Founder effects in human populations
... Due to various migrations throughout human history, founder effects are somewhat common among humans in different times and places. The effective founder population of Quebec was only 2,600. After twelve to sixteen generations, with an eightyfold growth but only minimal gene dilution from intermarri ...
... Due to various migrations throughout human history, founder effects are somewhat common among humans in different times and places. The effective founder population of Quebec was only 2,600. After twelve to sixteen generations, with an eightyfold growth but only minimal gene dilution from intermarri ...
Honors Genetics Chapter 4 Vocabulary We learned several new
... 16. The progressively earlier onset and severity of a disorder from generation to generation GENETIC ANTICIPATION 17. Extranuclear inheritance through the mitochondrial or chloroplast DNA HEREDITY 18. Expression of one gene or gene pair modifies the expression of another gene EPISTASIS 19. The joint ...
... 16. The progressively earlier onset and severity of a disorder from generation to generation GENETIC ANTICIPATION 17. Extranuclear inheritance through the mitochondrial or chloroplast DNA HEREDITY 18. Expression of one gene or gene pair modifies the expression of another gene EPISTASIS 19. The joint ...
Population Genetics: Genetic Drift, Natural Selection, and Mutation.
... Vocabulary: Mitosis: The identical division of a parent cell into two daughter cells. Meiosis: The creation of four haploid non-identical daughter cells from a single diploid parental cell. Meiosis results in the creation of gamete cells. Heterozygous: Two alleles for the same gene are different. Ho ...
... Vocabulary: Mitosis: The identical division of a parent cell into two daughter cells. Meiosis: The creation of four haploid non-identical daughter cells from a single diploid parental cell. Meiosis results in the creation of gamete cells. Heterozygous: Two alleles for the same gene are different. Ho ...
BIOLOGY 210 FALL 2004
... Course goals and requirements: This course is designed for students to gain a fundamental understanding of human genetics. Genetics is the study of inherited traits and their variation. We will explore all aspects of genetics, including DNA, genes, chromosomes, and genomes. We will examine genetics ...
... Course goals and requirements: This course is designed for students to gain a fundamental understanding of human genetics. Genetics is the study of inherited traits and their variation. We will explore all aspects of genetics, including DNA, genes, chromosomes, and genomes. We will examine genetics ...
here - Quia
... 10. Given a DNA template, know how to transcribe and translate it. 11. Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA. 12. Discuss the different types of mutations and their effect on protein synthesis. 13. Identify the location where protein synthesis in a eukaryotic cell. 14. List and explain ...
... 10. Given a DNA template, know how to transcribe and translate it. 11. Distinguish between prokaryotic and eukaryotic DNA. 12. Discuss the different types of mutations and their effect on protein synthesis. 13. Identify the location where protein synthesis in a eukaryotic cell. 14. List and explain ...
Multiple choice questions
... Are always in front of genes Consist of consensus sequences Are binding sites for RNA polymerases Are rich in G and C nucleotides Are only found with protein-coding genes Are very similar in prokaryotes and eukaryotes ...
... Are always in front of genes Consist of consensus sequences Are binding sites for RNA polymerases Are rich in G and C nucleotides Are only found with protein-coding genes Are very similar in prokaryotes and eukaryotes ...
Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium Gene Pools Gene Pool Practice Hardy
... gene pool divided by the total # of allele in the gene pool ...
... gene pool divided by the total # of allele in the gene pool ...
Genetics Online Scavenger Hunt
... What is a Gene? What is a Chromosome? What is a protein? What is Heredity? What is a Trait? 3. As you go from one tutorial to the next answer the corresponding questions for each topic. ...
... What is a Gene? What is a Chromosome? What is a protein? What is Heredity? What is a Trait? 3. As you go from one tutorial to the next answer the corresponding questions for each topic. ...
Document
... Multiple alleles involves a situation when more than two alleles are found on a gene. Polygenic inheritance is a situation when multiple genes determine the phenotype of a trait. Evolution and its Evidence Natural selection is the process that allows for only some individuals to survive when t ...
... Multiple alleles involves a situation when more than two alleles are found on a gene. Polygenic inheritance is a situation when multiple genes determine the phenotype of a trait. Evolution and its Evidence Natural selection is the process that allows for only some individuals to survive when t ...
click here
... 1. The recognition sequence is GG(A/T)CC. For positions 1,2,4 and 5 in this sequence only 1 base out of four will lead to cutting. For positions 3 in the sequence, two bases out of 4 will lead to cutting. Therefore, the odds of having this exact sequence in a random DNA molecule will be: 1/4 x1/4 x ...
... 1. The recognition sequence is GG(A/T)CC. For positions 1,2,4 and 5 in this sequence only 1 base out of four will lead to cutting. For positions 3 in the sequence, two bases out of 4 will lead to cutting. Therefore, the odds of having this exact sequence in a random DNA molecule will be: 1/4 x1/4 x ...
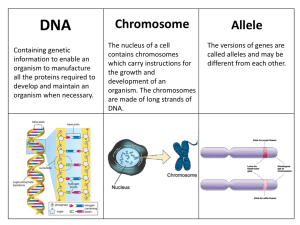
Chromosome Allele - GZ @ Science Class Online
... 2 different alleles this is called heterozygous and the cell always uses the ...
... 2 different alleles this is called heterozygous and the cell always uses the ...
Chapter 14
... • Enzymes repair most DNA that is mismatched during replication, but rarely, some DNA is not repaired. • The rate of mutation can be increased by some environmental factors. Such factors, called mutagens, include many forms of radiation and some kinds of chemicals. ...
... • Enzymes repair most DNA that is mismatched during replication, but rarely, some DNA is not repaired. • The rate of mutation can be increased by some environmental factors. Such factors, called mutagens, include many forms of radiation and some kinds of chemicals. ...
Gene mutations and their effects
... chromosomes may be broken. Although cells have enzymes that can repair such breaks, chromosomes can still undergo permanent change, for two reasons: • a break is not always repaired • if two breaks do occur, the ‘wrong’ ends may be rejoined. As a result of a structural change, a chromosome will no ...
... chromosomes may be broken. Although cells have enzymes that can repair such breaks, chromosomes can still undergo permanent change, for two reasons: • a break is not always repaired • if two breaks do occur, the ‘wrong’ ends may be rejoined. As a result of a structural change, a chromosome will no ...
Part_2
... people to think this gene is the explanation for why people are unique Too early! "In virtually all cases, the link of genes or genomic patterns with human brain evolution is only tentative and based on suggestive evidence," says Bruce Lahn, a human geneticist at the University of Chicago, Illinoi ...
... people to think this gene is the explanation for why people are unique Too early! "In virtually all cases, the link of genes or genomic patterns with human brain evolution is only tentative and based on suggestive evidence," says Bruce Lahn, a human geneticist at the University of Chicago, Illinoi ...
Genetics
... factors (genes) for certain characteristics are passed from parents to the next generation separate from the other factors or genes that transmit other traits. ...
... factors (genes) for certain characteristics are passed from parents to the next generation separate from the other factors or genes that transmit other traits. ...
Unit 2 - Molecular and genetic factors in disease
... genes on the X chromosomes and this process of inactivation is random , This can have a bearing on the expression of diseases which are due to mutations in genes on the X chromosome as either the normal or the mutant gene may be inactivated. ...
... genes on the X chromosomes and this process of inactivation is random , This can have a bearing on the expression of diseases which are due to mutations in genes on the X chromosome as either the normal or the mutant gene may be inactivated. ...
Review of Genetics Genes Punnett Square Example Incidence of
... did not have them. The woman in this couple has no freckles. What percentage of the children will have freckles? ...
... did not have them. The woman in this couple has no freckles. What percentage of the children will have freckles? ...
Human Genome Project
... Precisely diagnose disease and ensure the most effective treatment Developing new treatments at the molecular level ...
... Precisely diagnose disease and ensure the most effective treatment Developing new treatments at the molecular level ...
natural selection - sciencesebastian
... generation until the population grew large enough for sampling errors to be minimal. • Founder effects have been demonstrated in human populations that started from a small group of colonists. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
... generation until the population grew large enough for sampling errors to be minimal. • Founder effects have been demonstrated in human populations that started from a small group of colonists. Copyright © 2002 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings ...
Model organisms: the genes we share
... Model organisms: the genes we share Introduction In this activity you will discover why scientists use different organisms to study human genetics and human disease. Model organisms can be used to test hypotheses or treatments such as new drugs. With model organisms, answers to scientific questions ...
... Model organisms: the genes we share Introduction In this activity you will discover why scientists use different organisms to study human genetics and human disease. Model organisms can be used to test hypotheses or treatments such as new drugs. With model organisms, answers to scientific questions ...
Genes have fixed positions on chromosomes.
... Her first contribution was built on the idea that genes were located on chromosomes. She took the ten linkage groups of maize and connected each with a specific chromosome. Her microscopic observations were so exact that she was able to observe recombination events and show that they corresponded wi ...
... Her first contribution was built on the idea that genes were located on chromosomes. She took the ten linkage groups of maize and connected each with a specific chromosome. Her microscopic observations were so exact that she was able to observe recombination events and show that they corresponded wi ...