gene pool
... • B) Founder effect- when a few individuals from a population leave and start another population in a different location. This also decreases the size of the gene pool in the new population. ...
... • B) Founder effect- when a few individuals from a population leave and start another population in a different location. This also decreases the size of the gene pool in the new population. ...
Figure 2 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence
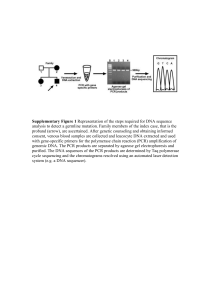
... Supplementary Figure 1 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence analysis to detect a germline mutation. Family members of the index case, that is the proband (arrow), are ascertained. After genetic counseling and obtaining informed consent, venous blood samples are collected and leucocy ...
... Supplementary Figure 1 Representation of the steps required for DNA sequence analysis to detect a germline mutation. Family members of the index case, that is the proband (arrow), are ascertained. After genetic counseling and obtaining informed consent, venous blood samples are collected and leucocy ...
hox genes - WordPress.com
... is junk DNA •PROMOTER REGIONS are associated with genes and help initialize transcription of the gene into a protein •GENETIC SWITCHES play a role regulating the EXPRESSION of genes ...
... is junk DNA •PROMOTER REGIONS are associated with genes and help initialize transcription of the gene into a protein •GENETIC SWITCHES play a role regulating the EXPRESSION of genes ...
The Human Genome
... • The weaker allele not expressed is the “recessive” allele. Though not expressed, it is part of your “genotype” & can be passed on to your kids. Recessive trait is usually only expressed when you inherit the recessive allele from both parents. • Dominant alleles indicated by upper-case letters • Mo ...
... • The weaker allele not expressed is the “recessive” allele. Though not expressed, it is part of your “genotype” & can be passed on to your kids. Recessive trait is usually only expressed when you inherit the recessive allele from both parents. • Dominant alleles indicated by upper-case letters • Mo ...
Reproductive cloning
... – therapeutic cloning: cloned embryo is destroyed to harvest embryonic stem cells, which will be automatically tolerated by the recipient of the therapy – Reproductive cloning, the cloned embryo is allowed to develop into adults – many ethical issues ...
... – therapeutic cloning: cloned embryo is destroyed to harvest embryonic stem cells, which will be automatically tolerated by the recipient of the therapy – Reproductive cloning, the cloned embryo is allowed to develop into adults – many ethical issues ...
BILL #37: Learning Guide: Chromosome Behavior and LInked Genes
... To Think About: How does the behavior of chromosomes support Mendelian inheritance patterns? How does linkage affect inheritance? How does the chromosomal basis of recombination generate variation? What is the connection between new combinations of alleles and evolution? 1st Interact: Take notes on ...
... To Think About: How does the behavior of chromosomes support Mendelian inheritance patterns? How does linkage affect inheritance? How does the chromosomal basis of recombination generate variation? What is the connection between new combinations of alleles and evolution? 1st Interact: Take notes on ...
genes - Brookwood High School
... 3. Recombinant DNA: DNA that contains genes from more than 1 organism. ...
... 3. Recombinant DNA: DNA that contains genes from more than 1 organism. ...
Presentation
... pathogenic organism lives and reproduces within red blood cells. So nature’s way of trying to defend against this was to “change by mutation” a single nucleotide within the DNA sequence for the gene that is responsible for making red blood cells. This change collapses the red blood cell inward, so t ...
... pathogenic organism lives and reproduces within red blood cells. So nature’s way of trying to defend against this was to “change by mutation” a single nucleotide within the DNA sequence for the gene that is responsible for making red blood cells. This change collapses the red blood cell inward, so t ...
Sample File
... A gene is a portion of the DNA molecule that contains a sequence of base pairs that encode a particular protein. Mendel deduced the presence and activity of genes by experimenting with garden peas to determine how traits are passed from one generation to the next. He discovered that inheritance ...
... A gene is a portion of the DNA molecule that contains a sequence of base pairs that encode a particular protein. Mendel deduced the presence and activity of genes by experimenting with garden peas to determine how traits are passed from one generation to the next. He discovered that inheritance ...
epigenomics - IES Valldemossa
... chemical switches within our cells collectively known as the epigenome. ...
... chemical switches within our cells collectively known as the epigenome. ...
review_for_final_exam_jan_2016
... Segregation (What is it? What happens during segregation?) Punnett Squares (What are they used for? How to use them for both mono and dihybrid crosses) Summary of Mendel’s principles (page 272) karyotype, sex chromosomes, autosomes, X and Y chromosomes, pedigree ...
... Segregation (What is it? What happens during segregation?) Punnett Squares (What are they used for? How to use them for both mono and dihybrid crosses) Summary of Mendel’s principles (page 272) karyotype, sex chromosomes, autosomes, X and Y chromosomes, pedigree ...
Lecture 36 “Genes, Development, and Evolution” PPT Review What
... 2.) Chick Embryo slide: What gene(s) must be expressed for the forelimb to form? What gene(s) must be expressed for the ribs to form? Using this, why are there no forelimbs in snakes? 3.) Snake example: what would cause them to “lose” their hindlimbs? When this pathway is functioning “normally”, wha ...
... 2.) Chick Embryo slide: What gene(s) must be expressed for the forelimb to form? What gene(s) must be expressed for the ribs to form? Using this, why are there no forelimbs in snakes? 3.) Snake example: what would cause them to “lose” their hindlimbs? When this pathway is functioning “normally”, wha ...
pNZ:vig Vector information: IRES
... Suitable host strain: NZ9000 and other NICE system vectors derivatives ...
... Suitable host strain: NZ9000 and other NICE system vectors derivatives ...
Model organism databases and tools
... Department of Neurobiology A.I.Virtanen Institute for Molecular Sciences ...
... Department of Neurobiology A.I.Virtanen Institute for Molecular Sciences ...
BIOLOGY CHP 9 Fundamental of Genetics
... A pair of traits is __________________ during ___________ formation Each _________ cell only receives ______ gene not two 3. The Law of Independent Assortment One _________________ does not affect another Traits for different _________________ are distributed to _____________ separately GENES and CH ...
... A pair of traits is __________________ during ___________ formation Each _________ cell only receives ______ gene not two 3. The Law of Independent Assortment One _________________ does not affect another Traits for different _________________ are distributed to _____________ separately GENES and CH ...
CentralDogmaNotes
... • The information content of DNA is in the form of specific sequences of nucleotides • The DNA inherited by an organism leads to specific traits by dictating the synthesis of proteins • Gene expression, the process by which DNA directs protein synthesis, includes two stages: transcription and transl ...
... • The information content of DNA is in the form of specific sequences of nucleotides • The DNA inherited by an organism leads to specific traits by dictating the synthesis of proteins • Gene expression, the process by which DNA directs protein synthesis, includes two stages: transcription and transl ...
Basics of DNA
... for several amino acids to form a gene A gene can be as short as 50 nucleotides and as long as 250 million. Humans have over 3 billion nucleotides or 1 billion codons Each gene codes for a certain trait. ...
... for several amino acids to form a gene A gene can be as short as 50 nucleotides and as long as 250 million. Humans have over 3 billion nucleotides or 1 billion codons Each gene codes for a certain trait. ...