parallax measurements that build on radar ranging in our solar system – Using parallax and the relationship between luminosity, distance, and brightness, we can calibrate a series of st ...
PDF - Oxford Academic - Oxford University Press
... details. For example, it predicts that the universe is expanding and that distant galaxies are receding from us at a speed that is approximately proportional to their distance. This has been amply confirmed by redshift measurements throughout the 20th century. The Big Bang universe was hotter and de ...
... details. For example, it predicts that the universe is expanding and that distant galaxies are receding from us at a speed that is approximately proportional to their distance. This has been amply confirmed by redshift measurements throughout the 20th century. The Big Bang universe was hotter and de ...
Astronomy 140 Lecture Notes, Spring 2008 c
... By measuring the spectrum of a star, one can determine its temperature by comparing the line strengths of lines with highly excited lower levels to the strengths of lines with low excitation lower levels. Since the populations in states with energy E is proportional to exp(−E/kT ) (Boltzmann), this ...
... By measuring the spectrum of a star, one can determine its temperature by comparing the line strengths of lines with highly excited lower levels to the strengths of lines with low excitation lower levels. Since the populations in states with energy E is proportional to exp(−E/kT ) (Boltzmann), this ...
PPT
... • Pls see papers written by Prof.Fang Li-Zhi such as: 1. Fang Li-zhi and W. Thews Wavelet in Physics. Would Scientific Singapore 2. Fang Li-zhi et al’s papers appeared in ApJ. ...
... • Pls see papers written by Prof.Fang Li-Zhi such as: 1. Fang Li-zhi and W. Thews Wavelet in Physics. Would Scientific Singapore 2. Fang Li-zhi et al’s papers appeared in ApJ. ...
swire
... SWIRE Science Goals To enable fundamental studies of cosmology and galaxy evolution in the Mid- and Far-IR for 0.5
... SWIRE Science Goals To enable fundamental studies of cosmology and galaxy evolution in the Mid- and Far-IR for 0.5
Galaxies over the Latter Half of Cosmic Time
... A new survey project called All-Wavelength Extended Groth Strip International Survey (AEGIS) has created one of the largest Hubble pictures to date. The image is 1/6º wide by 1º long, stretching twice the width of the full Moon. It is a mosaic of 63 tiles, each exposed through green and red filters, ...
... A new survey project called All-Wavelength Extended Groth Strip International Survey (AEGIS) has created one of the largest Hubble pictures to date. The image is 1/6º wide by 1º long, stretching twice the width of the full Moon. It is a mosaic of 63 tiles, each exposed through green and red filters, ...
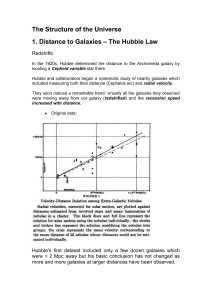
Hubble Diagram Instruction Sheet
... The Hubble diagram demonstrated that a galaxy’s redshift increased linearly with its distance from Earth. The farther away a galaxy is, the faster it moves away from us. The simplest explanation for Hubble’s observation was that the entire universe is expanding, just as Einstein's equations predicte ...
... The Hubble diagram demonstrated that a galaxy’s redshift increased linearly with its distance from Earth. The farther away a galaxy is, the faster it moves away from us. The simplest explanation for Hubble’s observation was that the entire universe is expanding, just as Einstein's equations predicte ...
poster_IAU244 - ANU - Australian National University
... and star formation in galaxies as a function of redshift and environment. Our study combines deep radio observations of HI 21cm emission using the Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (GMRT) in India with optical imaging and spectroscopy. The main results presented here are from a sample of 348 Hα-emitti ...
... and star formation in galaxies as a function of redshift and environment. Our study combines deep radio observations of HI 21cm emission using the Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope (GMRT) in India with optical imaging and spectroscopy. The main results presented here are from a sample of 348 Hα-emitti ...
astro-ph/0210527 PDF
... results. One could formally go about this, for example, by choosing some random microscopic state normally associated with equilibrium and declaring microscopic states which were dynamically nearby to that state to be in the same coarse grained “bin”, and, and by similarly making other coarse grain ...
... results. One could formally go about this, for example, by choosing some random microscopic state normally associated with equilibrium and declaring microscopic states which were dynamically nearby to that state to be in the same coarse grained “bin”, and, and by similarly making other coarse grain ...
The View from No-when - UC San Diego Department of Philosophy
... [1995]), nothing in the original explanation necessarily referred to the direction of time. Though I just stated the Boltzmannian account of entropy increase in terms of entropy increasing into the future, the explanation can be turned around and made for the past temporal direction as well. Given a ...
... [1995]), nothing in the original explanation necessarily referred to the direction of time. Though I just stated the Boltzmannian account of entropy increase in terms of entropy increasing into the future, the explanation can be turned around and made for the past temporal direction as well. Given a ...
The history of a discovery - Institut d`Astrophysique Spatiale
... • the heavy elements (and associated dust) abundance in the universe is increasing with time • a naïve view would thus predict a decreasing FIR/visible ratio with redshift • a few galaxies had been shown to have a large ratio but the bulk of the galaxies were expected to have rather small one (a few ...
... • the heavy elements (and associated dust) abundance in the universe is increasing with time • a naïve view would thus predict a decreasing FIR/visible ratio with redshift • a few galaxies had been shown to have a large ratio but the bulk of the galaxies were expected to have rather small one (a few ...
Chapter 14 Cosmology II
... The reasonable explanation is that spacetime is undergoing a transformation that changes the coordinate speed of light while keeping the laws of physics unchanged including a constant proper speed of light . This is similar to the covariance of the laws of physics in ...
... The reasonable explanation is that spacetime is undergoing a transformation that changes the coordinate speed of light while keeping the laws of physics unchanged including a constant proper speed of light . This is similar to the covariance of the laws of physics in ...
Observational Data
... different models of massive galaxy formation. Baugh et al (2000) predicted ~6 massive galaxies of Mstar=1E11Mo for 1.7
... different models of massive galaxy formation. Baugh et al (2000) predicted ~6 massive galaxies of Mstar=1E11Mo for 1.7
galaxy distance
... stars and gas or dust, held together by gravity. This one was spotted a recordbreaking 670 million years from the Big Bang, the massive explosion that many scientists say created the universe. Since objects in space are so far away, distance is measured in light years. The findings show a surprisingl ...
... stars and gas or dust, held together by gravity. This one was spotted a recordbreaking 670 million years from the Big Bang, the massive explosion that many scientists say created the universe. Since objects in space are so far away, distance is measured in light years. The findings show a surprisingl ...
The Comprehensible Universe
... Abstract -- The Universe perhaps may look and can be modeled as Earth like body and thus the origin of different natural features and their functions, based on certain physical laws, on the Earth can be compared and explained with formation of different features and their functions, based on somewha ...
... Abstract -- The Universe perhaps may look and can be modeled as Earth like body and thus the origin of different natural features and their functions, based on certain physical laws, on the Earth can be compared and explained with formation of different features and their functions, based on somewha ...
Dark Matter, Dark Energy, and the Fate of the Universe
... applying Newton’s laws of motion and gravitation. Armed with a spectrograph, Zwicky measured the redshifts of the galaxies in a particular cluster and used these redshifts to calculate the speeds at which the individual galaxies are moving away from us. He determined the recession speed of the clust ...
... applying Newton’s laws of motion and gravitation. Armed with a spectrograph, Zwicky measured the redshifts of the galaxies in a particular cluster and used these redshifts to calculate the speeds at which the individual galaxies are moving away from us. He determined the recession speed of the clust ...
Chapter22.1
... What have we learned? • What do we mean by dark matter and dark energy? – Dark matter is the name given to the unseen mass whose gravity governs the observed motions of stars and gas clouds. – Dark energy is the name given to whatever might be causing the expansion of the universe to accelerate. ...
... What have we learned? • What do we mean by dark matter and dark energy? – Dark matter is the name given to the unseen mass whose gravity governs the observed motions of stars and gas clouds. – Dark energy is the name given to whatever might be causing the expansion of the universe to accelerate. ...
e-group-theme-1-a-b-and-c-ao2-essays
... claim, science establishes that the Big Bang theory proves there was a start to the universe. The Big Bang theory is supported by Red Shift discovered by Hubble, this empirical evidence indicates that everything is spreading apart from one single point in the universe. The planets further away are r ...
... claim, science establishes that the Big Bang theory proves there was a start to the universe. The Big Bang theory is supported by Red Shift discovered by Hubble, this empirical evidence indicates that everything is spreading apart from one single point in the universe. The planets further away are r ...
Document
... Correlation between black hole mass and velocity dispersion of host stellar system ì = 4:02 æ 0:32; ë ì = 4:02 æ 0:32; ë = 8:13 æ 0:06 Tremaine et al. 2002 ...
... Correlation between black hole mass and velocity dispersion of host stellar system ì = 4:02 æ 0:32; ë ì = 4:02 æ 0:32; ë = 8:13 æ 0:06 Tremaine et al. 2002 ...
Big Bang

The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological model for the universe from the earliest known periods through its subsequent large-scale evolution. The model accounts for the fact that the universe expanded from a very high density and high temperature state, and offers a comprehensive explanation for a broad range of observed phenomena, including the abundance of light elements, the cosmic microwave background, large scale structure, and Hubble's Law. If the known laws of physics are extrapolated beyond where they are valid, there is a singularity. Modern measurements place this moment at approximately 13.8 billion years ago, which is thus considered the age of the universe. After the initial expansion, the universe cooled sufficiently to allow the formation of subatomic particles, and later simple atoms. Giant clouds of these primordial elements later coalesced through gravity to form stars and galaxies.Since Georges Lemaître first noted, in 1927, that an expanding universe might be traced back in time to an originating single point, scientists have built on his idea of cosmic expansion. While the scientific community was once divided between supporters of two different expanding universe theories, the Big Bang and the Steady State theory, accumulated empirical evidence provides strong support for the former. In 1929, from analysis of galactic redshifts, Edwin Hubble concluded that galaxies are drifting apart, important observational evidence consistent with the hypothesis of an expanding universe. In 1965, the cosmic microwave background radiation was discovered, which was crucial evidence in favor of the Big Bang model, since that theory predicted the existence of background radiation throughout the universe before it was discovered. More recently, measurements of the redshifts of supernovae indicate that the expansion of the universe is accelerating, an observation attributed to dark energy's existence. The known physical laws of nature can be used to calculate the characteristics of the universe in detail back in time to an initial state of extreme density and temperature.