L. Moustakas
... massive galaxies are already in place. Are these galaxies freshly 'assembled'? Or did that happen much earlier, still? Why and how would 'monolithic' collapse happen? This is a major challenge... Even so, a lot is happening at that time. There is a lot of obscured AGN activity, that may be tracing ...
... massive galaxies are already in place. Are these galaxies freshly 'assembled'? Or did that happen much earlier, still? Why and how would 'monolithic' collapse happen? This is a major challenge... Even so, a lot is happening at that time. There is a lot of obscured AGN activity, that may be tracing ...
Gravitational Lensing: An Unique Probe of Dark Matter and Dark...
... the critical lines of massive clusters where magnifications of 20-30 are typical (Ellis et al. 2001, Kneib et al. 2004); these systems would not have been detected without the boost in signal provided by gravitational lensing. As early galaxies are likely to be less massive and luminous than their ...
... the critical lines of massive clusters where magnifications of 20-30 are typical (Ellis et al. 2001, Kneib et al. 2004); these systems would not have been detected without the boost in signal provided by gravitational lensing. As early galaxies are likely to be less massive and luminous than their ...
Collider physics and cosmology
... – What is its mass? – What are its spin and other quantum numbers? – Is it absolutely stable? – What is the symmetry origin of the dark matter particle? – Is dark matter composed of one particle species or many? – How and when was it produced? – Why does WDM have the observed value? – What was its r ...
... – What is its mass? – What are its spin and other quantum numbers? – Is it absolutely stable? – What is the symmetry origin of the dark matter particle? – Is dark matter composed of one particle species or many? – How and when was it produced? – Why does WDM have the observed value? – What was its r ...
The Universe
... As an example of such an interaction, the Milky Way galaxy and the nearby Andromeda Galaxy are moving toward each other at about 130 km/s, and—depending upon the lateral movements—the two may collide in about five to six billion years. Although the Milky Way has never collided with a galaxy as larg ...
... As an example of such an interaction, the Milky Way galaxy and the nearby Andromeda Galaxy are moving toward each other at about 130 km/s, and—depending upon the lateral movements—the two may collide in about five to six billion years. Although the Milky Way has never collided with a galaxy as larg ...
The Universe
... As an example of such an interaction, the Milky Way galaxy and the nearby Andromeda Galaxy are moving toward each other at about 130 km/s, and—depending upon the lateral movements—the two may collide in about five to six billion years. Although the Milky Way has never collided with a galaxy as larg ...
... As an example of such an interaction, the Milky Way galaxy and the nearby Andromeda Galaxy are moving toward each other at about 130 km/s, and—depending upon the lateral movements—the two may collide in about five to six billion years. Although the Milky Way has never collided with a galaxy as larg ...
Galaxy evolution - Pontifical Academy of Sciences
... assembly, secular evolution must have played a role in shaping the structure of disk galaxies as we see them at z=0. Bars can drive a substantial redistribution of mass and angular momentum in the disk. A possible product of bar-driven evolution is the formation of a bulgelike component. Which struc ...
... assembly, secular evolution must have played a role in shaping the structure of disk galaxies as we see them at z=0. Bars can drive a substantial redistribution of mass and angular momentum in the disk. A possible product of bar-driven evolution is the formation of a bulgelike component. Which struc ...
Future stability of homogeneous cosmological models with matter
... Assume Greek indices run from 0 to 3 and Latin indices from 1 to 3. The zeroth coordinate represents the time coordinate. In mathematical cosmology one usually assumes M = I × S where S is spatially compact (also Einstein did this in his first paper Kosmologische Betrachtungen zur Allgemeinen Relati ...
... Assume Greek indices run from 0 to 3 and Latin indices from 1 to 3. The zeroth coordinate represents the time coordinate. In mathematical cosmology one usually assumes M = I × S where S is spatially compact (also Einstein did this in his first paper Kosmologische Betrachtungen zur Allgemeinen Relati ...
Stars and Galaxies
... close to one another. You can see that some of the stars are brighter than others, but you can’t see how far they are from you or from each other. Usually, they lie at greatly different distances and just happen to line up and form a pattern. In Figure 1, three constellations are shown with some of ...
... close to one another. You can see that some of the stars are brighter than others, but you can’t see how far they are from you or from each other. Usually, they lie at greatly different distances and just happen to line up and form a pattern. In Figure 1, three constellations are shown with some of ...
Powerpoint Presentation (large file)
... Colliding galaxies produce starbursts, spiral arms, and other spectacular phenomena ...
... Colliding galaxies produce starbursts, spiral arms, and other spectacular phenomena ...
Document
... Colliding galaxies produce starbursts, spiral arms, and other spectacular phenomena ...
... Colliding galaxies produce starbursts, spiral arms, and other spectacular phenomena ...
Galaxies Chapter Twenty
... Colliding galaxies produce starbursts, spiral arms, and other spectacular phenomena ...
... Colliding galaxies produce starbursts, spiral arms, and other spectacular phenomena ...
(PDF, Unknown) - Natural Philosophy Alliance
... Another consequence of this electrodynamic theory of gravitation is that the force of gravity is decreasing over time. The emission of the radiation above causes a decay of the force of gravity due to a decrease in the value of the mass. The rate of decay depends on an atom's position in an astronom ...
... Another consequence of this electrodynamic theory of gravitation is that the force of gravity is decreasing over time. The emission of the radiation above causes a decay of the force of gravity due to a decrease in the value of the mass. The rate of decay depends on an atom's position in an astronom ...
Lecture 21 (pdf from the powerpoint)
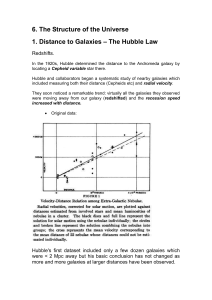
... Distances to other galaxies • We can use Cepheid variable stars to measure the distance to other galaxies • A Cepheid’s luminosity is proportional to its period, so if we know how rapidly it brightens and dims, we know much energy it emits • If we see a Cepheid in another galaxy, we measure its per ...
... Distances to other galaxies • We can use Cepheid variable stars to measure the distance to other galaxies • A Cepheid’s luminosity is proportional to its period, so if we know how rapidly it brightens and dims, we know much energy it emits • If we see a Cepheid in another galaxy, we measure its per ...
Magnificent Cosmos - Academic Program Pages at Evergreen
... star’s blazing coronal gases—remains unclear. These effect of the starlight. As a star sways to and fro relative to findings are mysterious, given that the radius of Jupiter’s Earth, its light waves become cyclically stretched, then com- orbit is five times larger than that of Earth. These pressed—s ...
... star’s blazing coronal gases—remains unclear. These effect of the starlight. As a star sways to and fro relative to findings are mysterious, given that the radius of Jupiter’s Earth, its light waves become cyclically stretched, then com- orbit is five times larger than that of Earth. These pressed—s ...
Fermilab www.fnal.gov
... scientists made vital contributions to the construction of the Large Hadron Collider, including the superconducting magnets that focus particle beams into collision. Fermilab also make major contributions to the construction of the CMS detector, and roughly 100 Fermilab employees work on the CMS exp ...
... scientists made vital contributions to the construction of the Large Hadron Collider, including the superconducting magnets that focus particle beams into collision. Fermilab also make major contributions to the construction of the CMS detector, and roughly 100 Fermilab employees work on the CMS exp ...
Detection of Point Sources in Maps of the
... model of Big Bang cosmology, is based on the theory of inflation and on the Λ-CDM model, that includes cold dark matter (CDM) and a cosmological constant. The theory of inflation predicts a nearly scale-invariant spectrum of primordial density pertubations, homegeneity and isotropy on the largest sc ...
... model of Big Bang cosmology, is based on the theory of inflation and on the Λ-CDM model, that includes cold dark matter (CDM) and a cosmological constant. The theory of inflation predicts a nearly scale-invariant spectrum of primordial density pertubations, homegeneity and isotropy on the largest sc ...
PH607lec11
... Another question is why, if all galaxies are mergers of smaller ones, many of them don't look it. Beautiful spiral galaxies, for instance, appear neat and symmetrical, not as though they were formed from violent collisions of multiple smaller galaxies. Merging galaxies look like train wrecks. Maybe ...
... Another question is why, if all galaxies are mergers of smaller ones, many of them don't look it. Beautiful spiral galaxies, for instance, appear neat and symmetrical, not as though they were formed from violent collisions of multiple smaller galaxies. Merging galaxies look like train wrecks. Maybe ...
Parallel Universes - MIT Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space
... successful explanation of most of the history of our universe. It had explained how a primordial fireball expanded and cooled, synthesized Helium and other light elements during the first few minutes, became transparent after 400,000 years releasing the cosmic microwave background radiation, and gra ...
... successful explanation of most of the history of our universe. It had explained how a primordial fireball expanded and cooled, synthesized Helium and other light elements during the first few minutes, became transparent after 400,000 years releasing the cosmic microwave background radiation, and gra ...
dark matter effective field theories in stars
... cross-section, i.e., where we focus on the second term in the thermally averaged annihilation cross-section expansion, ...
... cross-section, i.e., where we focus on the second term in the thermally averaged annihilation cross-section expansion, ...
Parallel Universes
... successful explanation of most of the history of our universe. It had explained how a primordial fireball expanded and cooled, synthesized Helium and other light elements during the first few minutes, became transparent after 400,000 years releasing the cosmic microwave background radiation, and gra ...
... successful explanation of most of the history of our universe. It had explained how a primordial fireball expanded and cooled, synthesized Helium and other light elements during the first few minutes, became transparent after 400,000 years releasing the cosmic microwave background radiation, and gra ...
Galaxies
... • It depends how fast the gas is used up to form galaxies • If star formation is fast, no gas is left elliptical galaxy • If star formation is slow, gas forms disk spiral galaxy ...
... • It depends how fast the gas is used up to form galaxies • If star formation is fast, no gas is left elliptical galaxy • If star formation is slow, gas forms disk spiral galaxy ...
Dark Matter Capture in the first stars
... v.s. dynamical time of <103yr: the core may fill in with DM again s.t. annihilation heating continues for a longer time Are there still some dark stars around today? ...
... v.s. dynamical time of <103yr: the core may fill in with DM again s.t. annihilation heating continues for a longer time Are there still some dark stars around today? ...
Big Bang

The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological model for the universe from the earliest known periods through its subsequent large-scale evolution. The model accounts for the fact that the universe expanded from a very high density and high temperature state, and offers a comprehensive explanation for a broad range of observed phenomena, including the abundance of light elements, the cosmic microwave background, large scale structure, and Hubble's Law. If the known laws of physics are extrapolated beyond where they are valid, there is a singularity. Modern measurements place this moment at approximately 13.8 billion years ago, which is thus considered the age of the universe. After the initial expansion, the universe cooled sufficiently to allow the formation of subatomic particles, and later simple atoms. Giant clouds of these primordial elements later coalesced through gravity to form stars and galaxies.Since Georges Lemaître first noted, in 1927, that an expanding universe might be traced back in time to an originating single point, scientists have built on his idea of cosmic expansion. While the scientific community was once divided between supporters of two different expanding universe theories, the Big Bang and the Steady State theory, accumulated empirical evidence provides strong support for the former. In 1929, from analysis of galactic redshifts, Edwin Hubble concluded that galaxies are drifting apart, important observational evidence consistent with the hypothesis of an expanding universe. In 1965, the cosmic microwave background radiation was discovered, which was crucial evidence in favor of the Big Bang model, since that theory predicted the existence of background radiation throughout the universe before it was discovered. More recently, measurements of the redshifts of supernovae indicate that the expansion of the universe is accelerating, an observation attributed to dark energy's existence. The known physical laws of nature can be used to calculate the characteristics of the universe in detail back in time to an initial state of extreme density and temperature.