Gene Technology
... Requires recognition of coding sequences of gene, including promotors and enhancers ...
... Requires recognition of coding sequences of gene, including promotors and enhancers ...
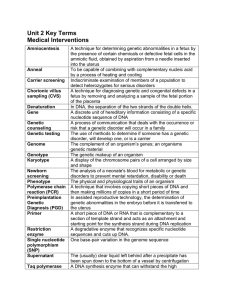
Unit 2 Terms
... and shape The analysis of a neonate's blood for metabolic or genetic disorders to prevent mental retardation, disability or death The physical and physiological traits of an organism A technique that involves copying short pieces of DNA and then making millions of copies in a short period of time In ...
... and shape The analysis of a neonate's blood for metabolic or genetic disorders to prevent mental retardation, disability or death The physical and physiological traits of an organism A technique that involves copying short pieces of DNA and then making millions of copies in a short period of time In ...
Human Genetics Presentations
... dad and a mom who is a carrier for colorblindness to have a child that is colorblind? ...
... dad and a mom who is a carrier for colorblindness to have a child that is colorblind? ...
Section 14–1 Human Heredity
... This section explains what scientists know about human chromosomes, as well as the inheritance of certain human traits and disorders. It also describes how scientists study the inheritance of human traits. ...
... This section explains what scientists know about human chromosomes, as well as the inheritance of certain human traits and disorders. It also describes how scientists study the inheritance of human traits. ...
DNA TESTING FOR INHERITED DISEASES IN DOGS The specific
... When we begin to study a new disease, we first need to establish the mode of inheritance. Disorders which are inherited in a simple fashion, either recessive or dominant, can now be studied at a molecular level - this includes many forms of PRA and haemophilias. Diseases where more than one gene is ...
... When we begin to study a new disease, we first need to establish the mode of inheritance. Disorders which are inherited in a simple fashion, either recessive or dominant, can now be studied at a molecular level - this includes many forms of PRA and haemophilias. Diseases where more than one gene is ...
The making of the Fittest: Natural Selection and Adaptation
... All the cells of the body contain the same genes, but only a subset of those genes is active in any particular cell type. For example, liver cells express a different set of genes than muscle cells. The expression of genes that control development—the process by which a fertilized egg divides, grows ...
... All the cells of the body contain the same genes, but only a subset of those genes is active in any particular cell type. For example, liver cells express a different set of genes than muscle cells. The expression of genes that control development—the process by which a fertilized egg divides, grows ...
Lyonization - National Foundation for Ectodermal Dysplasias
... the egg by the sperm. At this stage, when the dividing conceptus about 16-32 cells big, in each cell one of the two X chromosomes turns off. It stops producing information. This is referred to as X-inactivation, or lyonization (the term lyonization is in honor of Mary Lyon, the scientist who first o ...
... the egg by the sperm. At this stage, when the dividing conceptus about 16-32 cells big, in each cell one of the two X chromosomes turns off. It stops producing information. This is referred to as X-inactivation, or lyonization (the term lyonization is in honor of Mary Lyon, the scientist who first o ...
ECE/PSY171 Chapter 2 Biological Beginnings WHAT IS THE
... Dominant-recessive genes principle-In some cases, one gene of a pair always exerts its effects; it is dominant, overriding the potential influence of the other gens called the recessive gene. A recessive gene exerts its influence only if the two pair are both recessive. If you inherit a recessive ge ...
... Dominant-recessive genes principle-In some cases, one gene of a pair always exerts its effects; it is dominant, overriding the potential influence of the other gens called the recessive gene. A recessive gene exerts its influence only if the two pair are both recessive. If you inherit a recessive ge ...
Chapter 16
... • Relative frequency: how often an allele shows up in a gene pool • Evolution: is a group process “ any change in the relative frequency of alleles in a population” ...
... • Relative frequency: how often an allele shows up in a gene pool • Evolution: is a group process “ any change in the relative frequency of alleles in a population” ...
Meiosis and Sex
... 2. Understand genetic linkage 3. Explain sex-linked genes and why more common in males ...
... 2. Understand genetic linkage 3. Explain sex-linked genes and why more common in males ...
Chromosome vs. Gene Mutations
... Chromosome Damage: Part of a chromosome is repeated. Part of a chromosome is missing. Reversing a fragment of the chromosome. Rearrangement of parts between nonhomologous pairs of chromosomes. ...
... Chromosome Damage: Part of a chromosome is repeated. Part of a chromosome is missing. Reversing a fragment of the chromosome. Rearrangement of parts between nonhomologous pairs of chromosomes. ...
Evolution and Genetics
... Antibiotic-resistant strains of microorganisms that cause diseases, such as tuberculosis, are increasing in number due to natural selection ...
... Antibiotic-resistant strains of microorganisms that cause diseases, such as tuberculosis, are increasing in number due to natural selection ...
Genetic Engineering of Late Blight Resistance in Potato
... Sanwen Huang, Dongyu Qu, Jianfei Xu, Zhiqi Jia, Cuihua Xin, Ying Li, Zhonghua Zhang ...
... Sanwen Huang, Dongyu Qu, Jianfei Xu, Zhiqi Jia, Cuihua Xin, Ying Li, Zhonghua Zhang ...
Human Genetics
... - It also includes DNA sequences that do not encode genes Genomics is a field that analyzes and compares genomes of different species ...
... - It also includes DNA sequences that do not encode genes Genomics is a field that analyzes and compares genomes of different species ...
Genetic Vocabulary - Renton School District
... • Dominance: term given to gene that is expressed phenotypically, no matter what the genotypic make-up; if this gene is present the trait will be seen • Recessive: term given to gene that is only expressed phenotypically if the offspring carries both genes—in other words, received a recessive gene f ...
... • Dominance: term given to gene that is expressed phenotypically, no matter what the genotypic make-up; if this gene is present the trait will be seen • Recessive: term given to gene that is only expressed phenotypically if the offspring carries both genes—in other words, received a recessive gene f ...
Genetics and muscular dystrophy
... eventually ask the same question: How did this happen to my child or spouse? Genetic diseases are seemingly random but scientifically are easily explained. Many people have asked me questions about genetic diseases and the following information is helpful to understand genetic diseases. Chromosomes ...
... eventually ask the same question: How did this happen to my child or spouse? Genetic diseases are seemingly random but scientifically are easily explained. Many people have asked me questions about genetic diseases and the following information is helpful to understand genetic diseases. Chromosomes ...
GENETICS 310-PRINCIPLES OF HEREDITY
... MY OBJECTIVE: You will appreciate and be able to convey to others the many ways genetics impacts our daily lives. TEXT: (recommended) Human Genetics by Ricki Lewis (5th-10th) editions all OK EXTRAS: Lecture notes, study guides (learning objectives) and PDF versions of old tests with and without answ ...
... MY OBJECTIVE: You will appreciate and be able to convey to others the many ways genetics impacts our daily lives. TEXT: (recommended) Human Genetics by Ricki Lewis (5th-10th) editions all OK EXTRAS: Lecture notes, study guides (learning objectives) and PDF versions of old tests with and without answ ...
Genetic dissection of trisomy 21 pathology using a
... C. Canzonetta, S. Devita, E.M Fisher, V. Tybulewicz, J. Groet and Dean Nizetic Since Down Syndrome (DS) is not an inherited disease, and the DNA sequence of the supernumerary chromosome 21 causing it is perfectly normal, standard genetics cannot be used to pinpoint the causative roles of individual ...
... C. Canzonetta, S. Devita, E.M Fisher, V. Tybulewicz, J. Groet and Dean Nizetic Since Down Syndrome (DS) is not an inherited disease, and the DNA sequence of the supernumerary chromosome 21 causing it is perfectly normal, standard genetics cannot be used to pinpoint the causative roles of individual ...
Student Notes
... The activity and role of transposable elements and retrotransposons. How evo-devo relates to our understanding of the evolution of genomes. The role homeotic genes and homeoboxes How could so many proteins be made with so few genes? Only 1.5% of the human genome codes for proteins or is transc ...
... The activity and role of transposable elements and retrotransposons. How evo-devo relates to our understanding of the evolution of genomes. The role homeotic genes and homeoboxes How could so many proteins be made with so few genes? Only 1.5% of the human genome codes for proteins or is transc ...
BY 123 SI Session #9 Chapter 15 Siby123.yolasite.com Terms to
... a. The genes are on the same chromosome, but they are more than 50 map units (50%) apart. b. The genes assort independently even though the chromosomes they are on travel to the metaphase plate together c. Their alleles segregate in anaphase I, and each gamete receives a single allele for all of the ...
... a. The genes are on the same chromosome, but they are more than 50 map units (50%) apart. b. The genes assort independently even though the chromosomes they are on travel to the metaphase plate together c. Their alleles segregate in anaphase I, and each gamete receives a single allele for all of the ...
PROS AND CONS OF GENETIC ENGINEERING
... • Changing the traits of one organism by inserting genetic material (DNA / genes) from a different organism into its genetic material (genome). ...
... • Changing the traits of one organism by inserting genetic material (DNA / genes) from a different organism into its genetic material (genome). ...