Inheriting Characteristics
... • A human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, you have 2 of each chromosome (unless you’re a boy) • This means there are 46 chromosomes in total • You inherit half your chromosomes from your mother and half from your father. Making 23 pairs. • Chromosomes carry genes ...
... • A human cell contains 23 pairs of chromosomes, you have 2 of each chromosome (unless you’re a boy) • This means there are 46 chromosomes in total • You inherit half your chromosomes from your mother and half from your father. Making 23 pairs. • Chromosomes carry genes ...
McCance: Pathophysiology, 6th Edition
... inactivated). It may involve methylation. 22. Gender is determined embryonically by the presence of the SRY gene on the Y chromosome. Embryos that have a Y chromosome (and thus the SRY gene) become males, whereas those lacking the Y chromosome become females. When the Y chromosome lacks the SRY gene ...
... inactivated). It may involve methylation. 22. Gender is determined embryonically by the presence of the SRY gene on the Y chromosome. Embryos that have a Y chromosome (and thus the SRY gene) become males, whereas those lacking the Y chromosome become females. When the Y chromosome lacks the SRY gene ...
Chapter 24
... fertilizes a diploid egg, the fertilized egg is triploid, with three copies of each chromosome. Most human polyploids die as embryos or fetuses, but occasionally an infant survives for a few days, with defects in nearly all organs. However, many agriculturally important plants are polyploids. Some o ...
... fertilizes a diploid egg, the fertilized egg is triploid, with three copies of each chromosome. Most human polyploids die as embryos or fetuses, but occasionally an infant survives for a few days, with defects in nearly all organs. However, many agriculturally important plants are polyploids. Some o ...
For SNP microarray analysis processed before Oct. 15, 2012
... with the Illumina HD HumanOmni1-quad BeadChip platform. This chip contains approximately 1,140,419 probes including both single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) and non-SNP alleles. The test is used to identify chromosomal imbalances throughout the human genome. These imbalances include deletions, dup ...
... with the Illumina HD HumanOmni1-quad BeadChip platform. This chip contains approximately 1,140,419 probes including both single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) and non-SNP alleles. The test is used to identify chromosomal imbalances throughout the human genome. These imbalances include deletions, dup ...
DNA - heredity2
... • The different traits for a specific gene are called alleles – e.g. Blue, green and brown eyes are different alleles for eye colour. ...
... • The different traits for a specific gene are called alleles – e.g. Blue, green and brown eyes are different alleles for eye colour. ...
No Slide Title
... • Self-pollinated for several generations to get “true-breeding” • Always produce offspring w/ the desired trait 2. F1 Generation ...
... • Self-pollinated for several generations to get “true-breeding” • Always produce offspring w/ the desired trait 2. F1 Generation ...
Chapter 11 Study Guide Vocabulary: Gene pool allele frequency
... 3. Describe a population that has a normal distribution of height. 4. Name three different forms of natural selection with respect to distribution of traits (also draw the curves). 5. Is natural selection the only means by which things evolve? 6. Distinguish between gene flow and genetic drift. 7. D ...
... 3. Describe a population that has a normal distribution of height. 4. Name three different forms of natural selection with respect to distribution of traits (also draw the curves). 5. Is natural selection the only means by which things evolve? 6. Distinguish between gene flow and genetic drift. 7. D ...
Human Heredity Notes
... How to Study: take sample cells from fetus & photograph metaphase chromosomes – line them up according to length & location of centromere = karyotype A. Dominant Autosomal Heredity Huntington’s disease – a rare genetic disorder caused by a dominant gene progressive degeneration of the nervous syst ...
... How to Study: take sample cells from fetus & photograph metaphase chromosomes – line them up according to length & location of centromere = karyotype A. Dominant Autosomal Heredity Huntington’s disease – a rare genetic disorder caused by a dominant gene progressive degeneration of the nervous syst ...
DEP Chapter 3 Presentation
... interactional, and unique; just four chemicals are the basic building blocks of the genetic code ...
... interactional, and unique; just four chemicals are the basic building blocks of the genetic code ...
Gene Section DIRC3 (disrupted in renal carcinoma 3) in Oncology and Haematology
... The gene spans 3071 bp and contains 12 exons. The last exon contains a consensus polyadenylation site sequence (AGTAA) at 20 nt upstream up the poly(a) addition site. DIRC3 expression could be detected in the placenta, but low expression was found in most tissues and the gene may act as a non-coding ...
... The gene spans 3071 bp and contains 12 exons. The last exon contains a consensus polyadenylation site sequence (AGTAA) at 20 nt upstream up the poly(a) addition site. DIRC3 expression could be detected in the placenta, but low expression was found in most tissues and the gene may act as a non-coding ...
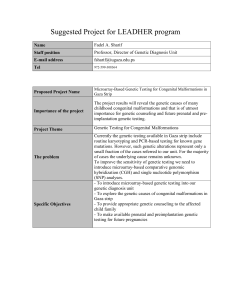
Suggested Project for LEADHER program Name Fadel A. Sharif
... Currently the genetic testing available in Gaza strip include routine karyotyping and PCR-based testing for known gene mutations. However, such genetic alterations represent only a small fraction of the cases referred to our unit. For the majority of cases the underlying cause remains unknown. To im ...
... Currently the genetic testing available in Gaza strip include routine karyotyping and PCR-based testing for known gene mutations. However, such genetic alterations represent only a small fraction of the cases referred to our unit. For the majority of cases the underlying cause remains unknown. To im ...
Mendelian Inheritence in Man - Genomecluster at Oakland University
... distinct subunits, insulin is under the control of a single genetic locus; chains A and B are derived from a one-chain precursor, proinsulin, which was discovered by {72:Steiner and Oyer (1967)}. Proinsulin is converted to insulin by the enzymatic removal of a segment that connects the amino end of ...
... distinct subunits, insulin is under the control of a single genetic locus; chains A and B are derived from a one-chain precursor, proinsulin, which was discovered by {72:Steiner and Oyer (1967)}. Proinsulin is converted to insulin by the enzymatic removal of a segment that connects the amino end of ...
Advancements in Genetic Engineering
... might create unhuman feelings or even actions to the minor populations. Due to the profound impact and the complexity of effects on various aspects, it might be too early to provide an ultimate solution, the application and constant examination of personal feeling and society impact will inspire us ...
... might create unhuman feelings or even actions to the minor populations. Due to the profound impact and the complexity of effects on various aspects, it might be too early to provide an ultimate solution, the application and constant examination of personal feeling and society impact will inspire us ...
Nature vs nurture article
... rages on, as scientist fight over how much of who we are is shaped by genes and how much by the environment. The Nature Theory - Heredity Scientists have known for years that traits such as eye color and hair color are determined by specific genes encoded in each human cell. The Nature Theory takes ...
... rages on, as scientist fight over how much of who we are is shaped by genes and how much by the environment. The Nature Theory - Heredity Scientists have known for years that traits such as eye color and hair color are determined by specific genes encoded in each human cell. The Nature Theory takes ...
Lesson 3. Genetic Disorders, Karyotypes - Blyth-Biology11
... • Turner Syndrome occurs when the individual only gets one sex chromosome; an X • The result is an infertile female with a broad chest, poor breast development, low set ears, short stature and poor hearing amongst other things. ...
... • Turner Syndrome occurs when the individual only gets one sex chromosome; an X • The result is an infertile female with a broad chest, poor breast development, low set ears, short stature and poor hearing amongst other things. ...
Genetics Vocabulary Answers The offspring of organisms often grow
... The offspring of organisms often grow up to look like one or both of their parents. This is because offspring inherit information from their parents that directs their development. ...
... The offspring of organisms often grow up to look like one or both of their parents. This is because offspring inherit information from their parents that directs their development. ...
Pathology
... 1) Know the major types of mutations and be able to give an example of each. Point Mutation (missense, nonsense) – replacement of one base pair with another creating a codon for a different amino acid (missense) or a stop codon (nonsense). Ex: Sickle cell anemia. Frameshift (deletion or insertion) – ...
... 1) Know the major types of mutations and be able to give an example of each. Point Mutation (missense, nonsense) – replacement of one base pair with another creating a codon for a different amino acid (missense) or a stop codon (nonsense). Ex: Sickle cell anemia. Frameshift (deletion or insertion) – ...
PROCESS OF EVOLUTION I Evolution in a Genetic Context
... Genotypic frequency: the number of a specific genotype divided by the total number of genotypes in the population A change in allelic & genotypic frequencies are used to measure evolution ...
... Genotypic frequency: the number of a specific genotype divided by the total number of genotypes in the population A change in allelic & genotypic frequencies are used to measure evolution ...
Study of Holocaust survivors finds trauma passed on to children
... fathered heavier sons than those who smoked after. ...
... fathered heavier sons than those who smoked after. ...
Abstract
... Evolutionary history contributes to differences in disease risks across populations, and genetic risk scores can be calculated by integrating GWAS results with whole genome sequence data. On a broad scale, hereditary disease risks are similar for ancient hominins and modern-day humans. There is evid ...
... Evolutionary history contributes to differences in disease risks across populations, and genetic risk scores can be calculated by integrating GWAS results with whole genome sequence data. On a broad scale, hereditary disease risks are similar for ancient hominins and modern-day humans. There is evid ...
Ch 11 homework
... 6. The feature of "sticky ends" that makes them especially useful in DNA recombination is their ability to (1) A) bind to DNA and thereby activate transcription. B) bind to ribosomes and thereby activate translation. C) form hydrogen-bonded base pairs with complementary single-stranded stretches of ...
... 6. The feature of "sticky ends" that makes them especially useful in DNA recombination is their ability to (1) A) bind to DNA and thereby activate transcription. B) bind to ribosomes and thereby activate translation. C) form hydrogen-bonded base pairs with complementary single-stranded stretches of ...
2 Types of Selective Breeding
... For thousands of years people have tried to produce __________________________ with desirable traits _________ methods that people use to develop organisms with desirable traits: 1) Selective Breeding – a process of selecting a few organisms with _______________ to serve as parents of the __________ ...
... For thousands of years people have tried to produce __________________________ with desirable traits _________ methods that people use to develop organisms with desirable traits: 1) Selective Breeding – a process of selecting a few organisms with _______________ to serve as parents of the __________ ...