Genetic Markers
... • Millions of sites in human DNA are different between individuals • Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in genes or in non-coding DNA may or may not affect phenotype • SNPs can cause Restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) if in a restriction enzyme site • Tandem repeat sequences (or m ...
... • Millions of sites in human DNA are different between individuals • Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in genes or in non-coding DNA may or may not affect phenotype • SNPs can cause Restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) if in a restriction enzyme site • Tandem repeat sequences (or m ...
Evolution- over time new types of organisms are developed from
... Homologous Structures- anatomical structures that happen in different species that originated by heredity from a structure in the most recent common ancestor of the species Analogous Structures- closely related functions but don’t derive from the same ancestral structures Vestigial Structures- struc ...
... Homologous Structures- anatomical structures that happen in different species that originated by heredity from a structure in the most recent common ancestor of the species Analogous Structures- closely related functions but don’t derive from the same ancestral structures Vestigial Structures- struc ...
Basic Principles of Genetics: Printable Crossword Puzzle
... 5. Mendel's principle of genetic inheritance stating that different pairs of genes are passed to offspring independently so that new combinations of genes, present in neither parent, are possible. 9. An alternate form of the same gene. 11. The genetic makeup of an individual for a trait or for all o ...
... 5. Mendel's principle of genetic inheritance stating that different pairs of genes are passed to offspring independently so that new combinations of genes, present in neither parent, are possible. 9. An alternate form of the same gene. 11. The genetic makeup of an individual for a trait or for all o ...
Biol 505 EXAM 1 (100 points): Due Wed 10/14/09 at the beginning
... drawing,identify (1) origin, (2) polarity (5’ and 3’ ends) of all template strands and newly synthesized strands, (3) leading and lagging strands, (4) Okazaki fragments, and (5) location of primers. 5. What are the major classes of RNA? Where would you expect to find each class of RNA within eukaryo ...
... drawing,identify (1) origin, (2) polarity (5’ and 3’ ends) of all template strands and newly synthesized strands, (3) leading and lagging strands, (4) Okazaki fragments, and (5) location of primers. 5. What are the major classes of RNA? Where would you expect to find each class of RNA within eukaryo ...
Mechanisms of Evolution
... • Allele frequency = how often an allele appears in a population. – Remains relatively stable, particularly if the population is large and well-adapted to its environment. – Many factors can change allele frequency: • 1. Mutation • 2. Migration • 3. Random change • 4. Artificial or Natural Selection ...
... • Allele frequency = how often an allele appears in a population. – Remains relatively stable, particularly if the population is large and well-adapted to its environment. – Many factors can change allele frequency: • 1. Mutation • 2. Migration • 3. Random change • 4. Artificial or Natural Selection ...
Genetic Keywords - St. Jude Children`s Research Hospital
... change (mutation) is present in one or more genes within the body’s cells. Hereditary: Passed down from one generation to the next within a family. ...
... change (mutation) is present in one or more genes within the body’s cells. Hereditary: Passed down from one generation to the next within a family. ...
Mutations
... Genotypic variation leads to phenotypic variation. Genotypic variation is stored in a population’s gene pool. Made up of all alleles in a population Allele combinations form when organisms have offspring. ...
... Genotypic variation leads to phenotypic variation. Genotypic variation is stored in a population’s gene pool. Made up of all alleles in a population Allele combinations form when organisms have offspring. ...
PPT File
... heritable traits passed from one generation to the next or where heritable variation came from. ...
... heritable traits passed from one generation to the next or where heritable variation came from. ...
Lesson Overview
... heritable traits passed from one generation to the next or where heritable variation came from. ...
... heritable traits passed from one generation to the next or where heritable variation came from. ...
EXAM 3-A
... 23. Through ______________ individuals with phenotypes more attractive to mates tend to reproduce more than other individuals, hence the alleles associated with the favored phenotype increase in frequency in the population over time. a) natural selection b) sexual selection c) directional selection ...
... 23. Through ______________ individuals with phenotypes more attractive to mates tend to reproduce more than other individuals, hence the alleles associated with the favored phenotype increase in frequency in the population over time. a) natural selection b) sexual selection c) directional selection ...
Population
... equilibrium can result in evolution. The five requirements for genetic equilibrium can be disrupted by the following outside forces: ...
... equilibrium can result in evolution. The five requirements for genetic equilibrium can be disrupted by the following outside forces: ...
The Family that Walks on All Fours: Evolution in Reverse
... 19 What does it mean if changing their environment (physical therapy) creates a change in the genetic disorder of the quadruped children? 20 What was the scientific resolution of this family’s genetic disorder? How has moths of physical therapy changed the family? ...
... 19 What does it mean if changing their environment (physical therapy) creates a change in the genetic disorder of the quadruped children? 20 What was the scientific resolution of this family’s genetic disorder? How has moths of physical therapy changed the family? ...
Genetic modification: an overview for non
... is called genetic modification or genetic engineering. There are three major differences between selective breeding and genetic modification: ...
... is called genetic modification or genetic engineering. There are three major differences between selective breeding and genetic modification: ...
Evolution: Constructing a Fundamental Scientific Theory
... Evolutionary Synthesis Four mechanisms for evolution: Mutation: a change in genetic information; adds new genetic material; can be good/bad/neutral Gene flow: organism’s migrate and mate with a new group. The merging of new gene pools creates variation Genetic drift: when a group is small, some tra ...
... Evolutionary Synthesis Four mechanisms for evolution: Mutation: a change in genetic information; adds new genetic material; can be good/bad/neutral Gene flow: organism’s migrate and mate with a new group. The merging of new gene pools creates variation Genetic drift: when a group is small, some tra ...
Population Genetics Ch 11
... No mutations - no new alleles can be added to gene pool Random mating - no sexual selection No natural selection - all traits aid in survival equally ...
... No mutations - no new alleles can be added to gene pool Random mating - no sexual selection No natural selection - all traits aid in survival equally ...
MECHANISMS AND PATTERNS OF EVOLUTION
... continuous. New species would arise by the very gradual collection of minor changes in a population (2) Punctuated Equilibrium – A theory that proposes that species are relatively stable for long periods of time (several million years). This stability is interrupted by brief periods during which maj ...
... continuous. New species would arise by the very gradual collection of minor changes in a population (2) Punctuated Equilibrium – A theory that proposes that species are relatively stable for long periods of time (several million years). This stability is interrupted by brief periods during which maj ...
4- Random change student
... The Hardy-Weinberg principle shows that if a certain set of conditions are met, the gene pool remains unchanged generation after generation. By showing what needs to happen to keep the gene pool unchanged, the principle also outlines what has to happen to change the gene pool. When the gene pool cha ...
... The Hardy-Weinberg principle shows that if a certain set of conditions are met, the gene pool remains unchanged generation after generation. By showing what needs to happen to keep the gene pool unchanged, the principle also outlines what has to happen to change the gene pool. When the gene pool cha ...
Cracking the code of life
... Period: _______ 1. What percentage of genes do humans share with bananas? 2. What do you think the message is that has gotten passed from the first form of life? ...
... Period: _______ 1. What percentage of genes do humans share with bananas? 2. What do you think the message is that has gotten passed from the first form of life? ...
AS 90715 version 2 Describe the role of DNA in relation to gene
... gene-environment interactions: Gene-environment interactions include examples of modification of phenotype by environment, eg determination of sex in crocodile hatchlings by temperature. mutations: selected from o gene mutations o chromosomal mutations the control of metabolic pathways by gene ...
... gene-environment interactions: Gene-environment interactions include examples of modification of phenotype by environment, eg determination of sex in crocodile hatchlings by temperature. mutations: selected from o gene mutations o chromosomal mutations the control of metabolic pathways by gene ...
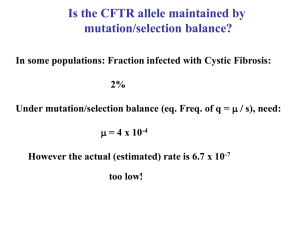
Is the CFTR allele maintained by mutation/selection balance?
... are determined by different, selective processes. ...
... are determined by different, selective processes. ...
Opposing Effects Of Sodium Function Channel
... 3. / One of the four variants of the SCN2A gene 6. / Repeating words or phrases that they hear, a behavior called 8. / are integral membrane proteins that form ion channels, conducting sodium ions (Na ) through a cell's plasma membrane. 10. benign. 11. / the changing of the structure of a gene, resu ...
... 3. / One of the four variants of the SCN2A gene 6. / Repeating words or phrases that they hear, a behavior called 8. / are integral membrane proteins that form ion channels, conducting sodium ions (Na ) through a cell's plasma membrane. 10. benign. 11. / the changing of the structure of a gene, resu ...