Ch - TeacherWeb
... Human gene diversity is estimated to be about 14%, which means that a. 86% of our genes are identical b. on average, 14% of an individual's gene loci are heterozygous c. only 14% of nucleotide sites differ between individuals d. nucleotide diversity must be very great between individuals e. the huma ...
... Human gene diversity is estimated to be about 14%, which means that a. 86% of our genes are identical b. on average, 14% of an individual's gene loci are heterozygous c. only 14% of nucleotide sites differ between individuals d. nucleotide diversity must be very great between individuals e. the huma ...
Multiple Choice Questions – Answers
... cells. Mitotic division results in daughter cells containing a full number of genes as the parent cell they came from. 5. The type of cell division that occurs in the gamete cells is known as: A Cytosis B Meiosis [True] C Osmosis D Mitosis The correct answer is B. Meiosis is the cell division proces ...
... cells. Mitotic division results in daughter cells containing a full number of genes as the parent cell they came from. 5. The type of cell division that occurs in the gamete cells is known as: A Cytosis B Meiosis [True] C Osmosis D Mitosis The correct answer is B. Meiosis is the cell division proces ...
Shaelynn Sleater-Squires La Kretz Graduate Grant 2014-2015
... of natural spaces spawns small wildlife populations, which are prone to loss of genetic diversity due to drift and inbreeding risk, thus putting their long-term viability in jeopardy. Mammalian carnivores seem to be particularly susceptible to local extinction in fragmented areas due to their small ...
... of natural spaces spawns small wildlife populations, which are prone to loss of genetic diversity due to drift and inbreeding risk, thus putting their long-term viability in jeopardy. Mammalian carnivores seem to be particularly susceptible to local extinction in fragmented areas due to their small ...
Genetics Vocabulary Note-Taking Chart
... The passing of traits from parents to The heredity of the English Royal family offspring was well known. Alleles, n. Alternate form of a gene. The alleles for You ________________ one allele from a trait occupy the your ______________ and one from your _____________________ on homologous ___________ ...
... The passing of traits from parents to The heredity of the English Royal family offspring was well known. Alleles, n. Alternate form of a gene. The alleles for You ________________ one allele from a trait occupy the your ______________ and one from your _____________________ on homologous ___________ ...
MCA Review Part 3 File
... Sexual vs Asexual Reproduction 3. There are both advantages and disadvantages to both sexual and asexual reproduction. Fill in the charts below: Sexual Reproduction: ...
... Sexual vs Asexual Reproduction 3. There are both advantages and disadvantages to both sexual and asexual reproduction. Fill in the charts below: Sexual Reproduction: ...
Microevolution_Macroevolution
... level. So instead of focusing on an individual beetle species, a macroevolutionary lens might require that we zoom out on the tree of life, to assess the diversity of the entire beetle clade and its position on the tree. ...
... level. So instead of focusing on an individual beetle species, a macroevolutionary lens might require that we zoom out on the tree of life, to assess the diversity of the entire beetle clade and its position on the tree. ...
DNA Ligase Joke (insert laughter here)
... These families provided the samples that allowed the gene mutation causing this disease in TMEM43 to be found in Dr. Young’s laboratory. “This made it possible to determine the way the mutation affects individuals across a lifespan and which diagnostic tests are most effective,” said Dr. Hodgkinson. ...
... These families provided the samples that allowed the gene mutation causing this disease in TMEM43 to be found in Dr. Young’s laboratory. “This made it possible to determine the way the mutation affects individuals across a lifespan and which diagnostic tests are most effective,” said Dr. Hodgkinson. ...
HSproteinsynth
... these base pairs are organized into about 1,000 genes. A gene is simply a template for a protein, and often these proteins are enzymes. ...
... these base pairs are organized into about 1,000 genes. A gene is simply a template for a protein, and often these proteins are enzymes. ...
Slide 1
... combining withfrom yourtheir partner’s one from their dad. We will look at size genes today. Turn over the cards to see which gene characteristics (allelles) your lambfrom will carry Each remove the two size gene cards the pack and place them Record your lamb’s gene characteristics on your sheet col ...
... combining withfrom yourtheir partner’s one from their dad. We will look at size genes today. Turn over the cards to see which gene characteristics (allelles) your lambfrom will carry Each remove the two size gene cards the pack and place them Record your lamb’s gene characteristics on your sheet col ...
Evolution CRCT - Effingham County Schools
... B. The animals had no relationship to one another. C. Today's horses and these animals probably lived together at some time in the past. D. Today's horses are faster than these animals were. ...
... B. The animals had no relationship to one another. C. Today's horses and these animals probably lived together at some time in the past. D. Today's horses are faster than these animals were. ...
Transposable elements I. What is a transposable element?
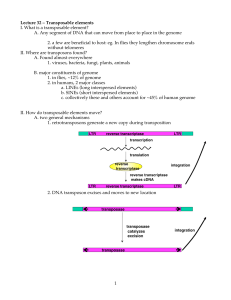
... Lecture 32 – Transposable elements I. What is a transposable element? A. Any segment of DNA that can move from place to place in the genome 2. a few are beneficial to host: eg. In flies they lengthen chromosome ends without telomeres II. Where are transposons found? A. Found almost everywhere 1. vir ...
... Lecture 32 – Transposable elements I. What is a transposable element? A. Any segment of DNA that can move from place to place in the genome 2. a few are beneficial to host: eg. In flies they lengthen chromosome ends without telomeres II. Where are transposons found? A. Found almost everywhere 1. vir ...
Autosomal Recessive Inheritance
... By now you should have discussed this condition with your paediatrician or the National Metabolic Service. You should know what the diagnosis is and how it affects your child. You should also know that it is a genetic disorder that has been inherited from both mum and dad in an autosomal recessive w ...
... By now you should have discussed this condition with your paediatrician or the National Metabolic Service. You should know what the diagnosis is and how it affects your child. You should also know that it is a genetic disorder that has been inherited from both mum and dad in an autosomal recessive w ...
Evolution of Populations (3.1) – Part 2
... A. This set of math equations is used to follow allele frequency within a population or “Gene pool”. 1. If the numbers (rates) change from generation to generation, the population is evolving over time. 2. If the numbers (rates) do not change from generation to generation, the population is not evol ...
... A. This set of math equations is used to follow allele frequency within a population or “Gene pool”. 1. If the numbers (rates) change from generation to generation, the population is evolving over time. 2. If the numbers (rates) do not change from generation to generation, the population is not evol ...
Evolutionary Genetics
... population size (~ 400,000 to 50,000 years ago). Humans are genetically very similar, due in part to a recent population explosion from a relatively small number of individuals within the last few hundreds of thousands of years. ...
... population size (~ 400,000 to 50,000 years ago). Humans are genetically very similar, due in part to a recent population explosion from a relatively small number of individuals within the last few hundreds of thousands of years. ...
iiiliiiltiiliiiitii lilliitlii$itttit ffffli|tiiiiiiHii.
... cells and can causemutations to arise as these cells divide. Manv chemicalsalso can interfere with DNA replication and lead to mutation. Whenever a cell copiesits DNA, there is a small chance it may misread the sequenceand add the wrong nucleotide. Our cells have proofreading proteins that can fix m ...
... cells and can causemutations to arise as these cells divide. Manv chemicalsalso can interfere with DNA replication and lead to mutation. Whenever a cell copiesits DNA, there is a small chance it may misread the sequenceand add the wrong nucleotide. Our cells have proofreading proteins that can fix m ...
Biology Homework Chapter 8
... 4. Describe how multifactorial inheritance explains continuous variation in a trait such as height. ...
... 4. Describe how multifactorial inheritance explains continuous variation in a trait such as height. ...
Chapter 10.3 Notes The Theory of Natural Selection **Key Concept
... a. Darwin noticed a lot of variation in domesticated plants and animals b. Artificial selection is the process by which humans select traits through breeding ...
... a. Darwin noticed a lot of variation in domesticated plants and animals b. Artificial selection is the process by which humans select traits through breeding ...
Figures from Chapter 3
... • Genetic endowment • Common to the species • Governs maturation and aging ...
... • Genetic endowment • Common to the species • Governs maturation and aging ...
Unit 1: Cells, Cell Reproduction, and Development
... In what type of cells does mitosis occur in, and what it is purpose? What are the four phases of mitosis, and in what order do they occur in? What happens during each phase of mitosis? In what type of cells does meiosis occur in, and what it is purpose? What happens during each division of meiosis? ...
... In what type of cells does mitosis occur in, and what it is purpose? What are the four phases of mitosis, and in what order do they occur in? What happens during each phase of mitosis? In what type of cells does meiosis occur in, and what it is purpose? What happens during each division of meiosis? ...
Genetics-Essentials-Concepts-and-Connections
... characteristics during one’s lifetime cannot be passed on to offspring. (F) 19. Many human traits, such as skin and hair color, exhibit blending inheritance, in which genetic information is mixed and is not separated in future generations. (F) 20. Bacteria and viruses can be used to study genes and ...
... characteristics during one’s lifetime cannot be passed on to offspring. (F) 19. Many human traits, such as skin and hair color, exhibit blending inheritance, in which genetic information is mixed and is not separated in future generations. (F) 20. Bacteria and viruses can be used to study genes and ...
Genetic Disorders - armstrong
... remarkable ability to recognize mistakes and fix them before it passes them along to its descendants. But a cell's DNA repair mechanisms can fail, or be overwhelmed, or become less efficient with age. Over time, mistakes can accumulate. ...
... remarkable ability to recognize mistakes and fix them before it passes them along to its descendants. But a cell's DNA repair mechanisms can fail, or be overwhelmed, or become less efficient with age. Over time, mistakes can accumulate. ...
Genetics is
... We now use “ ____________________” to help us predict what the offspring may look like. 15.) Mendel concluded from his experiments that each ____________ has ___ factors for EACH _________________! We now call them _________ which are found on __________________. 16.) ___________- are different gene ...
... We now use “ ____________________” to help us predict what the offspring may look like. 15.) Mendel concluded from his experiments that each ____________ has ___ factors for EACH _________________! We now call them _________ which are found on __________________. 16.) ___________- are different gene ...