Genetics - the science of heredity and variation
... parents and offspring; sum of qualities genetically derived from one’s parents Allele - one of a pair of genes that occupy the same location on homologous chromosomes and affect the same trait in animals Diploid - refers to paired chromosomes in body cells Gametes - male or female reproductive cells ...
... parents and offspring; sum of qualities genetically derived from one’s parents Allele - one of a pair of genes that occupy the same location on homologous chromosomes and affect the same trait in animals Diploid - refers to paired chromosomes in body cells Gametes - male or female reproductive cells ...
Designer Babies & the government
... what body type they will have their hair and eye color what sorts of illnesses they will be naturally resistant to and even, conceivably, their IQ and personality type. ...
... what body type they will have their hair and eye color what sorts of illnesses they will be naturally resistant to and even, conceivably, their IQ and personality type. ...
Chapter 1-2: Genetics Progressed from Mendel to DNA in Less Than
... mechanism of inheritance, the stage was set in the discovery of its structure. 1953: Watson & Crick described the molecular structure of DNA. ...
... mechanism of inheritance, the stage was set in the discovery of its structure. 1953: Watson & Crick described the molecular structure of DNA. ...
Heredity
... genes in human DNA, determine the sequences of the 3 billion chemical base pairs that make up human DNA, store this information in databases, improve tools for data analysis, transfer related technologies to the private sector, and address the ethical, legal, and social issues (ELSI) that may arise ...
... genes in human DNA, determine the sequences of the 3 billion chemical base pairs that make up human DNA, store this information in databases, improve tools for data analysis, transfer related technologies to the private sector, and address the ethical, legal, and social issues (ELSI) that may arise ...
Nitrogen Base Pairs
... Same gene pairs 9.What is a mutation? Are they always harmful? Permanent change to an organism No create variety ...
... Same gene pairs 9.What is a mutation? Are they always harmful? Permanent change to an organism No create variety ...
GENE THERAPY
... cloning. They were packed in defective retrovirus, most of the viral genes were replaced by the ADA gene. Lymphocytes were isolated from the patients. The recombinant retroviruses were used to infect the lymphocytes. The infected cells expressing the ADA Gene were injected back into the pateint. ...
... cloning. They were packed in defective retrovirus, most of the viral genes were replaced by the ADA gene. Lymphocytes were isolated from the patients. The recombinant retroviruses were used to infect the lymphocytes. The infected cells expressing the ADA Gene were injected back into the pateint. ...
U.S. Meat Animal Research Center (MARC)
... Current limitations in genomic research Single gene selection is worse than single trait selection Need to incorporate with EPDs We need to rapidly identify sufficient number of genes that explain the majority of the genetic variation Need for additional laboratory tools ...
... Current limitations in genomic research Single gene selection is worse than single trait selection Need to incorporate with EPDs We need to rapidly identify sufficient number of genes that explain the majority of the genetic variation Need for additional laboratory tools ...
7.3 Gene Linkage and Mapping
... Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance-based on research of Thomas Morgan Hunt • Genes are located on chromosomes and the behavior of chromosomes during meiosis accounts for inheritance patterns. “Random Assortment” • Chromosomes exchange homologous genes during meiosis explains how linked genes can sepa ...
... Chromosomal Theory of Inheritance-based on research of Thomas Morgan Hunt • Genes are located on chromosomes and the behavior of chromosomes during meiosis accounts for inheritance patterns. “Random Assortment” • Chromosomes exchange homologous genes during meiosis explains how linked genes can sepa ...
Speciation
... of a new species Species: A group of similar organisms that breed together and produce fertile offspring. Gene pools must become separated for them to become different species. ...
... of a new species Species: A group of similar organisms that breed together and produce fertile offspring. Gene pools must become separated for them to become different species. ...
Recombinant DNA - University of Central Oklahoma
... • GE = genetic engineering/genetically engineered • GM = genetically modified • GMO = genetically modified organism • Pharm crop = a GE crop that creates its own pharmaceutical byproducts in virtually all parts of the ...
... • GE = genetic engineering/genetically engineered • GM = genetically modified • GMO = genetically modified organism • Pharm crop = a GE crop that creates its own pharmaceutical byproducts in virtually all parts of the ...
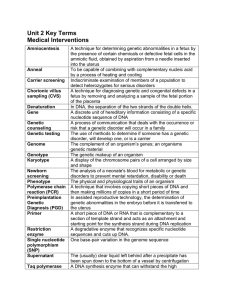
Unit 2 Terms
... measurement of internal body structures and the detection of bodily abnormalities Using a somatic or body cell from a multicellular organism to make one or more genetically identical individuals The alteration of the genes of a person afflicted with a genetic disease A procedure in which gametes are ...
... measurement of internal body structures and the detection of bodily abnormalities Using a somatic or body cell from a multicellular organism to make one or more genetically identical individuals The alteration of the genes of a person afflicted with a genetic disease A procedure in which gametes are ...
Gene Technology
... • Genetic engineering – moving genes from one organism into another • DNA extracted out of cells using a simple chemical process. Cells are opened and then DNA is separated from the rest of the cell parts. ...
... • Genetic engineering – moving genes from one organism into another • DNA extracted out of cells using a simple chemical process. Cells are opened and then DNA is separated from the rest of the cell parts. ...
DNA Recombination
... the material coded for by the mammalian gene. For example, if the human gene for the production of insulin is inserted into a bacterial cell, the altered bacterium will produce insulin. As the bacterial cell divides, the offspring will also have the ability to produce insulin. Objective: In this lab ...
... the material coded for by the mammalian gene. For example, if the human gene for the production of insulin is inserted into a bacterial cell, the altered bacterium will produce insulin. As the bacterial cell divides, the offspring will also have the ability to produce insulin. Objective: In this lab ...
Applying Our Knowledge of Genetics
... • Gene therapy involves the insertion of a properly working gene into a patient that has a faulty gene in hopes that the new, healthy gene could be used to cure the disorder. • A vector, or DNA delivery system, would need to be used to insert the “foreign” DNA into the patient’s cells. • Some vector ...
... • Gene therapy involves the insertion of a properly working gene into a patient that has a faulty gene in hopes that the new, healthy gene could be used to cure the disorder. • A vector, or DNA delivery system, would need to be used to insert the “foreign” DNA into the patient’s cells. • Some vector ...
Hematologic Malignancies - Jacquie Hirsch For ALL Foundation
... DNA is the genetic code inherited from your parents DNA is arranged in structures called chromosomes (X-like). ...
... DNA is the genetic code inherited from your parents DNA is arranged in structures called chromosomes (X-like). ...
Double helix- a double twist
... A gene is a special section on the DNA that has the instructions to make a specific protein. Each gene codes for one protein. The specific order of the bases tells your cell what protein to make. ...
... A gene is a special section on the DNA that has the instructions to make a specific protein. Each gene codes for one protein. The specific order of the bases tells your cell what protein to make. ...
Genetics Review Questions
... 7. PP and pp represent a purebred organism. 8. A hybrid gene pair is also referred to as heterozygous. 9. Offspring inherit one gene from each parent. 10. Pp has genes that are different and represent a hybrid organism. 11. What did Karl Correns discover? incomplete dominance 12. The likelihood that ...
... 7. PP and pp represent a purebred organism. 8. A hybrid gene pair is also referred to as heterozygous. 9. Offspring inherit one gene from each parent. 10. Pp has genes that are different and represent a hybrid organism. 11. What did Karl Correns discover? incomplete dominance 12. The likelihood that ...
Genes and Inheritance
... In females recombination occurs in mammals early in life. Cells sit dormant in the ovary until puberty. ...
... In females recombination occurs in mammals early in life. Cells sit dormant in the ovary until puberty. ...
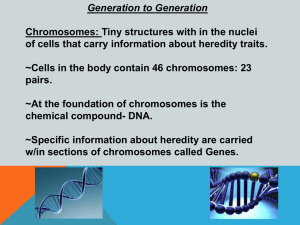
Genes
... blindness, and death during early childhood. Cystic Fibrosis: Makes breathing and digestion difficult, its caused by abnormal genes, one from each parent. Down Syndrome: Caused by a chromosomal abnormality known as Trisony-21,( the presence of three copies of the 21st chromosome). As a result, the a ...
... blindness, and death during early childhood. Cystic Fibrosis: Makes breathing and digestion difficult, its caused by abnormal genes, one from each parent. Down Syndrome: Caused by a chromosomal abnormality known as Trisony-21,( the presence of three copies of the 21st chromosome). As a result, the a ...