Mutations - WordPress.com
... • Also known as point mutations – involve changes to the bases in the DNA sequence = they occur within a gene. • A change in the base sequence then results = producing a new allele. • 3 bases are called a triplet – these code for an amino acid – which make up proteins. ** Any change in the bases ma ...
... • Also known as point mutations – involve changes to the bases in the DNA sequence = they occur within a gene. • A change in the base sequence then results = producing a new allele. • 3 bases are called a triplet – these code for an amino acid – which make up proteins. ** Any change in the bases ma ...
Introduction to Genetics PP
... • What did the F1 hybrids look like? Did they look like a blend of both parents? No! • All F1 offspring only showed the character of one parent. ...
... • What did the F1 hybrids look like? Did they look like a blend of both parents? No! • All F1 offspring only showed the character of one parent. ...
Review Questions yeast lecture 18
... 2. What is a model organism (=what are the basic requirements for a model organism) (1) ...
... 2. What is a model organism (=what are the basic requirements for a model organism) (1) ...
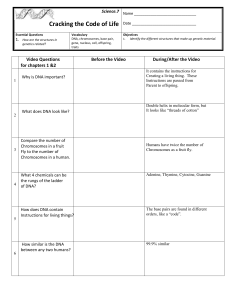
Science.7 Cracking the Code of Life Name Date Essential Questions
... Objectives 1. Identify the different structures that make up genetic material. ...
... Objectives 1. Identify the different structures that make up genetic material. ...
Strand 5 Multiple Choice Questions 030413
... C. Fossil species W had greater genetic variability than fossil species V, allowing fossil species W to adapt and survive longer. D. Fossil species W had lower reproductive success than fossil species V, allowing smaller populations to adapt and survive. ...
... C. Fossil species W had greater genetic variability than fossil species V, allowing fossil species W to adapt and survive longer. D. Fossil species W had lower reproductive success than fossil species V, allowing smaller populations to adapt and survive. ...
IB Biology--Chromosome Review Activity
... Page 2 of 5 8. The ______________is the specified position of a gene on a chromosome. 9. Use the 10p42 reference to a chromosome to identify the significance of the 10, the p, and the ...
... Page 2 of 5 8. The ______________is the specified position of a gene on a chromosome. 9. Use the 10p42 reference to a chromosome to identify the significance of the 10, the p, and the ...
Computational Insights and the Theory of Evolution
... landscapes of this form • Unless peak > 2 plateau, in sexual reproduction the plateau will dominate and the peaks will become extinct • In asexual reproduction, the peaks will always dominate and the plateau will ...
... landscapes of this form • Unless peak > 2 plateau, in sexual reproduction the plateau will dominate and the peaks will become extinct • In asexual reproduction, the peaks will always dominate and the plateau will ...
Natural selection
... The Hardy-Weinberg principle states that allele frequencies in a population will remain constant unless one or more factors cause those frequencies to change. When allele frequencies remain constant it is called genetic equilibrium. ...
... The Hardy-Weinberg principle states that allele frequencies in a population will remain constant unless one or more factors cause those frequencies to change. When allele frequencies remain constant it is called genetic equilibrium. ...
Senescence
... Mutations will accumulate – a cost of clonal reproduction Even though the nucleus of the egg is removed, some of the egg-donors genes remain, in the mitochondria – thus the first generation is not a perfect clone ...
... Mutations will accumulate – a cost of clonal reproduction Even though the nucleus of the egg is removed, some of the egg-donors genes remain, in the mitochondria – thus the first generation is not a perfect clone ...
violence-gene-articl..
... The finding thrilled some scientists--here, finally, was an explanation for criminality--and appalled others, who feared that if genes dictate behavior, it could lead to genetic typecasting of entire races. But lots of violent men don't have the defective gene, while many non-criminals do. Here, too ...
... The finding thrilled some scientists--here, finally, was an explanation for criminality--and appalled others, who feared that if genes dictate behavior, it could lead to genetic typecasting of entire races. But lots of violent men don't have the defective gene, while many non-criminals do. Here, too ...
Glia and Genetic
... i. Mutation in the Huntingtin gene on chr4 (unknown function) ii. Autosomal dominant w/ full penetrance 1. inherit gene develop disease 2. identical twins (monozygotic, same genes) – 100% concordance 3. fraternal twins (dizygotic, 50% genes identical) – 50% c. Pathogenesis: i. Normal gene has 11-3 ...
... i. Mutation in the Huntingtin gene on chr4 (unknown function) ii. Autosomal dominant w/ full penetrance 1. inherit gene develop disease 2. identical twins (monozygotic, same genes) – 100% concordance 3. fraternal twins (dizygotic, 50% genes identical) – 50% c. Pathogenesis: i. Normal gene has 11-3 ...
High School Biology/Life Science Core Course Content
... New traits may result from new combinations of Account for the appearance of a novel trait that existing genes or from mutations of genes in arose in a given population. (5.3.12.E.1) reproductive cells within a population. Instructional Focus: • Recognizing how heritable characteristics can strongly ...
... New traits may result from new combinations of Account for the appearance of a novel trait that existing genes or from mutations of genes in arose in a given population. (5.3.12.E.1) reproductive cells within a population. Instructional Focus: • Recognizing how heritable characteristics can strongly ...
Ch. 9: Presentation Slides
... spontaneous mutation original found in cv. McIntosh) is caused by mutation at one single locus Wild type ...
... spontaneous mutation original found in cv. McIntosh) is caused by mutation at one single locus Wild type ...
Student Name: Teacher
... Break down quickly after transferring genetic material. Insert DNA into the organisms they affect. Store large strands of DNA or even entire chromosomes. ...
... Break down quickly after transferring genetic material. Insert DNA into the organisms they affect. Store large strands of DNA or even entire chromosomes. ...
Chapter7-Natural_Selection
... genetics of a population over generations (evolution). • Other factors that can change genetics of a population include migration, sexual selection, mutations, and effects of random events in small populations. ...
... genetics of a population over generations (evolution). • Other factors that can change genetics of a population include migration, sexual selection, mutations, and effects of random events in small populations. ...
Topic 4: Genetics - Peoria Public Schools
... 63. The Human Genome Project sequenced the entire human genome and found there to be 25000 to 30000 genes. Not only did the project strive to find the total genes but it attempted to find each gene’s location and each gene’s base sequence. 64. Benefits of the Human Genome Project include the ability ...
... 63. The Human Genome Project sequenced the entire human genome and found there to be 25000 to 30000 genes. Not only did the project strive to find the total genes but it attempted to find each gene’s location and each gene’s base sequence. 64. Benefits of the Human Genome Project include the ability ...
Aquaculture Science
... • Developed by R.C. Punnett • illustrates the possible combinations for a particular trait rr r ...
... • Developed by R.C. Punnett • illustrates the possible combinations for a particular trait rr r ...
Evoluce genomů
... two substitution occured in the human lineage during the 4-6 Myr since it separated from chimpanzees! this gene is virtually invariant in another 28 orders of mammals that last shared common ancestor around 100 million years ago ...
... two substitution occured in the human lineage during the 4-6 Myr since it separated from chimpanzees! this gene is virtually invariant in another 28 orders of mammals that last shared common ancestor around 100 million years ago ...
PowerPoint Lecture Chapter 11
... lifestyle and marry other members of their community. By chance, at least one of the original 30 Amish settlers in this community carried a recessive allele that results in short arms and legs and extra fingers and toes in offspring. Because of small gene pool, many individuals inherited the recessi ...
... lifestyle and marry other members of their community. By chance, at least one of the original 30 Amish settlers in this community carried a recessive allele that results in short arms and legs and extra fingers and toes in offspring. Because of small gene pool, many individuals inherited the recessi ...
Week10
... • The key to understanding evolution in nature lies in the basic biology of reproduction • The chromosome is the basic carrier of the genes, which are the units of the genetic code that control an individual’s characteristics. Each gene can take on one of a number of possible forms, called an allele ...
... • The key to understanding evolution in nature lies in the basic biology of reproduction • The chromosome is the basic carrier of the genes, which are the units of the genetic code that control an individual’s characteristics. Each gene can take on one of a number of possible forms, called an allele ...
Human Genome Project - College Heights Secondary School
... How they did it… • DNA from 5 humans • 2 males, 3 females • 2 caucasians, one each of asian, african, hispanic • Cut up DNA with restriction enzymes ...
... How they did it… • DNA from 5 humans • 2 males, 3 females • 2 caucasians, one each of asian, african, hispanic • Cut up DNA with restriction enzymes ...
CDOs (Creative Designer Organisms)
... demonstration of the presence of transmissible antibiotic-resistance genes in the human food chain. The resistant bacteria probably originated from antibiotic treatment of the cows. As lactococci may be found together with enterococci and staphylococci as part of the cows microflora, resistance tran ...
... demonstration of the presence of transmissible antibiotic-resistance genes in the human food chain. The resistant bacteria probably originated from antibiotic treatment of the cows. As lactococci may be found together with enterococci and staphylococci as part of the cows microflora, resistance tran ...