Transcription and Translation
... the appearance in a phenotype characteristic or effect attributed to a particular gene ...
... the appearance in a phenotype characteristic or effect attributed to a particular gene ...
The Universal Genetic Code - Willimon-PHS
... character - a recognizable feature controlled by genetics (ex: fur color) trait - a version of a character (ex: white fur) allele - the section of DNA that codes for a specific trait genotype - an organism’s genetic makeup for a character (ex: Ww) phenotype - an organism’s appearance for a character ...
... character - a recognizable feature controlled by genetics (ex: fur color) trait - a version of a character (ex: white fur) allele - the section of DNA that codes for a specific trait genotype - an organism’s genetic makeup for a character (ex: Ww) phenotype - an organism’s appearance for a character ...
Review - Molecular and Cell Biology
... most mutations are spontaneous and rare DNA repair mechanisms eliminate most mutations mutagens such as Xrays or chemicals like EMS can greatly increase the mutation rate, and are essential tools for experimental isolation of mutants Mutations can affect the DNA sequence of genes in a variety of way ...
... most mutations are spontaneous and rare DNA repair mechanisms eliminate most mutations mutagens such as Xrays or chemicals like EMS can greatly increase the mutation rate, and are essential tools for experimental isolation of mutants Mutations can affect the DNA sequence of genes in a variety of way ...
Genomes and their evolution
... •During a process called, transposition, a transposable element moves from one site in a cells DNA to a different target sit by a type of recombination process. •These stretches of DNA move from one location to another in the genome with the aid of an enzyme, transposase. •Transposase can interrupt ...
... •During a process called, transposition, a transposable element moves from one site in a cells DNA to a different target sit by a type of recombination process. •These stretches of DNA move from one location to another in the genome with the aid of an enzyme, transposase. •Transposase can interrupt ...
Population Genetics & Evolution
... • Gene flow - transport of genes by migrating individuals Genes are lost from the gene pool when an individual leaves a population; genes are added when an individual enters a population QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
... • Gene flow - transport of genes by migrating individuals Genes are lost from the gene pool when an individual leaves a population; genes are added when an individual enters a population QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. ...
Document
... Genetic Engineering- manipulating genes for practical purposes Examples 1. Medicine Many medicines, such as the ones used to treat burns, are produced by genetic engineering techniques. 2. Vaccines A person vaccinated with a genetically engineered vaccine will make antibodies against the virus. The ...
... Genetic Engineering- manipulating genes for practical purposes Examples 1. Medicine Many medicines, such as the ones used to treat burns, are produced by genetic engineering techniques. 2. Vaccines A person vaccinated with a genetically engineered vaccine will make antibodies against the virus. The ...
Biology or Genes?
... – Incest taboos prohibit mating between closely related individuals, making inbreeding less common than random • Increases heterozygosity ...
... – Incest taboos prohibit mating between closely related individuals, making inbreeding less common than random • Increases heterozygosity ...
Document
... predict the probability of traits in offspring. 24. DOMINANT- a trait or characteristic that shows up most often in an organism. 25. RECESSIVE- a trait that is less likely to show up in an organism. 26. ALLELE- another word for a “gene” 27. HETEROZYGOUS- having 2 different genes (alleles) for a sing ...
... predict the probability of traits in offspring. 24. DOMINANT- a trait or characteristic that shows up most often in an organism. 25. RECESSIVE- a trait that is less likely to show up in an organism. 26. ALLELE- another word for a “gene” 27. HETEROZYGOUS- having 2 different genes (alleles) for a sing ...
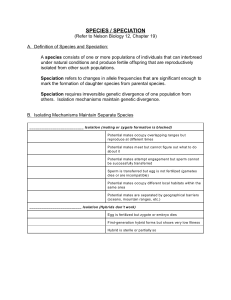
species / speciation
... A species consists of one or more populations of individuals that can interbreed under natural conditions and produce fertile offspring that are reproductively isolated from other such populations. Speciation refers to changes in allele frequencies that are significant enough to mark the formation o ...
... A species consists of one or more populations of individuals that can interbreed under natural conditions and produce fertile offspring that are reproductively isolated from other such populations. Speciation refers to changes in allele frequencies that are significant enough to mark the formation o ...
to the definitions in Word format
... splicing are terms for the process of manipulating genes, generally if the process is outside the organism's natural reproductive process. The genotype is the specific genetic genome of an individual, in the form of DNA Phenotype: The phenotype of an individual organism is either its total physical ...
... splicing are terms for the process of manipulating genes, generally if the process is outside the organism's natural reproductive process. The genotype is the specific genetic genome of an individual, in the form of DNA Phenotype: The phenotype of an individual organism is either its total physical ...
Structural Changes
... • _______ X ______ --> hybrid has 18 chromosomes, but meiosis is abnormal. • Nondisjunction in a meristematic cell --> 36 chromosomes. • The cell is said to be allopolyploid (allotetraploid). • Normal meiosis! • These plants are self-fertile, so can produce offspring, even if there is only one such ...
... • _______ X ______ --> hybrid has 18 chromosomes, but meiosis is abnormal. • Nondisjunction in a meristematic cell --> 36 chromosomes. • The cell is said to be allopolyploid (allotetraploid). • Normal meiosis! • These plants are self-fertile, so can produce offspring, even if there is only one such ...
Guided Notes-Genetic Code
... What is the three base code known as? How many codons are there? How many code for amino acids? There are 61 codons that code for amino acids but only 20 amino acids. Explain Give an example of above What are the other three codons for? Is there a start codon? Is the genetic code universal? What is ...
... What is the three base code known as? How many codons are there? How many code for amino acids? There are 61 codons that code for amino acids but only 20 amino acids. Explain Give an example of above What are the other three codons for? Is there a start codon? Is the genetic code universal? What is ...
Guided Reading Chapter 2: Modern Genetics
... 7. Is the following sentence true or false? Cloning can be done only in animals. 8. In genetic engineering, genes from one organism are transferred into the _______________ of another organism. 9. Complete this flowchart about genetic engineering in bacteria. Human DNA is spliced into the __________ ...
... 7. Is the following sentence true or false? Cloning can be done only in animals. 8. In genetic engineering, genes from one organism are transferred into the _______________ of another organism. 9. Complete this flowchart about genetic engineering in bacteria. Human DNA is spliced into the __________ ...
Is this human gene robbery
... point. . Leading biotechnology companies feel a blanket denial of patents on genes and DNA sequences is a retrograde step, since it will slow down interest and investment in the development of new drugs through application of gene-based genetic technologies. WHAT’S PATENTABLE? ...
... point. . Leading biotechnology companies feel a blanket denial of patents on genes and DNA sequences is a retrograde step, since it will slow down interest and investment in the development of new drugs through application of gene-based genetic technologies. WHAT’S PATENTABLE? ...
6.2 Human Genetic Disorders
... 7.2.d Students know plant and animal cells contain many thousands of different genes and typically have two copies of every gene. The two copies (or alleles) of the gene may or may not be identical, and one may be dominant in determining the phenotype while the other is recessive. ...
... 7.2.d Students know plant and animal cells contain many thousands of different genes and typically have two copies of every gene. The two copies (or alleles) of the gene may or may not be identical, and one may be dominant in determining the phenotype while the other is recessive. ...
USC3002_2008.Lect5 - Department of Mathematics
... 3. Replication : How is the blueprint replicated whenever a cell divides so that each new cell may have a copy ? ...
... 3. Replication : How is the blueprint replicated whenever a cell divides so that each new cell may have a copy ? ...
Artificial Selection
... • Humans choosing traits desirable to them rather than nature choosing traits that are passed on • Humans have an effect on the evolution of a species rather than letting nature choose the path of evolution ...
... • Humans choosing traits desirable to them rather than nature choosing traits that are passed on • Humans have an effect on the evolution of a species rather than letting nature choose the path of evolution ...
Chapter 11 Quiz
... 7. Use Figure 11±3 to answer the following question. If a pea plant that is heterozygous for round, yellow peas (RrYy) is crossed with a pea plant that is homozygous for round peas but heterozygous for yellow peas (RRYy), how many different phenotypes are their offspring expected to show? a. 2 b. 4 ...
... 7. Use Figure 11±3 to answer the following question. If a pea plant that is heterozygous for round, yellow peas (RrYy) is crossed with a pea plant that is homozygous for round peas but heterozygous for yellow peas (RRYy), how many different phenotypes are their offspring expected to show? a. 2 b. 4 ...
EOC Practice Quiz (5) - Duplin County Schools
... 11. Transgenic organisms are useful because they a. are a source of human proteins. b. produce crops resistant to insect damage. c. improve the food supply. d. all of the above. 12. Any organism that has a gene from another species in its genome is considered transgenic. a. True b. false 13. Which o ...
... 11. Transgenic organisms are useful because they a. are a source of human proteins. b. produce crops resistant to insect damage. c. improve the food supply. d. all of the above. 12. Any organism that has a gene from another species in its genome is considered transgenic. a. True b. false 13. Which o ...
Paul Wordsworth
... people that exhibits dominant inheritance. This means that parents with the condition have a 50% chance of passing the condition on to their child each time they conceive. It is caused by a very specific change (mutation) in a single gene (FGFR3) on chromosome 4 that controls bone growth. As describ ...
... people that exhibits dominant inheritance. This means that parents with the condition have a 50% chance of passing the condition on to their child each time they conceive. It is caused by a very specific change (mutation) in a single gene (FGFR3) on chromosome 4 that controls bone growth. As describ ...
Mendel and Heredity
... Why are some physical traits more common than others? An organism’s physical traits are determined by its genetic makeup. Most organisms inherit two versions of a gene for each physical trait. Sometimes, one gene is “dominant” over another “recessive” gene. When and organism inherits two dominant ge ...
... Why are some physical traits more common than others? An organism’s physical traits are determined by its genetic makeup. Most organisms inherit two versions of a gene for each physical trait. Sometimes, one gene is “dominant” over another “recessive” gene. When and organism inherits two dominant ge ...
Mendellian Madness! - Effingham County Schools
... dihybrid cross involves 2 characters, such as seed color and seed shape. ...
... dihybrid cross involves 2 characters, such as seed color and seed shape. ...
Unit 4 Resources - Schoolwires.net
... 8. The amino acid __________________________ is represented by the mRNA codon ACA. 9. ________________________ and ________________________ are mRNA codons for phenylalanine. 10. There can be more than one __________________________ for the same amino acid. 11. For any one codon, there can be only o ...
... 8. The amino acid __________________________ is represented by the mRNA codon ACA. 9. ________________________ and ________________________ are mRNA codons for phenylalanine. 10. There can be more than one __________________________ for the same amino acid. 11. For any one codon, there can be only o ...